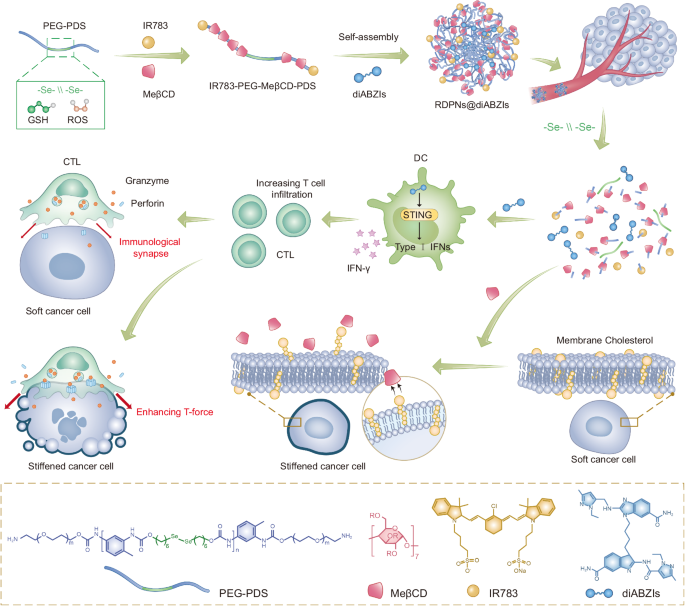
Synthesis and characterization of RDPNs@diABZIs
MeβCD-based supramolecular polyrotaxanes (MSPs) with diselenide-bridged axle polymer by end-capping with two NIR fluorescence probes IR783 (IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS) was synthesized, as detailed within the experimental part (Supplementary Fig. 1)36,37. As a management, MSPs with dicarbonyl-bridged axle polymer by end-capping with two NIR fluorescence probes IR783 (IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PTD) have been additionally synthesized. H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectra have been used to characterize the profitable synthesis of polyrotaxane (Supplementary Figs. 2–6). By evaluating the combination of the proton indicators from MeβCD with these from the PEG section, the typical variety of MeβCD models within the polyrotaxane was calculated to be 16.8 (Supplementary Fig. 6). Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) curves have been proven that the typical molecular weight (Mn) of IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS was decided to be 39.4 kDa, 22.6 kDa greater than PEG-PDS (Mn = 16.8 kDa), offering direct proof for the formation of a polyrotaxane with roughly 17 MeβCD models (Fig. 2a). Moreover, thermogravimetric evaluation confirmed that MeβCD is integrated inside the polymer PEG-PDS (Fig. 2b). The Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrum of PEG-MeβCD-PDS displayed double attribute peaks at 3433 cm-1 and at 3274 cm-1, akin to the N-H stretching of -NH2 teams (Supplementary Fig. 7). In distinction, the FT-IR spectrum of IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS confirmed the disappearance of the height at 3274 cm-1, indicating the conversion of -NH2 to -NHR through the coupling response. These adjustments confirmed the profitable coupling of IR783 to PEG-MeβCD-PDS. Furthermore, the absorption spectrum of IR783 confirmed barely red-shifting in contrast with that of IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS, indicating that IR783 is current on PEG-MeβCD-PDS (Fig. 2c). Beneath the identical IR783 concentrations, the fluorescence depth of IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS elevated in comparison with that of free IR783 (Supplementary Fig. 8). These outcomes urged that IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS was efficiently ready, with IR783 capped into the polymer appearing as a stopper. Finally, polyrotaxane IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS was self-assembled into redox-responsive diselenide-bridged polyrotaxanes nanoformulations (RDPNs) in aqueous resolution, with nonresponsive polyrotaxanes nanoparticles (NPNs) as management. STING agonists diABZIs have been additional encapsulated into the hydrophobic core of the nanoparticles (RDPNs@diABZIs) via easy ultrasonication38. The diABZIs-loaded RDPNs (RDPNs@diABZIs) have been ready with a diABZIs loading effectivity of 5.67% (Supplementary Fig. 13). Dynamic mild scattering (DLS) outcomes revealed that the hydrodynamic sizes of RDPNs, NPNs, and RDPNs@diABZIs have been 94.09 ± 6.8 nm, 131.71 ± 9.4 nm, and 142.7 ± 8.5 nm, respectively (Fig. second). Moreover, the floor zeta potentials of those constructed NPs have been discovered to be negatively charged, which have been -1.05 ± 0.17 mV, -0.58 ± 0.12 mV, and -1.19 ± 0.35 mV, respectively (Fig. 2e). Furthermore, RDPNs@diABZIs remained secure in numerous buffers for 2 weeks, demonstrating their stability in physiological techniques, which supplied assurance for subsequent experiments (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Figs. 9–11). The degradation habits of RDPNs was investigated