Chemical compounds, reagents and media
All liquid, strong and gentle media have been ready with LB Broth Lennox (1% (w/v) tryptone, 0.5% (w/v) yeast extract, 0.5% (w/v) NaCl) and supplemented with antibiotics, inducers and cations as wanted and described under. Backside and prime agar have been ready with 1.5% (w/v) and 0.7% (w/v) agar, respectively. LB Broth Lennox was used for routine cultivation of E. coli and for experiments in wealthy medium. Expression of dCas13d was induced by the addition of anhydrotetracycline (aTc; Sigma-Aldrich, CAS 13803-65-1). crRNAs encoded on auxiliary crRNA expression plasmid pBFC1171 have been induced utilizing 1 µM crystal violet (for pooled crRNA libraries concentrating on E. coli), whereas crRNAs encoded on pBFC0984 have been expressed from robust constitutive promoter BBa_J23119. Antibiotics have been used at a focus of 34 μg ml−1 for chloramphenicol and 100 μg ml−1 for carbenicillin. SM buffer (Teknova) was used for phage dilution. All bacterial and phage strains used on this work are listed in Supplementary Knowledge 2.
Competent cell manufacturing
Business chemically competent and electrocompetent cells have been used when out there. Customized chemically competent cells have been cultured in ZymoBroth and made competent utilizing Combine & Go buffers (Zymo) in response to manufacturer-recommended protocol. For customized electrocompetent cells, in a single day E. coli cultures in 2×YT medium with acceptable antibiotics have been inoculated into the identical medium to an optical density (OD) of 0.05 and grown to mid-exponential section (OD600 = 0.4–0.6). Cells have been pelleted, washed twice with chilled H2O and twice with chilled 10% glycerol, and resuspended in chilled 10% glycerol to realize a ~300× focus of the collected tradition. Aliquots have been instantly frozen at −80 °C.
Full-plasmid sequencing
All plasmid constructs have been sequenced utilizing the full-plasmid sequencing companies on the UC Berkeley DNA Sequencing core (Illumina or Oxford Nanopore), Primordium (Oxford Nanopore) or Plasmidsaurus (Oxford Nanopore).
Phage propagation and scaling
Phages have been propagated by means of generally used protocols in LB media or LB prime agar overlays (0.7%). Until said in any other case, phages have been propagated on E. coli BW25113 (lacI+rrnBT14 ΔlacZWJ16 hsdR514 ΔaraBADAH33 ΔrhaBADLD78 rph-1 Δ(araB–D)567 Δ(rhaD–B)568 ΔlacZ4787(::rrnB-3) hsdR514 rph-1). Phages N4, T4, T5 and T7 have been scaled on E. coli BW25113. Phage SUSP1 was a present from Dr Sankar Adhya and scaled on E. coli BW25113. Phages EdH4 and MM02 have been obtained from the DSMZ tradition assortment and scaled on E. coli BW25113 (DSM 103295 and DSM 29475, respectively). Phage λ cI857 bor::kanR was a present from Dr Drew Endy and scaled as described beforehand. Phage MS2 was a present from Vivek Mutalik and scaled in E. coli pressure NEB-5α F’Iq (NEB) with 2 mM CaCl2. Phage M13 was obtained from ATCC (15669-B1) and was additionally propagated on NEB 5-α F’Iq genotype cells (NEB) with 2 mM CaCl2. All phages have been titred by means of 2 µl spots of 10× serial dilution of phage in SM buffer on E. coli BW25113 or NEB-5α F’Iq in a 0.7% prime agar overlay.
CRISPRi-ART vector development
The Ruminococcus flavefaciens Cas13d (RfxCas13d) coding sequence was amplified from addgene plasmid pXR001: EF1a-CasRx-2A-EGFP, a present from Patrick Hsu (Addgene plasmid 109049; http://n2t.internet/addgene:109049; RRID: Addgene_109049). The first CRISPRi-ART vector pBFC0984 was constructed by assembling a p15A chloramphenicol-resistant spine with the catalytically deactivated dRfxCas13d coding sequence underneath transcriptional management of the aTc-inducible pTet promoter, together with a 2xBsaI Golden Gate spacer cloning web site for expression of crRNAs from the robust constitutive promoter BBa_J23119. Plasmid pBA556 is just like pBFC0984 however missing the crRNA cassette. Plasmid pBFC0984 was used as a spacer entry vector for all particular person and twin crRNA constructs, in addition to for all phage crRNA libraries. To scale back the chance of leaky crRNA expression that might result in pooled crRNA library bias for libraries concentrating on the E. coli transcriptome, we additionally constructed a pBA556-compatible auxiliary crRNA vector pBFC1171 consisting of a low-copy SC101 origin, bla ampicillin/carbenicillin resistance marker and a 2xBsaI Golden Gate spacer cloning web site for expression of crRNAs from the non-leaky, robust, crystal violet-inducible promoter pJEx60. Plasmid pBFC1171 was used as a spacer entry vector for all E. coli crRNA libraries. For management crRNA-only samples, plasmid pBFC0843 was constructed and used rather than pBA556 together with the pBFC1171-harboured crRNA library. Plasmid pBFC0843 is dRfxCas13d-null and crRNA-null and possesses a p15A origin, chloramphenicol resistance marker and a pTet promoter and not using a downstream CDS.
