Chemical compounds and reagents
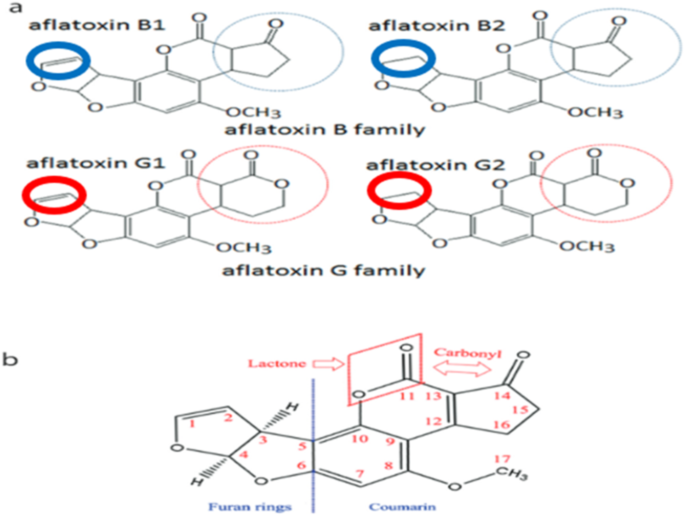
All chemical compounds and reagents used on this examine have been of analytical grade. Aflatoxin B1 customary (purity ≥ 98%) was bought from Sigma-Aldrich (Taufkirchen, Germany). All chemical compounds and medium parts have been obtained from Merck Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany).
Biodegradation agent
The fungal isolate beneath investigation (coded as OBCC 5014) was remoted from a mushroom pattern collected in Osmaneli, Bilecik, Türkiye. This specific isolate was chosen amongst 94 macrofungal isolates for its AFB1 and OTA degradation capability27. The isolate was preserved within the tradition assortment of the Leibniz College Hannover’s Institute of Meals Chemistry beneath code # 329. By analysing the standard bodily traits, seen each with the bare eye and beneath the microscope and evaluating them with descriptions discovered within the related literature, the fungal pattern was tentatively recognized as a pressure of Trametes hirsuta29. To verify the normal identification, the sequence of the inner transcribed spacer (ITS) rDNA area of the isolate was decided after which in comparison with sequences obtainable within the GenBank database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/). For that objective, the isolate 329 was grown on customary nutrient liquid – Agar (SNL) medium (g/L; D (+)-glucose monohydrate 30.0, L-asparagine monohydrate 4.5, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.5, magnesium sulphate hydrate 0.5, yeast extract 3.0, agar-agar 15.0, and hint component answer 1 mL/L). The mycelium was transferred to Eppendorf tubes, the place a digestion buffer and small glass beads within the Precellys have been used for DNA extraction. DNA was extracted beneath nitrogen at 3760 g for 3 cycles of 20 seconds every (20 second intervals) after which made prepared for PCR. The quantity of extracted DNA was decided utilizing a NanoDrop photometer (Eppendorf BioSpectrometer). Then, PCR amplification of the rDNA area was carried out in 50-µL response combination utilizing ITS1 (5’-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3’) and ITS4 (5’-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3’) primers29. Within the subsequent step, 1 µL of template DNA (obtained from the isolate 329 at a focus of 100–150 ng/µL) was added to the 24 µL grasp combine for PCR amplification of the rDNA area. The PCR program was as follows: Warmth Lid at 110 °C; 1 cycle of 30 s at 98 °C; 35 cycles of 10 s at 98 °C, 30 s at 48.5 °C, 90 s at 72 °C; and a last cycle of 10 min at 72 °C (Bio-Rad). Following the PCR course of, the dimensions of amplified DNA was estimated to be roughly 600 bp on the agarose gel. The rDNA was extracted utilizing the innuPREP DOUBLEpure Package. DNA focus was verified utilizing the NanoDrop photometer (6 ng/µl is ample for 600 bp DNA). Lastly, the samples have been despatched to Microsynth/Seqlab. The rDNA area sequence was used to carry out a BLAST search inside the GenBank database30.