beneath oxidative circumstances (H2O2), mimicking the in vivo TME situation39,40,41. As revealed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photographs, in contrast with the uniform spherical construction of RDPNs beneath PBS circumstances, RPDNs aggregated and swelled after 12 h of publicity to H2O2 resolution and totally collapsed into small fragments inside 24 h. (Fig. 2g). Moreover, DLS outcomes additionally revealed that because the focus of hydrogen peroxide elevated, the hydrodynamic sizes have been steadily elevated, indicating the RPDNs aggregated and swelled (Fig. 2h). Quite the opposite, the nonresponsive poly-MeβCD nanoparticles (NPNs) confirmed negligible adjustments in morphology and hydrodynamic sizes, and no degradation within the oxidative situation after 24 h of incubation (Supplementary Fig. 12). To analyze whether or not the degradation of RPDNs can induce the discharge of diABZIs, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to watch the discharge habits. RPDNs confirmed an growing launch of diABZIs because the focus of hydrogen peroxide elevated (Fig. 2i and Supplementary Fig. 13). They confirmed a burst launch of roughly 78.5% of the cumulative complete diABZIs within the oxidative situation after 6 h of incubation, becoming nicely with the degradation habits.
a GPC curves of PEG-PDS and IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS. GPC was carried out utilizing N,N-dimethylformamide because the eluent. b TGA curves of MeβCD, PEG-PDS and IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS from 30 °C to 800 °C at a fee of 10 °C min-1 beneath nitrogen ambiance. c Absorbance spectra of IR-783 and IR783-PEG-MeβCD-PDS. d, e The hydrodynamic diameters and zeta potential of NPNs, RDPNs, and RDPNs@diABZIs. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. f The typical hydrodynamic diameter of RDPNs@diABZIs have been measured in PBS buffer over 2 weeks. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. g, h TEM photographs and hydrodynamic diameters of RDPNs in numerous therapies with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Scale bar, 400 nm. i In vitro diABZIs launch profile of RDPNs@diABZIs co-cultured with or with out completely different concentrations of H2O2. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. Knowledge have been expressed as means ± SD.
Most cancers-cell stiffness is enhanced by depletion of ldl cholesterol with RDPNs
Contributing to irregular era and cross-linking of extracellular matrix proteins, tumors are usually more durable than their corresponding regular tissues42. Apparently, membranes of most cancers cells are sometimes softer than non-malignant cells43,44,45. Most cancers cells soften cell membranes by way of growing ldl cholesterol, which reduces the drive exerted by T-cell synapses to assist most cancers cells evade T-cell killing. MeβCD, a cholesterol-depletion molecule, may improve most cancers cell membrane stiffness (Fig. 3a). In comparison with HC11 cells (murine breast epithelial cells), 4T1 cells (murine breast most cancers cells) confirmed a big improve in levels of cholesterol (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 14). We additional quantified the levels of cholesterol in tumor tissues and regular tissues remoted from 4T1-bearing mice. The levels of cholesterol in tumor tissues elevated by 2.67 instances in comparison with adjoining muscle tissues (Fig. 3c). Moreover, elevated levels of cholesterol have been analyzed in various kinds of tumor tissues (Supplementary Fig. 15). These outcomes present proof {that a} frequent characteristic of levels of cholesterol in numerous varieties of most cancers cells was greater than these of regular cells.