Particular person and twin crRNA cloning
To introduce crRNA spacers into pBFC0984, we employed BsaI-HFv2 (NEB, R3733L) Golden Gate meeting58. For particular person crRNAs, spacers have been designed as two complementary oligonucleotides with 4 bp 5’ overhangs that matched the staggered ends of the BsaI-digested vacation spot plasmid. For twin crRNAs, two pairs of oligos (every encoding one of many two spacers and a part of the central direct repeat) have been designed to ligate into the spine in the same method, inserting a spacer-repeat-spacer phase. These oligonucleotides have been phosphorylated utilizing T4 PNK (NEB) at 37 °C for 30 min after which duplexed at a focus of 10 μM. Duplex formation concerned melting at 100 °C for five min, adopted by sluggish cooling to room temperature over a span of 15 min. The PNK-annealed spacer duplexes (100 fmol) served because the insert templates in every Golden Gate response. Cloning reactions have been subsequently remodeled into competent E. coli (Mach1-T1R, NEB10B or IG10B) and clones verified by full-plasmid sequencing.
Cloning and expression of phage gene complementation plasmids
Every complemented phage gene was cloned as a fusion to the C terminus of sfGFP into the two×BsaI entry vector pBA1328 (low-copy SC101, kanamycin-resistant, tightly regulated pJEx promoter) utilizing BsaI Golden Gate cloning. Elimination of the phage gene begin codon and fusion to sfGFP shifts the crRNA binding web site firstly of the phage CDS far downstream of the RBS/translational begin web site of the sfGFP:phage gene fusion, stopping CRISPRi-ART knockdown of the complemented gene resulting from its distance from the RBS. This facilitates use of crRNAs concentrating on the phage-encoded CDS with out having to recode the complemented gene. Complementation plasmids have been co-transformed with CRISPRi-ART plasmids as wanted and maintained with 34 µg ml−1 chloramphenicol and 50 µg ml−1 kanamycin choice. Phage genes have been expressed from complementation plasmids utilizing CV induction of the pJEx promoter60 utilizing 200 nM CV. CV concentrations have been decided by working a titration sequence to find out the phenotypically efficient focus.
Quantifying CRISPRi-ART towards phages utilizing plaque assays with particular person and twin crRNAs
Bacteriophage plaque assays have been carried out utilizing a modified double agar overlay protocol as reported beforehand21. Until said in any other case, phage assays have been carried out utilizing DH10b-genotype E. coli (NEB, Intact Genomics), DH5α F’ genotype E. coli (NEB C2992) (phage M13) or E. coli Ok-12 F+ (Yale CGSC 4401, phage MS2) remodeled with a plasmid containing dRfxCas13d, dLbCas12a or dSpyCas9 underneath pTet management, with a crRNA (or sgRNA within the case of dSpyCas9) underneath constitutive management (Supplementary Knowledge 1). Cultures have been grown in a single day at 37 °C and 250 r.p.m. with acceptable antibiotics, and 100 µl of saturated in a single day tradition was combined with 5 ml molten LB Lennox prime agar supplemented with acceptable inducer (under) and antibiotics. This combination was decanted onto a corresponding 5 ml LB Lennox + chloramphenicol agar plate to ultimate overlay concentrations of 0.7% (w/v) agar, aTc (variable, under) and 34 µg ml−1 chloramphenicol. For dCas13d experiments, the next ultimate concentrations of aTc have been used to reduce background toxicity whereas sustaining phage inhibition: phages T4, MM02, and Lambda (20 nM), phage Goslar (50 nM), and phages EdH4, M13, MS2, N4, PTXU04, SUSP1, T5 and T7 (100 nM). For T4 phage experiments involving dLbCas12a, a decrease ultimate aTc focus of 10 nM was used resulting from expression toxicity.
