
Micro organism will be engineered to sense quite a lot of molecules, reminiscent of pollution or soil vitamins. Normally, nonetheless, these indicators can solely be detected by wanting on the cells beneath a microscope or equally delicate lab tools, making them impractical for large-scale use.
Utilizing a brand new technique that triggers cells to provide molecules that generate distinctive mixtures of colour, MIT engineers have proven that they’ll learn out these bacterial indicators from so far as 90 meters away. Their work may result in the event of bacterial sensors for agricultural and different functions, which may very well be monitored by drones or satellites.
“It is a new means of getting info out of the cell. In case you’re standing subsequent to it, you possibly can’t see something by eye, however from tons of of meters away, utilizing particular cameras, you may get the data when it activates,” says Christopher Voigt, head of MIT’s Division of Organic Engineering and the senior writer of the brand new research.
In a paper showing in Nature Biotechnology, the researchers confirmed that they might engineer two several types of micro organism to provide molecules that give off distinctive wavelengths of sunshine throughout the seen and infrared spectra of sunshine, which will be imaged with hyperspectral cameras.
These reporting molecules have been linked to genetic circuits that detect close by micro organism, however this strategy is also mixed with any present sensor, reminiscent of these for arsenic or different contaminants, the researchers say.
“The good factor about this know-how is which you can plug and play whichever sensor you need,” says Yonatan Chemla, an MIT postdoc who is among the lead authors of the paper. “There isn’t a cause that any sensor wouldn’t be suitable with this know-how.”
Itai Levin, Ph.D. can also be a lead writer of the paper. Different authors embody former undergraduate college students Yueyang Fan and Anna Johnson, and Connor Coley, an affiliate professor of chemical engineering at MIT.
Hyperspectral imaging
There are lots of methods to engineer bacterial cells in order that they’ll sense a selected chemical. Most of those work by connecting the detection of a molecule to an output reminiscent of inexperienced fluorescent protein (GFP). These work nicely for lab research, however such sensors cannot be measured from lengthy distances.
For long-distance sensing, the MIT staff got here up with the concept to engineer cells to provide hyperspectral reporter molecules, which will be detected utilizing hyperspectral cameras. These cameras, which have been first invented within the Nineteen Seventies, can decide how a lot of every colour wavelength is current in any given pixel. As a substitute of displaying up as merely pink or inexperienced, every pixel comprises info on tons of of various wavelengths of sunshine.
At present, hyperspectral cameras are used for functions reminiscent of detecting the presence of radiation. Within the areas round Chernobyl, these cameras have been used to measure slight colour modifications that radioactive metals produce within the chlorophyll of plant cells. Hyperspectral cameras are additionally used to search for indicators of malnutrition or pathogen invasion in vegetation.
That work impressed the MIT staff to discover whether or not they may engineer bacterial cells to provide hyperspectral reporters after they detect a goal molecule.

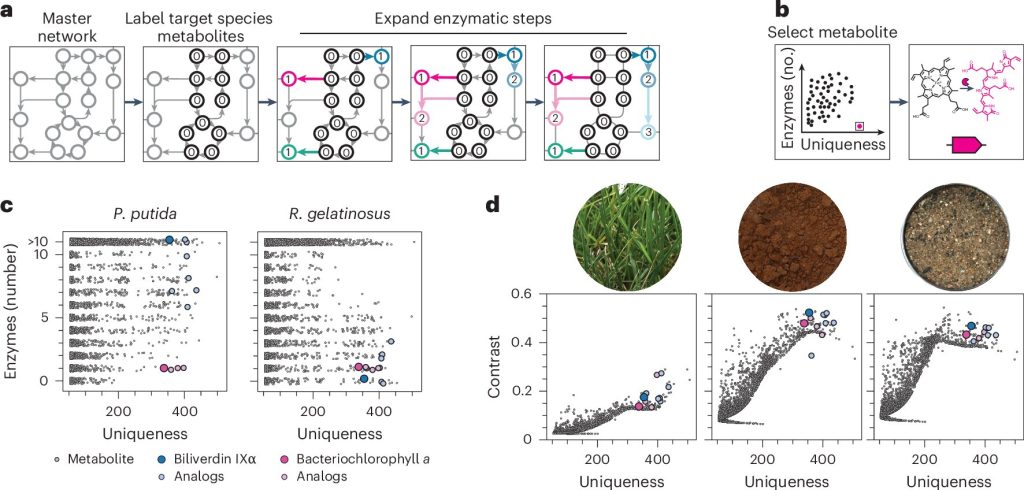
For a hyperspectral reporter to be most helpful, it ought to have a spectral signature with peaks in a number of wavelengths of sunshine, making it simpler to detect.