a Illustrations of mechanical immuno-suppression induced by the softened most cancers cells and mechanical immuno-activation induced by the stiffened most cancers cells ensuing from membrane ldl cholesterol depletion. b Levels of cholesterol in numerous cells. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. c Levels of cholesterol in 4T1 tumor tissues or the adjoining muscle tissues. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. d, e Relative intracellular and plasma membrane ranges of ldl cholesterol in 4T1 most cancers cells handled with PBS, MeβCD, NPNs, or RDPNs in vivo (d) and in vitro (e). n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. f, g The Filipin III staining of 4T1 tumor cells after completely different therapies. Experiments have been carried out thrice with comparable outcomes. Scale bar, 100 nm. h Relative cortical stiffness of 4T1 most cancers cells handled with completely different therapies. n = 6 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. i The schematic diagram of perforin forming pores in native most cancers cells or stiffness most cancers cells. j Viability of pre-treated 4T1 most cancers cells after incubation with perforin at indicated concentrations at 37 °C for 20 min. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. okay Lysis share of 4T1 most cancers cells pre-treated with activated CD8+ T cells at an E: T ratio of 10:1 for five h. n = 4 biologically impartial samples per group. Knowledge have been expressed as means ± SD. G1: PBS, G2: MeβCD, G3: NPNs, G4: RDPNs. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s submit hoc take a look at (b, d, e, h, okay) or Two-tailed Pupil’s t-test (c). *P P P P
To analyze the optimum therapeutic window for MeβCD in deleting membrane ldl cholesterol, we quantified the levels of cholesterol in 4T1 cells and T cells co-cultured with completely different concentrations of MeβCD in vitro. The half-maximal efficient focus (EC50) of MeβCD for ldl cholesterol depletion in tumor cells was 3.85 mM, whereas no important change was noticed within the membrane levels of cholesterol of T cells (Supplementary Fig. 16). The outcomes indicated that T cells have a better tolerance to MeβCD than 4T1 tumor cells. Moreover, the membrane ldl cholesterol degree of assorted most cancers cells was diminished after co-culturing with MeβCD, whereas the intracellular ldl cholesterol degree confirmed negligible adjustments (Supplementary Fig. 17). Subsequently, plasma membrane levels of cholesterol may very well be managed by way of MeβCD in numerous most cancers cells.
Subsequently, we assessed the cell viability of 4T1 cells, T cell, or L929 (mouse fibroblast cell line) cells co-cultured with completely different medicine for twenty-four h. The adjustments in L929 cells and T cells handled with RDPNs have been negligible (Supplementary Fig. 18). In distinction, the viability of 4T1 cells was considerably decreased. Furthermore, no apparent change within the viability of 4T1 cells was noticed after remedy with NPNs (Supplementary Fig. 19). Additional, the evaluation of reside/lifeless staining and Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) stream cytometry have been per the above outcomes (Supplementary Figs. 20, 21). These outcomes display that RDPNs exhibit selective cytotoxicity in opposition to most cancers cells, whereas inflicting no harm to T cells and regular cells.
To confirm whether or not RDPNs can also cut back membrane levels of cholesterol, 4T1 tumor-bearing mice have been used as fashions that have been handled with MeβCD, RDPNs, or NPNs intratumorally (i.t). We discovered that the membrane ldl cholesterol degree of most cancers cells handled with RDPNs dropped markedly to solely 47.8% relative to PBS group (G1). In distinction, the membrane ldl cholesterol degree of 4T1 most cancers cells handled with NPNs confirmed negligible adjustments (Fig. 3e). Moreover, comparable outcomes have been obtained by intravenous injection (Supplementary Fig. 22). Furthermore, the leads to vitro have been per in vivo (Fig. 3d). Additional, the membrane ldl cholesterol degree of 4T1 most cancers cells have been visualized or quantitatively analyzed by way of staining the Filipin III, a fluorescent dye that particularly binds to ldl cholesterol (Fig. 3f, g and Supplementary Fig. 23). The fluorescence photographs and the stream cytometry evaluation all revealed the excellent cholesterol-depleting functionality of RDPNs similar to the identical focus of MeβCD. To additional examine whether or not RDPNs affect the membrane levels of cholesterol of tumor-infiltrating T cells, we quantified the degrees in cells in vitro and in vivo. The outcomes confirmed that RDPNs had a negligible lower on the membrane levels of cholesterol of tumor-infiltrating T cells (Supplementary Fig. 24). We additional investigated the performance of tumor-infiltrating T cells after treating with RDPN. In comparison with the PBS group, the inhabitants of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells confirmed no important change after RDPNs remedy (Supplementary Fig. 25). Moreover, the inhabitants of CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells and CD8+GzmB+ T cells additionally remained unchanged. These outcomes display that RDPNs present a burst launch of MeβCD in tumors, decreasing membrane levels of cholesterol of tumor cells whereas having negligible results on membrane levels of cholesterol and performance of tumor-infiltrating T cells.