Usually, no supplementary CaCl2 or MgSO4 salts have been added apart from experiments involving phages MS2 and M13, which employed a ultimate focus of 1 mM CaCl2. Overlays have been left to dry for 15 min underneath microbiological flame. For every Cas–crRNA–phage mixture, 10× serial dilutions of the suitable phage have been carried out in SM buffer (Teknova), and a couple of µl of every dilution have been noticed onto the highest agar and allowed to dry for 10 min. Plaque assays have been incubated at 37 °C for 12–16 h. Put up incubation, plaques have been scanned utilizing a photograph scanner and plaque-forming models (p.f.u.s) enumerated. When no plaques however clearings have been noticed at excessive phage concentrations, we thought of these as ‘lysis from with out’ and indicated a scarcity of productive phage an infection61. We approximated these EOPs as 1 p.f.u. on the most concentrated dilution of clearing. EOPs have been calculated by normalizing the imply of p.f.u.s for a situation to the imply p.f.u.s of a unfavorable management (concentrating on RFP by default): imply(p.f.u.s situation)/imply(p.f.u.s unfavorable management). All plaque assays have been carried out in organic triplicate and EOP calculations carried out utilizing GraphPad PRISM.
Plaques have been additional analysed by dimension in Fiji62. Picture scale was set to 0 and particular person plaques have been chosen as areas of curiosity utilizing the total plaque space together with the turbid zone. The world of every plaque was calculated. Fold-change for plaque dimension measurements was calculated as: imply(area_condition)/imply(area_control).
Oligo pool design and amplification
Oligo swimming pools have been designed utilizing a customized script packaged and out there to be used at https://github.com/BenAdler14/CRISPRi-ART (ref. 63). Designed oligo swimming pools have been synthesized by Twist Bioscience and designed to encode PCR amplifiable crRNA libraries to be cloned into pBFC0984 or pBFC1171 utilizing BsaI Golden Gate meeting. Oligos containing inner BsaI websites (resulting from BsaI within the goal or a uncommon BsaI arising when concatenating the ultimate oligo parts) have been excluded from synthesis to cut back meeting errors. Duplicate oligos encoding crRNAs concentrating on multicopy or repetitive genomic options have been deduplicated earlier than synthesis. The crRNA libraries have been synthesized as swimming pools through which every distinct crRNA library was designed to be uniquely amplifiable with an orthogonal primer pair64. Every oligo was composed of the next key sequence components, concatenated within the 5’ to three’ course: a 20 nt subpool-specific ahead primer, 11 nt encoding the upstream BsaI web site and AAAC overhang, 31 nt variable spacer sequence, 1 nt to take care of the beginning base of the downstream terminator characteristic on the crRNA entry vector, 11 nt encoding the downstream TGCT overhang and BsaI web site, a 20 nt subpool-specific reverse primer matched to the upstream primer, and a 6 nt arbitrary DNA (Supplementary Fig. 1). Orthogonal primer pairs used for subpool amplification are listed in Supplementary Knowledge 4. Sense RBS management oligos (described under) have been synthesized as a part of a separate oligo pool from antisense RBS-targeting oligos to forestall amplification issues arising from hybridization of those complementary oligos. Oligo swimming pools have been resuspended in Qiagen EB (10 mM Tris, pH 8.5) to 10 ng μl−1 and saved at −80 °C when not in use. Subpools have been amplified utilizing subpool-specific primers following Twist suggestions and the KAPA HiFi HotStart DNA Polymerase equipment (7958889001). Particularly, 25 µl reactions have been assembled with 0.5 U KAPA HiFi HotStart DNA Polymerase, KAPA HiFi Constancy Buffer, 0.3 mM dNTPs, 5 ng oligo pool and 0.3 µM of every subpool-specific primer. The thermocycler programme included an preliminary melting step for 3 min at 95 °C; 8 cycles of 98 °C melting for 20 s, 50 °C annealing for 15 s, 72 °C extension for 15 s; and a ultimate extension at 72 °C for 1 min. Bioanalyzer confirmed profitable amplification of the anticipated 98 bp merchandise. These PCR merchandise have been purified utilizing a DNA Clear and Concentrator-5 equipment (Zymo, D4004), eluted with 10 µl milliQ H2O and used to assemble crRNA libraries as described under.