Cultivation situations
A colony of T. hirsuta was produced on an SNL-Agar medium. 5 mycelial discs (6 mm in diameter) have been reduce from the energetic rising fringe of the colony. The mycelial discs have been inoculated into 100 mL of potato malt peptone medium (PMP). Preculture within the medium was carried out at 150 rpm for 4 days at 28 °C. The inoculant was ready by homogenizing the cell suspension with a Waring laboratory blender (Heidolph Silent Crusher M, Germany) for 25 s at one-minute intervals earlier than harvesting the pellets and washing thrice with sterile distilled water (SDW). This mycelium suspension served as an inoculant for all experiments31.
For enzyme manufacturing, T. hirsuta isolate 329 was cultivated for 10 days at 125 rpm and 28 °C in full darkness in Modified Kirk Broth containing (g per liter) (glucose 10, soytone 5, yeast extract 1, wheat bran 0.2, ammonium tartrate 2, CaCl2.H2O 0.1, MgSO4.7H2O 0.5, KH2PO4 2, and hint component answer 1 mL. The pH was adjusted to five.0). After the cultivation interval, the fungal cultures have been harvested and filtered (0.45 μm) to separate the mycelium. The ensuing filtrate of T. hirsuta was used as an enzyme supply for AFB1 biodegradation. This cultivation situation was chosen based mostly on earlier optimization research carried out for one more organism (Panus neostrigosus) for AFB1 degradation, which offered a basis for figuring out efficient parameters for enzyme manufacturing and exercise27.
Evaluation of residual AFB1 by microplate reader
All the response combination, totalling 300 µL, was ready for analysis utilizing a microplate reader. To provoke the method, 135 µL of tradition supernatant derived from T. hirsuta was mixed with 150 µL of a sodium acetate answer at pH 5.5. The 15 µL of AFB1 was added to the response combination and the ultimate quantity was made as much as 300 µL. The ultimate focus of the combination is 5 µg/mL. The absorbance at 365 nm was recorded for one hour in a microplate reader (gadget and producer) at 28 °C.
Two unfavorable controls have been used: one with tradition supernatant containing autoclaved (inactive) enzymes and AFB1, and the opposite with energetic filtrate however with out AFB1. The experiment was repeated thrice with three parallel measurements every. This strong experimental design aimed to make sure the reliability and reproducibility of the outcomes. The lower in absorbance over the one-hour interval offered data concerning the degradation fee. The aim of this experiment was to rapidly test enzyme exercise27.
Evaluation of residual AFB1 by HPLC
The AFB1 biodegradation fee of Trametes hirsuta was decided utilizing a response combination composed of 500 µL of sodium acetate buffer (0.1 M, pH 5.5), 485 µL of tradition liquid, and 15 µL of AFB1 answer (last focus: 1.5 µg/mL). Management reactions have been carried out with out the enzyme to account for non-enzymatic degradation. The response combination was incubated at nighttime at 28 °C for 1 h earlier than being stopped with 500 µL of chloroform. After this course of, the combination was centrifuged at 239 g for 15 min, and the decrease chloroform layer was evaporated to dryness at room temperature. This course of was replicated in triplicate to make sure reproducibility and reliability of outcomes. The AFB1-containing residue was re-dissolved in 200 µL of methanol by vortexing for 1 min to make sure full dissolution. No distillation step was used for this course of. The methanol extract was instantly transferred right into a clear HPLC vial for evaluation26. The pattern was analysed by HPLC (Shimadzu) beneath the next situations: HP 1050 HPLC System Ti Collection (Hewlett–Packard), C18 Column (150 mm x 4,6 mm, 5-µm particle measurement, 110 Å pore measurement; Gemini Phenomenex, Aschaffenburg, Germany); stream fee: 1 mL/min; UV detector with 365 nm. A typical curve was ready utilizing numerous AFB1 concentrations to calculate the biodegradation charges in all experimental teams.