To analyze whether or not cancer-cell stiffness may very well be enhanced by depleting membrane ldl cholesterol, we immediately measured single-cell cortical stiffness utilizing Atomic Power Microscopy (AFM)46 (Fig. 3h). We discovered that the cortical stiffness of 4T1 most cancers cells handled with MeβCD and RDPNs decreased by 3.02 instances and a couple of.89 instances, respectively, relative to PBS group (G1). Furthermore, comparable outcomes have been noticed in different most cancers cells (Supplementary Fig. 26). These outcomes demonstrated that ldl cholesterol depletion within the cell membrane contributes to most cancers cell stiffness.
Most cancers-cell stiffness by RDPNs enhances T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity via T-cell forces
Most cancers-cell softness impairs T-cell forces additional stopping membrane pore formation by perforin47, which subsequently prevents the entry of granzyme B to provoke apoptosis. Most cancers-cell stiffening by way of ldl cholesterol depletion allowed for accelerating the velocity of pore formation by synergistic mechanical drive and perforin (Fig. 3i). To analyze whether or not cytotoxicity of various stiffness of most cancers cells is expounded to perforin concentrations within the absence of activated T cells, in another way pre-treated 4T1 cells have been co-cultured with various concentrations of perforin (Fig. 3j). Apparently, within the absence of activated T cells, the cell viability of most cancers cells of various stiffness was impartial of the focus of perforin. Subsequent, we co-cultured activated CD8+ T cells with pre-treated 4T1 cells. Just like pre-treated with MeβCD, RDPNs-pretreated 4T1 cells accelerated the velocity of pore formation in comparison with native 4T1 cells (G1) (Fig. 3k). These findings indicated that most cancers cell stiffening enhances T cell force-mediated cytotoxicity, mediated by elevated membrane pore formation by perforin.
Activation of cGAS-STING Pathway by RDPNs@diABZIs in vitro
STING agonists diABZIs can activate the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway (Fig. 4b)48,49. To monitored the cytotoxicity of RDPNs@diABZIs, we co-cultured 4T1 cells and L929 cells with RDPNs@diABZIs. The end result revealed that RDPNs@diABZIs displays selective toxicity in the direction of most cancers cells (Fig. 4a). To confirm whether or not RDPNs@diABZIs improve secretion of type-I Interferon (IFN-I) in APCs, we detected the degrees of IFN-β secretion. cGAMP, as a second messenger to activate STING, hardly ever elicited the secretion of IFN-β with a half-maximum efficient focus (EC50) of 84.61 ± 3.11 µM in THP-1 (Fig. 4c). This could contribute to its acts as a negatively charged molecule. Apparently, much like EC50 of 5.15 ± 0.59 µM of STING agonists diABZIs, RDPNs@diABZIs additionally induced a concentration-dependent secretion of IFN-β in THP-1 cells with EC50 of 5.70 ± 0.71 µM (Fig. 4c). In contrast with cGAMP, the supply of diABZIs or RDPNs@diABZIs elevated the IFN-β secretion ranges by order of magnitude. Equally, an enhancement in stimulating IFN-β secretion was noticed in Bone Marrow Dendritic Cells (BMDCs), the EC50 of diABZIs, RDPNs@diABZIs, and cGAMP was 5.71 ± 0.12 µM, 6.42 ± 0.21 µM, 92.36 ± 6.90 µM (Fig. 4d). In comparison with cells handled with free cGAMP, BMDCs stimulated by RDPNs@diABZIs exhibited considerably growing expression of co-stimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 (Fig. 4e–h). Western blot evaluation revealed a noticeable phosphorylation of STING (p-STING) and IRF-3 (p-IRF-3) in response to diABZIs and RDPNs@diABZIs (Fig. 4i, j). The expression ranges of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-1β additionally considerably elevated (Fig. 4k-m). These outcomes urged that RDPNs@diABZIs can activate the cGAS-STING pathway and have the potential to stimulate T-cell activation.