E. coli CRISPRi-ART single-nucleotide-tiling crRNA library design
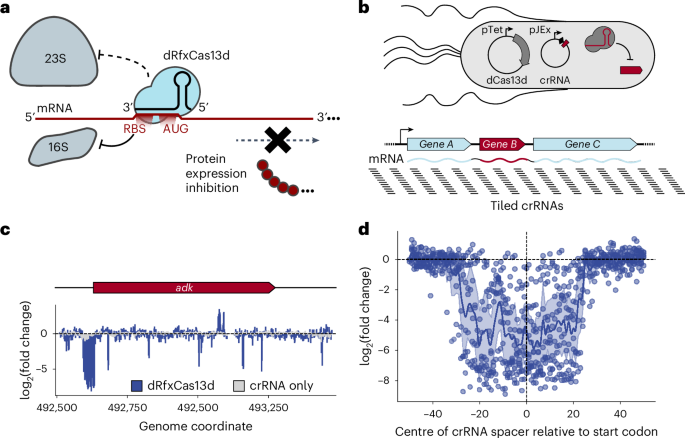
We designed a pooled, single-nucleotide-resolution library with 29,473 crRNAs tiled antisense to 18 E. coli BW25113 (accession CP009273) transcripts (Supplementary Knowledge 5). crRNAs have been tiled 100 nt past the ends of transcriptional begin and cease websites when identified65, or 100 nt past the outermost coding sequences when not beforehand reported. Metadata for the single-nucleotide-tiling crRNA library are proven in Supplementary Knowledge 5. For among the important genes on these transcripts, the attribute RBS-centred health defect tract was not noticed; we famous {that a} distinguishing characteristic of those genes was a markedly decrease protein synthesis fee66, suggesting that CRISPRi-ART is perhaps simpler at concentrating on extremely expressed proteins. To spotlight this vulnerable tract, 9 important genes with marked RBS-centred health defect tracts out of the 18 focused transcripts are plotted in Fig. 1d.
E. coli CRISPRi-ART pooled crRNA library development
Given the upper range of our 1-nt-tiling E. coli-targeting library, we used a crRNA library development method geared toward sustaining excessive library protection and avoiding bias within the cloning and propagation steps. PCR merchandise containing the crRNA libraries have been cloned into pBFC1171 utilizing BsaI Golden Gate meeting. To take away undigested entry vector, reactions have been subsequently handled with a follow-up digestion and cleanup process, consisting of BsaI digestion at 37 °C for 1 h, BsaI warmth inactivation at 85 °C for 20 min, Plasmid-Secure ATP-Dependent DNase (LGC Biosearch Applied sciences) exonuclease therapy at 37 °C for 1 h, Plasmid-Secure warmth inactivation at 75 °C for 30 min, and purification utilizing a DNA Clear and Concentrator-5 with 10 μl elution in milliQ H2O. Excessive-competency Endura (LGC Biosearch Applied sciences) electrocompetent cells have been electroporated with 1 µl of this product and recovered at 37 °C and 250 r.p.m. for 1 h. A small aliquot was serially diluted and spot plated to rely colonies, estimate library protection and sequence 10 colonies to verify environment friendly and numerous crRNA insertion, and the rest of the restoration saved at 4 °C in a single day. On the premise of transformation titres, an acceptable quantity of the restoration was plated onto pre-dried bioassay dishes containing LB agar plus carbenicillin, aiming for 100× c.f.u.s over library dimension and not more than 1,000,000 c.f.u.s on a single bioassay dish. After 14 h in a single day progress at 37 °C, colonies have been scraped from every bioassay dish into 50 ml LB plus carbenicillin, vortexed completely, pooled if unfold throughout a number of dishes, pelleted by centrifugation and midiprepped with 200 μl milliQ H2O elution (ZymoPURE II Plasmid Midiprep equipment, D4201) to gather plasmid library DNA (Supplementary Knowledge 1 and 2). To make sure full removing of undigested entry vector from the plasmid library, 2 µg of DNA was handled with the follow-up digestion and cleanup process described above.
Subsequent, experimental pressure E. coli BW25113 was remodeled with both pBA556 to construct pressure sBFC0264, or pBFC0843 to construct pressure sBFC0265, and subsequently made electrocompetent in preparation for transformation of crRNA library DNA. The one-nucleotide tiling library was electroporated into sBFC0264 and sBFC0265 (crRNA-only management library) and recovered at 37 °C and 250 r.p.m. for 1 h. Small aliquots of the recoveries have been serially diluted and spot plated onto LB agar plus chloramphenicol and carbenicillin to rely colonies, estimate library protection and sequence 10 colonies to verify upkeep of numerous crRNAs. The rest of the recoveries have been inoculated into 20 ml pre-warmed LB plus chloramphenicol and carbenicillin, grown at 37 °C and 250 r.p.m. till OD600 = 0.4–0.8, combined with equal quantity 40% sterile glycerol and frozen at −80 °C as 200 µl 20% revivable glycerol shares. One glycerol inventory for every library was thawed and titred on selective LB agar, indicating excessive viability after thawing with adequate c.f.u.s to take care of excessive library protection.