The researchers carried out quantum calculations to foretell the hyperspectral signatures of about 20,000 naturally occurring cell molecules, permitting them to establish these with probably the most distinctive patterns of sunshine emission. One other key characteristic is the variety of enzymes that may have to be engineered right into a cell to get it to provide the reporter—a trait that can fluctuate for several types of cells.
“The perfect molecule is one which’s actually completely different from all the things else, making it detectable, and requires the fewest variety of enzymes to provide it within the cell,” Voigt says.
On this research, the researchers recognized two completely different molecules that have been finest suited to two forms of micro organism. For a soil bacterium known as Pseudomonas putida, they used a reporter known as biliverdin—a pigment that outcomes from the breakdown of heme. For an aquatic bacterium known as Rubrivivax gelatinosus, they used a sort of bacteriochlorophyll.
For every bacterium, the researchers engineered the enzymes vital to provide the reporter into the host cell, then linked them to genetically engineered sensor circuits.
“You may add one in every of these reporters to a bacterium or any cell that has a genetically encoded sensor in its genome. So, it’d reply to metals or radiation or toxins within the soil, or vitamins within the soil, or no matter it’s you need it to answer. Then the output of that may be the manufacturing of this molecule that may then be sensed from far-off,” Voigt says.
Lengthy-distance sensing
On this research, the researchers linked the hyperspectral reporters to circuits designed for quorum sensing, which permit cells to detect different close by micro organism. They’ve additionally proven, in work achieved after this paper, that these reporting molecules will be linked to sensors for chemical substances together with arsenic.
When testing their sensors, the researchers deployed them in containers so they’d stay contained. The containers have been positioned in fields, deserts, or on the roofs of buildings, and the cells produced indicators that may very well be detected utilizing hyperspectral cameras mounted on drones. The cameras take about 20 to 30 seconds to scan the sphere of view, and laptop algorithms then analyze the indicators to disclose whether or not the hyperspectral reporters are current.
On this paper, the researchers reported imaging from a most distance of 90 meters, however they’re now engaged on extending these distances.
They envision that these sensors may very well be deployed for agricultural functions reminiscent of sensing nitrogen or nutrient ranges in soil. For these functions, the sensors is also designed to work in plant cells. Detecting landmines is one other potential software for one of these sensing.
Earlier than being deployed, the sensors would want to endure regulatory approval by the U.S. Environmental Safety Company, in addition to the U.S. Division of Agriculture if used for agriculture. Voigt and Chemla have been working with each companies, the scientific neighborhood, and different stakeholders to find out what sorts of questions have to be answered earlier than these applied sciences may very well be authorised.
“We have been very busy previously three years working to know what are the regulatory landscapes and what are the protection issues, what are the dangers, what are the advantages of this sort of know-how?” Chemla says.
Extra info:
Hyperspectral reporters for long-distance and wide-area detection of gene expression in dwelling micro organism, Nature Biotechnology (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41587-025-02622-y
Supplied by
Massachusetts Institute of Expertise
This story is republished courtesy of MIT Information (internet.mit.edu/newsoffice/), a well-liked website that covers information about MIT analysis, innovation and instructing.
Quotation:
Engineered micro organism emit indicators that may be noticed from a distance (2025, April 11)
retrieved 11 April 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-04-bacteria-emit-distance.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.