a Viability of L929 and 4T1 co-cultured with RDPNs@diABZIs for twenty-four h. n = 5 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated thrice. b Schematic illustration of the activation of the GAS-STING pathway in dendritic cells (DCs). c, d Dose-dependent ranges of secretion of IFN-β elicited by indicated formations in THP-1 and BMDCs. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated twice. e–h Consultant stream cytometric plots and quantification of DC maturation floor marker expression (CD80+, CD86+) in BMDCs handled with indicated formulations for twenty-four h. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated twice. i, j Western blot picture and semiquantitative evaluation of p-STING and p-IRF-3 in THP−1 cells handled with numerous therapies. n = 3 biologically impartial samples biologically impartial animals per group. The samples derive from the identical experiment and that blots have been processed in parallel. okay–m Cytokine secretion ranges within the supernatants of BMDCs handled with indicated formulations for twenty-four h. n = 3 biologically impartial samples per group, repeated twice. Knowledge have been expressed as means ± SD. G1: PBS, G2: cGAMP, G3: diABZIs, G4: RDPNs@diABZIs. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s submit hoc take a look at (g, h, j, okay, l). *P P P P
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetic evaluation
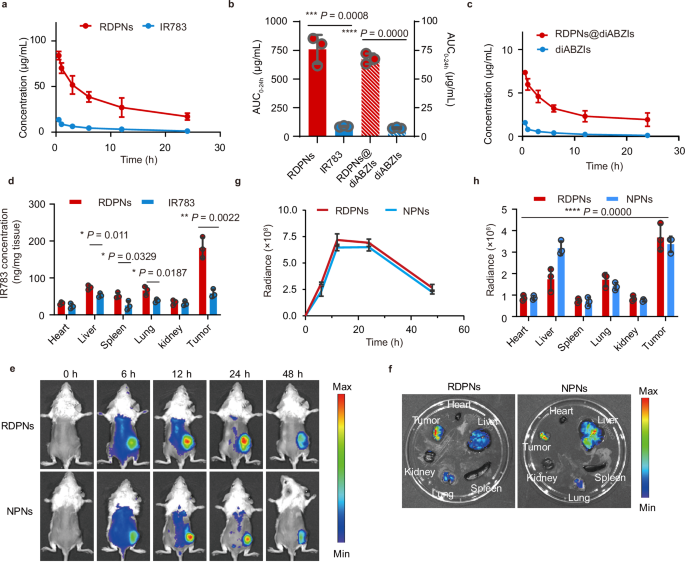
We evaluated the pharmacokinetics profiles by measuring the focus of IR783. The elimination half-life (t1/2) of RDPNs and free IR783, calculated have been 1.40 h and 0.31 h, respectively (Fig. 5a). Equally, t1/2 of RDPNs@diABZIs and diABZIs have been 1.5 h and 0.25 h, respectively (Fig. 5b). These present proof that nanomaterials can prolong the blood circulation time of IR783 in comparison with free IR783. Moreover, the world beneath the curve (AUC) for RDPNs was about 10 instances than IR783 (Fig. 5c). The focus of IR783 in tumors sacrificed from injected with RDPNs was considerably enhanced in contrast with that injected with free IR783 (Fig. 5d). Subsequently, we’ve motive to consider that RDPNs exhibit long-term retention traits within the tumor tissue.
a, c Plasma concentration-time profiles of IR783 and diABZIs submit i.v. injection.n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group, repeated twice. b The AUC0-t of IR783 and diABZIs evaluation. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group, repeated twice. d Quantification of RDPNs in tumor and main organs by fluorescence spectrophotometer. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. e, g The NIR fluorescence photographs and the relative fluorescence depth of tumors in vivo of the 4T1-tumor bearing mice after intravenous injection of NPNs or RDPNs. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group, repeated twice. f, h Ex vivo NIR photographs and relative fluorescence depth of various organs. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group, repeated twice. Knowledge have been expressed as means ± SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s submit hoc take a look at (h) or two-tailed Pupil’s t-test (b, d). *P P P P
Additional, to research the biodistribution of RDPNs within the tumor-bearing mice mannequin, we intravenously injected RDPNs or NPNs and monitored the fluorescence of IR783 utilizing small animal in vivo imaging. In vivo fluorescence photographs and quantitative evaluation all indicated enhanced tumor fluorescence sign with a peak at 12 h post-injection of RDPNs or NPNs (Fig. 5e, g). The fluorescence depth steadily decreases after 24 h, however fluorescence remains to be seen on the tumor web site at 48 h. The above outcomes indicated a robust drug retention impact of RDPNs or NPNs. Moreover, ex vivo photographs sacrificed at 48 h confirmed important nanomedicines accumulation within the tumor web site and little accumulation within the main organ (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, Kidney), which indicated that nanomedicines have been selectively collected to tumors (Fig. 5f, h).