E. coli pooled aggressive health assays
Library aliquots (200 µl) have been thawed on ice for 10 min. One aliquot for every library was inoculated into 3 ml LB plus chloramphenicol and carbenicillin in a deep 24-well block and cultivated in a Multitron (Infors) plate shaker at 37 °C and 750 r.p.m. till OD600 = 0.5–1.0. At this level, every tradition was centrifuged at 4,000 × g for five min, supernatants aspirated and pellets gently washed in 1 ml M9 base medium (with out casamino acids and and not using a carbon supply). This wash process was repeated for a complete of thrice earlier than a ultimate resuspension in 3 ml M9 base medium, and 30 µl of well-mixed cells have been inoculated into 3 ml of recent assay medium, aiming for an preliminary cell rely of three × 107 c.f.u.s. All assay media contained the related base medium, antibiotics, and 200 nM aTc for dRfxCas13d induction or 1 µM crystal violet for crRNA induction. LB Lennox was used as the bottom assay wealthy medium for single-nucleotide tiling (Fig. 1c,d). Aggressive progress assays proceeded in 24 deep-well blocks at 37 °C and 750 r.p.m. till OD600 = 0.5–1.0 (7–8 doublings), at which level 30 µl of well-mixed tradition was subcultured into the identical recent assay medium and the rest of the tradition pelleted and frozen for subsequent CRISPRi-ART-seq of the intermediate time level. The ultimate cultures have been cultivated underneath the identical situations for one more 7–8 doublings earlier than assortment and freezing at −80 °C for subsequent CRISPRi-ART-seq, totalling 14–16 doublings publish induction.
Phage CRISPRi-ART crRNA library design
The transcriptome-wide phage-targeting crRNA libraries have been designed to focus on the RBS area of all annotated CDSs, utilizing 7 crRNAs coarsely tiled in 5 nt increments antisense to the vulnerable RBS area highlighted in Fig. 1d (Supplementary Fig. 1). This enabled complete transcriptome-wide protection, with not less than one information overlapping each the RBS and begin codon of every goal gene. For every phage used on this research, gene coordinates and begin codon annotations have been obtained straight from NCBI, utilizing the accession numbers for phage T4 (NC_000866), T5 (NC_005859), SUSP1 (NC_028808) and PTXU04 (NC_048193).
Phage CRISPRi-ART pooled crRNA library development
Given the decrease range of our phage-targeting CRISPRi-ART libraries, we used a less complicated method for crRNA cloning through which our libraries have been remodeled into NEB10Beta (the assay pressure for T4 and SUSP1, and the cloning pressure for T5 and PTXU04). Oligo amplification, Golden Gate meeting, and follow-up digestion and cleanup steps have been carried out as described above, besides that pBFC0984 was used because the entry vector. Business electrocompetent NEB10Beta cells have been then remodeled with 1 µl of plasmid library DNA and recovered at 37 °C and 250 r.p.m. for 1 h. A small aliquot of every restoration was serially diluted and spot plated on LB agar plus chloramphenicol to titre the transformations, and the rest of the recoveries was saved at 4 °C in a single day. Transformation efficiencies have been excessive, producing not less than 100× larger c.f.u.s than library dimension, and sequencing of 10 colonies confirmed excessive cloning effectivity and crRNA range. On the premise of c.f.u. rely, an acceptable quantity of restoration was plated on commonplace pre-dried LB agar plus chloramphenicol plates to acquire 100× c.f.u.s over library dimension, aiming for lower than 100,000 c.f.u.s per plate. After 14 h in a single day progress at 37 °C, colonies have been scraped from every plate into 50 ml LB plus chloramphenicol, vortexed completely, and cultivated in non-baffled shake flasks at 37 °C and 250 r.p.m. After 3 h cultivation, 8 ml of tradition was combined with an equal quantity of 40% sterile glycerol and frozen at −80 °C as 1 ml 20% revivable glycerol shares. The rest of the tradition was pelleted and midiprepped. The T5 and PTXU04 plasmid library DNA samples have been additional handled with follow-up digestion and cleanup steps, after which electroporated into their ultimate assay strains E. coli IG10Beta and BL21, respectively, and validated and stocked as described right here for NEB10Beta.
