Sampling websites and knowledge assortment
The restoration therapies within the experimental website, Dawu city of Maqin nation which is a typical alpine space with a imply annual temperature (MAT) is 0.28 °C, altering from −15.9 °C to 13.0 °C and common annual rainfall is 516 mm, have been undertaken since 2000 when the severely degraded alpine grasslands have been replanted with the native perennial grass, Elymus nutans, Elymus sibiricus, Festuca sinensis, Poa crymophila40. To enhance the grassland, a mix of 4 native grass species was seeded. The seed are blended nicely and evenly distributed. The seeding charges have been 6 kg/hm2 for Elymus nutans, 6 kg/hm2 for Elymus sibiricus, 4.5 kg/hm2 for Festuca sinensis and 1.5 kg/hm2 for Poa crymophila in line with their seedling density ratios of 1:1:1:1. The location was plowed to take away toxic crops and annual weeds earlier than planting the grass combination. The location was plowed to take away toxic crops and annual weeds earlier than planting the grass combination. After planting the websites acquired no additional administration. All reseeded websites have been fenced to cut back disturbance and progressive succession. The samplings have been performed in 2017 to measure the soil microbe and chemistry of the restored alpine grasslands at completely different years: 1 12 months(1 y), 4 12 months(4 y), 6 12 months(6 y), 8 12 months(8 y), 9 12 months(9 y),12 12 months(12 y), 14 12 months(14 y), 16 12 months(16 y) and 18 12 months(18 y). In the meantime, the non-degraded alpine grasslands and unrestored severely degraded alpine grasslands have been sampled because the controls. All of the repeated samples of three soil cores utilizing an auger boring in every quadrat have been randomly collected and blended from every of 5 separate patches with the identical therapies (the restored grasslands in the identical successional years or the managed grasslands) throughout the area. The 5 separate sampling patches have been located inside independently restored fields, with a sampling quadrat randomly positioned inside every of the 5 patches. All of the restored/reseeded fields from 1-year to 18-year have been fenced to eliminate disturbance to protect the progressive succession. Subsequently, 5 patches throughout the bigger discipline have been sampled really from the fenced/undisturbed discipline or habitats. In complete, we collected 55 samples for the next analyses. Supplementary Fig. 8 confirmed the sampling websites. The scale of the patches assorted a bit as a result of distinction of their possession, as they belong to completely different households. Nonetheless, the topography or discipline situations weren’t a lot completely different, they have been flat fields with comparable soil and vegetation situations.
Soil physicochemical measurement
The physicochemical properties of the soil samples, together with complete nitrogen (TN), complete phosphorus (TP), complete potassium (TK), complete sulfur (TS), soil natural carbon (SOC), ammonia-nitrogen (N-NH4), nitrate nitrogen (N-NO3), nitrite nitrogen (N-NO2), accessible potassium (AK) and accessible phosphorus (AP), have been measured as beforehand reported8. All of the soil physicochemical quantification have been in triplicate.
Soil DNA extraction and amplicon sequencing
Complete microbial DNA was extracted from 0.5 g soils utilizing FastDNA®SPIN Package for Soil (MP Biomedicals, CA, USA) in line with the standardized protocol. DNA extracts have been dissolved with DES buffer, quantified, and certified utilizing a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Applied sciences, Wilmington, Germany). The V4-V5 areas of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene have been amplified utilizing the primers 515F (GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGG) and 907R(CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT). ITS1F (5-CTTGGTCATTTA-GAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS2R (5-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′) have been utilized to amply fungal ITS gene on the ITS2 area41. The PCR amplification cycles have been set as follows: 95 °C for two min, 25 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s, and a closing extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR merchandise have been purified and quantified as beforehand demonstrated8.
The PCR merchandise have been purified in similar portions and sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq2500 platform (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The uncooked paired-end reads have been denoised and assembled by utilizing DADA2 v1.1.3. USEARCH instrument was utilized to detect and take away chimera. The uncooked reads have been assigned to tell apart samples in line with the barcodes with Lima. FLASH was used to mix ahead with reverse sequences. 16S rRNA and ITS taxonomic annotation have been decided primarily based on the SILVA database (model 132) and the UNITE fungal. Operational taxonomic items (OTUs) with a 97% similarity cutoff have been clustered utilizing UPARSE42. The OTU desk was used for subsequent analyses.