RDPNs@diABZIs shift tumor immune microenvironment
The activation of the cGAS-STING pathway can prime innate and adaptive immune responses, which is useful for anti-tumor systemic immune responses50,51,52. An orthotropic 4T1 mouse breast tumor mannequin was established. Floor expression of CD86 of dendritic cells (DCs, CD45+CD11c+CD86+) of the tumor-draining lymph node (TDLN) in RDPNs@diABZIs-treated mice was elevated (Fig. 6a and Supplementary Fig. 27). Moreover, the whole cell quantity and the fraction of activated DCs additionally have been markedly elevated, which exhibited roughly 2.23-fold activated DCs than these handled with PBS. (Fig. 6b and Supplementary Figs. 27, 28). The entire cell quantity and the fraction of M1-like macrophages (CD11b+F4/80+CD86+) within the TME was considerably elevated in mice-treated RDPNs@diABZIs than different teams (Fig. 6c, d and Supplementary Figs. 29, 30). Quite the opposite, RDPNs@diABZIs decreased the whole cell quantity and the fraction of M2-like macrophages (CD11b+F4/80+CD206+) in TME in contrast with that acquired PBS solely (Fig. 6e, h and Supplementary Figs. 31, 32). These outcomes indicated repolarization or recruitment of macrophages with diminished immunosuppressive capability. Notably, in contrast with these handled with others, the tumors in mice that acquired RDPNs@diABZIs elevated the whole quantity and the fraction of pure killer cells infiltrated (Fig. 6i and Supplementary Figs. 34–35). We additional verified whether or not downregulating immune cells with immunosuppressive capability and upregulating that with immune-activated capability in TME can potentiate anti-tumor immune responses. RDPNs@diABZIs led to cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in TDLN elevated in contrast with different teams (Fig. 6f, j and Supplementary Figs. 36–38). Immunofluorescence staining of the CD8 marker in tumor slices retrieved after mice handled with RDPNs@diABZIs confirmed enhanced infiltration of CD8+ T cells (Supplementary Fig. 40). The mice that acquired RDPNs@diABZIs elicited 2.43-fold extra CD8+ T cells and 1.85-fold extra CD4+ T cells than that handled PBS solely. The growth of CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells in mice receiving RDPNs didn’t exceed the baseline degree, whereas diABZIs remedy resulted in a 2.67-fold improve in IFN-γ-secreting CTLs (Fig. 6g, okay and Supplementary Fig. 39). Notably, RDPNs@diABZIs additional elevated the frequency, with the expression degree of CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells in TDLNs being 4.84 instances greater than that of the PBS management group. We additional measured a kinetics examine over 7 days of pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum. The focus of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and Granzyme B in serum elevated quickly, peaking at 72 h post-treatment with RDPNs@diABZIs (Fig. 6l and Supplementary Figs. 41–43). Subsequently, the focus of pro-inflammatory cytokines decreased and returned near benchmark degree by 7 days after remedy. These findings point out that RDPNs@diABZIs can provoke systemic T-cell immune responses, with the related systemic irritation being transient, which is crucial to making sure its security.