Phage pooled crRNA aggressive health assays
Library aliquots (1 ml) have been thawed on ice for 10 min, inoculated into 25 ml LB Lennox plus chloramphenicol in non-baffled flasks, after which cultivated at 37 °C and 220 r.p.m. for 30 min. At this level, the cultures have been adjusted to twenty nM aTc to induce dRfxCas13d expression. Cultures have been grown underneath induction at 37 °C and 220 r.p.m. for one more 1.5–2 h. OD600 measurements have been used to estimate bacterial c.f.u.s ml−1, and ~5 × 105 c.f.u.s (to make sure not less than 100× protection over library dimension) have been put aside for plating. To those tubes containing E. coli expressing CRISPRi-ART libraries, phage shares diluted in SM buffer have been added to a multiplicity of an infection (MOI) of 0 or 10, combined, allowed to adsorb for 15 min after which plated on pre-dried LB agar plus chloramphenicol plates containing 200 nM aTc. After in a single day incubation at 30 °C, all colonies from a given plate have been pooled into 10 ml LB, pelleted and frozen at −80 °C for subsequent CRISPRi-ART-seq.
CRISPRi-ART-seq
Frozen pellets from health experiments have been thawed at room temperature after being saved at −80 °C. Plasmid DNA encoding the CRISPRi-ART crRNA library was remoted utilizing a QIAprep Spin Miniprep equipment (Qiagen) and quantified utilizing a Qubit Excessive Sensitivity Assay (Thermo) for every pattern. A PCR response was carried out utilizing 50 ng (or a most of 10 µl if the pattern was under 5 ng µl−1) of DNA from every pattern in a 50 μl response quantity, using Q5 HotStart polymerase and pre-barcoded primers. The P1 appending response consisted of an preliminary denaturation at 98 °C for 30 s, adopted by 20 cycles of denaturation at 98 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 30 s and a ultimate extension at 72 °C for two min. PCR reactions have been cleaned up utilizing SPRISELECT beads in response to producer directions, concentrating on product sizes of 250 bp (1.8×). Purified PCR merchandise have been quantified through Qubit for every pattern. Samples have been pooled utilizing 20 ng of every pattern. The pooled pattern was requantified through Qubit and normalized to fifteen nM for Illumina sequencing. The ultimate samples have been then sequenced on both an Illumina iSeq or Miseq, or pooled on a NextSeq, as laid out in Supplementary Knowledge 5.
crRNA learn counting, normalization and health calculations
For single-nucleotide-tiling assays towards E. coli important gene transcripts, crRNAs have been counted with 2fast2q67,68 (https://github.com/afombravo/2FAST2Q) utilizing the command ‘python3 -m fast2q -c–m 0–st 30–l 31–ph 0’ and an enter.csv file containing a crRNA ID and corresponding spacer sequence for all crRNAs inside the counted crRNA library. To account for variations in learn depth between particular person samples, uncooked characteristic counts have been internally normalized for every examined crRNA by changing to reads per million. To account for denominator results, 1 was added to every uncooked characteristic rely earlier than this normalization. For E. coli crRNA log(fold-change (FC)) calculations, crRNA characteristic counts in check samples have been averaged throughout replicates and divided by corresponding counts within the T = 0 situation. Two-way t-statistic P values have been calculated utilizing the scipy.stats module in Python3. FC was log base 2 remodeled utilizing the numpy module in Python3. A pairwise comparability of crRNA health values indicated robust correlations between all replicates, indicating excessive reproducibility of single-nucleotide tiling CRISPRi-ART assays in E. coli (Supplementary Fig. 2). Health values are plotted in Fig. 1c, which exhibits a single consultant gene, together with a comparability to crRNA-only controls. Determine 1d presents knowledge for 9 important genes from the 18 focused transcripts that exhibited a attribute health defect across the ribosome-binding web site area. Supplementary Fig. 3 gives another presentation of Fig. 1d, expanded to a 1,000 bp window across the begin codon.
For phage FC calculations, the smallest and largest deciles of crRNA (by read_counts) for MOI 0 or 10 situations have been discarded to eradicate extrema from gene health calculations earlier than plating. Remaining crRNA characteristic counts in check samples have been averaged throughout replicates and divided by corresponding counts within the MOI = 0 situation. To find out whether or not a gene conferred optimistic or unfavorable health to a phage, the distribution of crRNA FCs for every gene was in comparison with the distribution of crRNA FCs throughout the complete phage genome. A unidirectional Kolmogorov–Smirnov check (Ok–S check) (through the scipy.stats module in Python3) was used to determine whether or not these distributions considerably differed.