Microbial range patterns evaluation
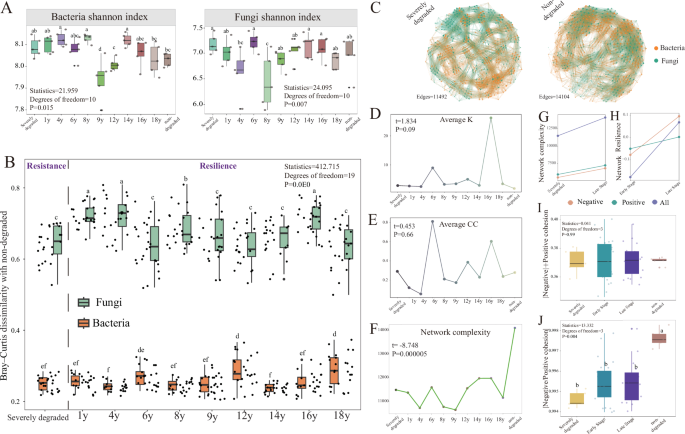
To check whether or not range patterns differed alongside the stage of grassland restoration succession, alpha range indices of micro organism and fungi have been evaluated with the vegan bundle in R.4.2.1. Kruskal-Wallis take a look at was utilized to research the results of grassland restoration on α-diversity. Principal Coordinates Evaluation (PCoA) primarily based on Bray-Curtis dissimilarity was utilized to discover the sample of the microbial group. The influences of grassland restoration on micro organism and fungi have been assessed by permutational multivariate evaluation of variance (PERMANOVA).
Co-occurrence community building
Microbial co-occurrence networks have been independently created for yearly utilizing the OTUs desk. Correlations with Spearman’s correlation coefficients (ρ) higher than 0.6 and corresponding P-values lower than 0.01 have been thought of vital. The ‘rcorr’ perform from the ‘Hmisc’ bundle was used to carry out pairwise comparisons primarily based on OTUs, with p-values adjusted accordingly. Co-occurrence networks have been constructed utilizing the ‘igraph’ bundle, the place every node represented one OTU and every edge represented a powerful and vital correlation. The ensuing networks have been visualized utilizing the interactive platform Gephi (0.9.7). We categorised the nodes into 4 classes primarily based on their within-module connectivity (Zi) and among-module connectivity (Pi) to determine the topological roles of taxa within the networks. To determine keystones within the community, we calculated the within-module connectivity (Zi) and among-module connectivity (Pi) of every node. In keeping with corresponding standards, we recognized module hubs (Zi ≥ 2.5, Pi Zi Pi ≥ 0.62) and community hubs (Zi ≥ 2.5, Pi ≥ 0.62), that are known as keystone.
Evaluation of the habitat specialists and generalists and core species
To find out the habitat specialization of microorganisms, we employed Levin’s area of interest breadth43. Briefly, the importance of the habitat specialization index was examined utilizing the Ecolutils in R for 1000 permutations. When the habitat specialization values exceed the higher 95% confidence interval or fall under the decrease 95% confidence interval of 1000 permutations, they’re recognized as habitat generalists or specialists. All statistical analyses have been performed utilizing R model 4.3.0.
We took the intersection between specialists, Keystone, and shared microorganisms to acquire core specialists13. Equally, we took the intersection between generalists, Keystone, and shared microorganisms to acquire core generalists.
Quantification of group meeting
The null mannequin was carried out to find out deterministic and processes and stochastic processes of each micro organism and fungi44. Bray-Curtis-based Raup-Crick (RCbray) and β nearest taxon index (βNTI) have been calculated to determine the group meeting of micro organism and fungi. The partial Mantel take a look at was performed to quantify the connection between the environmental variables and βNTI. The correlations between βNTI and the very important physicochemical components have been assessed by linear regression fashions.