a, b Consultant stream cytometry histogram and relative quantification of CD86 expressions by DCs (CD45+CD11c+CD86+) within the TDLNs. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. c, d Consultant stream cytometric evaluation and quantification of CD86 expressions in M1-like macrophages (CD45+CD11b+F4/80+CD86+) in tumors. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. e, h Consultant stream cytometry histogram and quantification of CD206 expressions in M2-like macrophages (CD45+CD11b+F4/80+CD206+) in tumors. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. f, j, Consultant stream cytometric evaluation and relative quantification of CD8+ T cells (CD3+CD8+) within the TDLNs. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. g, okay Consultant stream cytometric evaluation and relative quantification of CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells (CD45+CD8+IFN-γ+) within the TDLNs. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. i Quantification of NK cells (CD45+CD49b+) in spleen. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. l Serum cytokine focus of IFN-γ, TNF-α and Granzyme B. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. Knowledge have been expressed as means ± SD. (G1: PBS, G2: NPNs, G3: RDPNs, G4: diABZIs, G5: RDPNs@diABZIs. DCs, Dendritic cells. NK cells, Pure killer cells. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s submit hoc take a look at (b, c, h, i, j, okay, l). *P P P P
RDPNs@diABZIs set off strong anti-tumor therapeutic efficacy
Based mostly on the above outcomes, we subsequent evaluated the anti-tumor impact of RDPNs@diABZIs in vivo. An orthotropic 4T1-luc mouse breast tumor mannequin was established, and mice have been randomly divided into 5 teams: PBS (G1), NPNs (G2), RDPNs (G3), diABZIs (G4), and RDPNs@diABZIs (G5). Mice have been handled when the tumor quantity reached roughly 100 mm3 and have been intravenously injected with indicated formulations on days 0, 2, and 4. Mice handled with NPNs didn’t suppress tumor progress (Fig. 7a–d). Quite the opposite, the tumor quantity of mice handled with RDPNs was inhibited. These demonstrated that MeβCD launched from RDPNs decreasing membrane ldl cholesterol promotes most cancers cell stiffness and induces its apoptosis, however it may well’t be launched from NPNs. Undoubtedly, tumor progress charges markedly have been inhibited in mice that acquired diABZIs solely, which contributed to enhanced anti-tumor immune responses induced by diABZIs-activated cGAS-STING pathway. Notably, mice handled with RDPNs@diAZBIs confirmed strong tumor regression and long-term survival of no less than 2 months in about 83.3%. In line with the above outcomes, mice handled with RDPNs@diAZBIs obtained extra environment friendly therapeutic results than different group in response to the hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and TUNEL staining outcomes (Supplementary Figs. 44, 45). Subsequent, blood chemistry evaluation, together with alanine aminotransferase (ALT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate transaminase (AST), urine acid (UA), creatine kinase (CK), and creatinine (CRE) have been carried out for long-term toxicity analysis after therapies. The outcomes confirmed all therapies didn’t induce important unwanted side effects within the mice (Supplementary Fig. 46). Moreover, there have been no important pathological adjustments in main organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, Kidney) H&E slices photographs (Supplementary Fig. 47).
a Respective bioluminescence photographs of tumors in mice on day 0, day 5, day 10, and day 15. b, c Particular person and common tumor quantity curves with indicated therapies. n = 6 biologically impartial animals per group. d Survival curves after therapies. n = 6 biologically impartial animals per group. e, f Consultant stream cytometric evaluation and quantification of reminiscence T cells (CD3+CD8+CD44excessiveCD62Llow, gated on CD3+CD8+ T cells) within the spleen. n = 4 biologically impartial animals per group, repeated twice. g Survival curves after subcutaneous rechallenge. n = 5 biologically impartial samples per group. h, i Bioluminescent photographs and fluorescence depth of lung in BALB/C mice. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. j Relative fluorescence depth of ex vivo lungs. n = 3 biologically impartial animals per group. G1: PBS, G2: NPNs, G3: RDPNs, G4: diABZIs, G5: RDPNs@diABZIs. Knowledge are offered as imply ± s.d. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s submit hoc take a look at (e) or two-tailed Pupil’s t-test (i, j). *P P P P
We subsequent explored the mechanism of tumor regression and sturdy anti-tumor impact in mice-treated RDPNs@diAZBIs. To check the immunological reminiscence, the reminiscence T cells (CD8+CD44excessiveCD62Llow) of the spleen retrieved from mice-treated indicated therapies have been analyzed utilizing stream cytometry. In comparison with the PBS group (G1), mice handled with RDPNs@diABZIs exhibited a 2.33-fold improve within the fraction of reminiscence T cells, a greater end result than different teams (Fig. 7e, f and Supplementary Fig. 48). This proof urged that mice established sturdy immune reminiscence after RDPNs@diABZIs remedy. To additional decide whether or not the anti-tumor immune responses induced by RDPNs@diABZIs have been sturdy, the mice that survived following the primary inoculation have been re-challenged with 4T1-luc tumor cells by intravenous administration. Noticeable tumor nodules bioluminescence in lung in vivo and ex vivo was noticed in mice of the management group (Fig. 7g–j and Supplementary Fig. 49). In distinction, mice handled with RDPNs@diABZIs confirmed no tumor nodules bioluminescence in lung, indicating the institution of sturdy anti-tumor immune responses. These outcomes supplied proof that RDPNs@diABZIs elicited strong anti-tumor efficacy and induced sturdy anti-tumor immunological reminiscence.