For phage assays, health measurements have been calculated utilizing a customized conda surroundings packaging a SnakeMake pipeline and customized Python scripts (https://github.com/BenAdler14/CRISPRi-ART (ref. 63)). Briefly, paired-end reads have been trimmed and merged utilizing fastp69 with customized adapters equivalent to the dCas13d repeat and the crRNA terminator (GTTTCAAACCCCGACCAGTT, ATGCTTGGGCCCGAA). Merged reads have been counted utilizing fast2q67,68 (https://github.com/afombravo/2FAST2Q) (–m 2–l 30–ph 20–us GGTTTGAAAC–ds ATGCTTGGGC) towards a csv encoding the spacers inside the library. A top quality management metric was imparted on the unfavorable management situation (MOI 0), and the highest 10% and backside 10% most biased crRNAs within the unfavorable management have been excluded from evaluation. Included reads have been normalized to pseudocounts of 1 × 106 per index centred across the imply. For information health (crRNA log(FC)) calculations, crRNA characteristic counts in check samples have been by-sample and divided by the common corresponding counts throughout the bottom situations. For every crRNA characteristic inside a situation, log2(FC) values have been averaged and two-way t-statistic P values have been calculated utilizing the scipy.stats module in Python3. To find out whether or not crRNAs concentrating on a selected phage gene conferred optimistic health towards a phage, the distribution of crRNA FCs for every gene was in comparison with the distribution of crRNA FCs throughout the complete phage genome. A unidirectional Ok–S check (through the scipy.stats module in Python3) was used to determine whether or not a optimistic profit was conferred. The health threshold for the ‘Match’ standing was decided by the bottom health worth with a Ok–S P-statistic lower than 0.05. ‘Semi-fit’ standing was decided by focused genes with common information health above threshold however under statistical significance (that’s, giant guide-to-guide variability). A pairwise comparability of crRNA health values indicated robust correlations amongst all replicates, indicating excessive reproducibility of phage transcriptome-scale CRISPRi-ART assays (Supplementary Fig. 30). For phage T5, the best correlation was noticed between replicates of crRNAs with a health worth >−1 (Supplementary Fig. 21b inset).
Phage genome re-annotation
T4, T5, SUSP1 and PTXU04 bacteriophage genomes have been functionally annotated by means of a mix of automated and guide strategies. T4, T5 and SUSP1 phages have been mechanically annotated utilizing genomic annotations from CD-SEARCH70 and PHROGS71. As a result of PTXU04 CDSs exhibited restricted relation to identified proteins and PTXU04 shouldn’t be within the PHROGS database, PTXU04 was manually annotated with HHpred on the MPI Bioinformatics Toolkit (utilizing PDB_mmCIF70_18_Jun, COG_KOG_v1.0, NCBI_Conserved_Domains(CD)_v3.19, and PHROGs_v4 area databases)72. Every PTXU04 gene was manually assigned an annotation based mostly on both a transparent, assured hit (E-value −5) or repeated low-confidence annotations (for instance, phage tail protein). Further makes an attempt to annotate remaining hypothetical PTXU04 genes have been carried out utilizing AlphaFold prediction, adopted by structural alignment to PDB and AFDB to restricted success73,74,75,76. All annotations have been additional manually inspected towards identified gene content material in mannequin phages T4 (ref. 25) and T5 (refs. 16,77), and non-model phages SUSP1 (through progressiveMauve alignment with default parameters to associated Salmonella phage FelixO1)78,79 and PTXU04 (ref. 36). As well as, phage genomes have been annotated with phage-defence inhibitors present in T4 and T5 phages80,81,82,83. If battle arose throughout annotation task, annotations have been prioritized with the next confidence heuristic: literature > PHROGs > CD-SEARCH > HHpred. Any deviations have been made on the premise of annotation element and annotation confidence.
Along with the above annotations, genes have been assigned ‘class’ and ‘annotation high quality’ scores. The ‘class’ annotation included the next annotations: anti-defence, chaperonin, lysis, nucleotide metabolism, replication, transcription, translation, tRNA, virion, or unknown/different. ‘Anti-defence’ refers to genes concerned in subverting phage-defence programs, together with restriction modification programs. ‘Chaperonin’ refers to genes concerned in phage virion or protein maturation, however not a structural element of the phage virion. ‘Lysis’ refers to genes concerned in lysis, regulation of lysis timing or degradation of cell wall parts. ‘Nucleotide metabolism’ refers to genes chargeable for nucleotide biosynthesis, degradation, modification and regulation thereof, however circuitously part of replication. ‘Replication’ refers to genes concerned in phage replication liberally utilized. ‘Transcription’ refers to genes that modulate transcription in both the phage or host genome. ‘Translation’ refers to genes that modulate translation, together with genes that modulate RNA or tRNA stability. ‘tRNA’ refers to tRNA genes, however not genes that modify them. ‘Virion’ refers to genes which can be structural parts or a part of the virion produced in an infection. ‘Unknown/different’ refers to all different genes encoded in phage. ‘Annotation high quality’ was assigned manually based mostly on each confidence, element and identified literature of the annotation and its supply content material: ‘identified’ for genes with identified operate, ‘ambiguous’ for identified genes with ambiguity to substrate or function of the gene, and ‘unknown’ for genes of unknown operate.