Phylogenetic conservation and environmental threshold
Environmental threshold values of micro organism and fungi have been calculated by threshold indicator taxa evaluation (TITAN2) to unravel microbial response to environmental components45. TITAN2 categorizes the group into two teams: Z– taxa that negatively reply to elevated environmental gradient, and Z+ taxa that positively reply to elevated gradient. Taxa with none response to the environmental gradient weren’t thought of. TITAN then tracks the cumulative responses of declining taxa (sum(Z–)) and growing taxa (sum(Z+)) locally. Ecological thresholds are outlined because the factors the place the utmost combination change within the frequency and relative abundance of responding taxa happens. When the environmental values attain and exceed the ecological thresholds, the abundance and incidence frequency of species will lower within the Z– group whereas growing within the Z+ group. Subsequently, the vary of area of interest optima for the group is outlined because the gradient under sum(Z–) and above sum(Z+).
Phylogenetic indicators have been instrumental in testing whether or not the environmental choice was associated to the phylogeny46,47. Spearman correlations between environmental parameters and the relative abundance of OTUs have been calculated to determine the ecological choice48. Blomberg’s Okay statistic was carried out to excavate phylogenetic indicators for the environmental adaption of micro organism and fungi.
Assessing microbial group stability and high quality of plant-soil system
Group stability in response to disturbance contains two parts: resistance and resilience. On this research, to measure composition resistance, we used Bray-Curtis dissimilarity values to check non-degraded grassland samples with severely degraded ones. Equally, for composition resilience, we in contrast non-degraded grassland samples with restored ones utilizing Bray-Curtis dissimilarity values. We additionally used the resilience index measuring the extent of restoration by figuring out the spearman correlation between species. It calculates the ratio of the distinction in Spearman correlation between every pattern and severely degraded samples to the distinction in non-degraded and severely degraded samples as a way to characterize the community resilience. Furthermore, we additionally make the most of the AVD index36,49 and Cohesion index13,33 to evaluate the steadiness of microbial communities. AVD (common variation diploma) is outlined because the diploma to which microbial communities bear environmental modifications, implying the general stability of the microbial group. Decrease AVD recommended increased stability of the microbial group. The index plant-soil methods high quality index (PSQI) and the resilience index of plant-soil methods (PSQIR) have been quantified in earlier analysis32. We fastidiously chosen from 9 crops indicators and sixteen soil indicators to create the plant-soil system high quality index (PSQI) for assessing ecosystem modifications throughout restoration efforts. The final word ecological aim for the restored websites is to determine a thriving pure grassland with optimum plant and soil high quality. The particular targets for plant group composition is to have a protection fee of 100%, with the proportion of edible crops exceeding 70%, and reaching the peak of edible crops over 25 cm, primarily based on the requirements outlined by Ma et al.50. The restoration index on this article is calculated primarily based on this aim.
Statistics and reproducibility
We used 5 organic replicates in every year: non-degraded (n = 5), severely degraded (n = 5), and restored alpine grasslands at completely different years: 1 12 months (1 y, n = 5), 4 years (4 y, n = 5), 6 years (6 y, n = 5), 8 years (8 y, n = 5), 9 years (9 y, n = 5), 12 years (12 y, n = 5), 14 years (14 y, n = 5), 16 years (16 y, n = 5), and 18 years (18 y, n = 5). There have been early restoration phases (n = 25, from 1 y to 9 y) and late restoration phases (n = 20, from 12 y to 18 y). The range calculation and co-occurrence community indicators for every remedy have been primarily based on 5 organic replicates from every remedy. The full pattern dimension for calculating these parameters (Node fidelity, Node persistence, Area of interest width, Phylogenetic conservation and Environmental threshold, Quantification of group meeting) is all samples (n = 55). No statistical technique was used to predetermine pattern dimension. Our experiment doesn’t have any subjective bias in the direction of the experimental commentary outcomes, so we didn’t use blind experiments. No knowledge was excluded aside from outliers, that are outlined as observations which can be decrease than or increased than the whiskers on the field plot. The interquartile vary is the distinction between the third quartile and the primary quartile within the knowledge.
Reporting abstract
Additional data on analysis design is on the market within the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract linked to this text.