Protein purification
The tradition liquid was harvested after 10 days of submerged fermentation, as optimization research from earlier analysis recognized this because the optimum time for enzyme manufacturing. This liquid was then used because the supply for protein purification utilizing Quick Protein Liquid Chromatography (FPLC) and ultrafiltration. Partial purification was carried out to find out the enzyme with the simplest AFB1 degradation capability amongst these produced by T. hirsuta. Initially, the tradition liquid of the isolate was centrifuged (at 11180 g and 4 °C), adopted by filtration (utilizing a ten,000 MWCO ultrafiltration tube at 4 °C and 2260 g). Then, protein fractions extracted from the tradition liquid of the isolate have been remoted by FPLC utilizing an answer consisting of fifty mM bisTris (pH: 5.5) and 1 M NaCl in a 1:1 ratio. These protein fractions have been visualised utilizing sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) with a ten% SDS focus. A effectively was designated for the marker, and 10 µL of every pattern was loaded into the remaining wells. Separated proteins have been stained utilizing Coomassie Sensible Blue R-250 (Sigma-Aldrich), and their molecular plenty have been decided by comparability with low-range molecular mass markers from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany)31.
The following purification step concerned ultrafiltration. To separate the 2 main proteins of FPLC fraction 6 this fraction was subjected to filtration by centrifugation at 3,368 rpm at 4 °C utilizing 50,000 MWCO ultrafiltration tubes. Filtrate and retentate have been analysed within the microplate reader assay (2.4) and SDS-PAGE with a ten% SDS focus and marking with Coomassie Sensible Blue R-250.
Peptide mass fingerprinting
To determine the accountable enzyme, peptide mass fingerprinting was carried out. The respective protein band was excised from a SDS gel, reduce into small items, dried and incubated (30 min at 56 °C) with dithiothreitol (20 mM in 0.1 M NH4HCO3). After discarding the supernatant, the gel items have been rehydrated in iodine acetamide answer (55 mM in 0.1 M NH4HCO3) for 30 min at ambient temperature at nighttime. The supernatant was discarded, and proteins have been digested utilizing trypsin (34 U/mL, sequencing grade; Promega, Madison, WI, USA) in 0.1 M NH4HCO3 (37 °C for at the least 4 h). The tryptic peptides have been recognized by nLC-qTOF-ESI-MS/MS.
Samples have been injected right into a nano-liquid chromatography system (EASY-nLC II, Bruker Daltronik, Bremen, Germany) geared up with a 20 mm pre-column (C18-A1 3PCS; ThermoFisher Scientific, Dreieich, Germany) and a capillary column (0.15 × 250 mm) filled with Grace MS C18 (3 μm particles, 300 Å pore; Grace Discovery Sciences (Columbia, SC, USA). Oligopeptides have been eluted by a linear gradient (300 nL/min) of water and acetonitrile (every with 0.1% formic acid (v/v)) from 95% water to 95% acetonitrile inside 25 min and held for 15 min. The nano-LC system was linked to a MaXis influence QTOF mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltronik) geared up with a captive nanospray ion supply for electrospray ionization within the constructive mode. The orthogonal time-of-flight mass analyser was calibrated earlier than evaluation (ESI-Low Focus Tuning Combine, Agilent Applied sciences, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and operated with a mean mass decision > 30,000. Collision-induced ms/ms spectra (Ar) have been recorded, and peptides from m/z 200 to 2000 have been recorded and evaluated utilizing the Protein Scape 3.0 software program (Bruker Daltronic, Bremen, Germany). Oligopeptide sequences have been recognized utilizing the Mascot search algorithm and the NCBI protein database (NCBInr, Taxonomy Fungi, 15.02.2023)32.
The enzymatic exercise was calculated utilizing the Michaelis-Menten equation: the place v is the response velocity, Vmax is the utmost velocity (11.49 µM per minute), Km is the Michaelis-Menten fixed (23.67 µM), and [S] is the substrate focus.
Calculation of Vmax:
(v=frac{{{textual content{Vmax X }}left[ {text{S}} right]}}{{{textual content{Km}}+left[ {text{S}} right]}})
Statistical evaluation
For statistical analysis, every experiment was carried out in triplicate, and the ensuing knowledge have been expressed as imply values ± customary deviation (SD). Statistical significance of variations between experimental teams and controls was assessed utilizing one-way ANOVA. For all analyses, statistical significance was outlined as p