Usually, these have been in settlement with PHROG class, with the next exceptions for visualization simplicity: (1) all predicted phage structural parts have been grouped into the ‘virion’ class together with packaged phage proteins; (2) many genes which can be vital for phage lifecycle however of unknown molecular operate (for instance, T5 genes A1 and A2) have been grouped into ‘replication’; (3) any gene chargeable for helping folding or meeting was overridden to fall underneath the ‘chaperonins’ class; (4) genes chargeable for anti-phage defence by means of nucleotide modification have been labelled as ‘nucleotide metabolism’; (5) genes with overlapping class capabilities (for instance, RNase H) have been labelled with a main annotation on the premise of literature25 and (6) predicted subgenomic cell components (for instance, homing endonucleases) have been assigned ‘unknown/different’ for simplicity. All phage annotations are listed in Supplementary Knowledge 6.
Evaluation of phage CRISPRi-ART-seq
Following CRISPRi-ART-seq processing, phage genes have been interpreted for health. To determine FC thresholds for Match and Semi-fit genes, for every phage–MOI situation, we recognized the bottom health rating with a Ok–S P worth lower than 0.05 on the fitting tail of the health distribution (that’s, positively enriched). This worth was used as an inclusive FC threshold for health. Thus, we decided Match genes by means of the next metrics: T4 (10 MOI) (FC > 0.7, P −3, P 1.2, P −1.1, P 29). As a result of robust choice stress baseline imposed by phage predation at excessive MOI, we kept away from decoding important unfavorable health scores from phage assays on this research.
Volcano plot visualization of phage gene health was carried out utilizing Python in matplotlib, using FC for the imply of three organic replicates and −log10-transformed P values. Circos plots have been generated in Python utilizing pycircos (https://github.com/ponnhide/pyCircos), using phage annotations and imply health scores (and Match/Semi-fit/Not-fit classifications) from CRISPRi-ART-seq as outer and inside tracks, respectively. Genome-wide and genomic-region visualizations have been generated utilizing dna_features_viewer (https://edinburgh-genome-foundry.github.io/DnaFeaturesViewer/) and matplotlib in Python. Colouring of phage genes was assigned by CRISPRi-ART-seq health classification and crRNA health displayed because the median of three organic replicates. Median crRNA health throughout the complete phage genome is proven with a dashed line. Comparability of T4 gene health scores to T4 essentiality25 was carried out utilizing gene health scores and Match, Semi-fit and Not-fit classifications for the MOI 10 T4 an infection situation utilizing seaborn in Python.
crRNA effectiveness in concentrating on phage genomes (Supplementary Figs. 38–41) was decided by analysing the crRNAs concentrating on the highest 10 match genes in phages T4, T5, SUSP1 and PTXU04 (that’s, concentrating on genes which can be clearly Match). To evaluate absolute and relative crRNA effectiveness, the distribution of crRNA health scores and within-gene z-score (scipy.stats), respectively, have been plotted utilizing seaborn in Python. As well as, guides have been interpreted by rank, and the variety of prime 3 information RNAs inside a gene have been plotted by crRNA quantity utilizing seaborn in Python.
Development of phylogenetic tree of RIIA/RIIB homologues
Bacteriophage genomes have been acquired from the GenBank-derived INPHARED84 database of filtered, curated and annotated sequences (February 2024 accession). Protein sequences from these genomes have been searched with MMseqs2 (ref. 85) for homologues of RIIA and RIIB utilizing default parameters. Question sequences included RIIA and RIIB sequences from bacteriophages T4, SUSP1, N4, EdH4, MM02, T2 and T6. For every genome the place each RIIA and RIIB homologues have been discovered, the CDSs of those genes have been concatemerized right into a single polypeptide. Concatemerized sequences from the question genomes have been included on this assortment. Concatemerized sequences have been dereplicated with CD-HIT86 utilizing an identification cut-off of 0.9. Sequences have been then aligned utilizing MAFFT87 with default parameters. Gaps within the alignment have been eliminated utilizing TrimAL88 with a niche threshold (-gt) of 0.7. Trimmed alignments have been transformed to a phylogenetic tree with FastTree89 utilizing default parameters. Ensuing timber have been visualized and annotated utilizing iTOL90. Viral and host taxonomies within the annotations mirror values within the INPHARED database.
Statistical evaluation
For all pooled crRNA research and plaque assays, three impartial samples have been used. Statistical analyses are described within the strategies related to the respective experiments.
Reporting abstract
Additional info on analysis design is obtainable within the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract linked to this text.