
In a groundbreaking improvement from Tokyo Metropolitan College, researchers have unveiled a novel strategy for distinguishing cancerous cells from wholesome ones by meticulously monitoring their pure actions with out the necessity for any fluorescent labeling. Using phase-contrast microscopy, a label-free imaging method, the workforce noticed the distinct migratory behaviors of malignant fibrosarcoma cells and wholesome fibroblasts cultured on a dish. Their meticulous evaluation revealed that refined variations within the form and curvature of mobile trajectories function dependable indicators to distinguish between these two cell sorts with a formidable accuracy of as much as 94 p.c.
For hundreds of years, cell evaluation underneath the microscope has predominantly centered on static traits comparable to morphological options, inside composition, or the identification of particular molecular markers by varied staining strategies. Nevertheless, these strategies overlook the dynamic nature of dwelling cells, which repeatedly transfer and reshape themselves in response to each intrinsic applications and exterior cues. The researchers’ modern shift in the direction of investigating cell motility acknowledges that cell migration patterns — significantly these related to most cancers metastasis — carry profound organic significance that may be harnessed for diagnostic functions.
Monitoring cell motion with precision over time has traditionally offered formidable challenges. Guide commentary of restricted cell populations dangers bias, whereas many automated monitoring methods rely closely on fluorescent labels to reinforce visibility. Regardless of their utility, fluorescent dyes can inadvertently alter mobile properties, probably confounding outcomes and limiting medical translatability. The aspiration, subsequently, has been to ascertain a totally automated, high-throughput technique for monitoring cell migration in a label-free method, preserving cells in circumstances nearer to their physiological states.
The Tokyo Metropolitan College workforce, led by Professor Hiromi Miyoshi, achieved this ambition by leveraging phase-contrast microscopy, an optical imaging method prized for its capability to visualise clear specimens with out exogenous markers. Section-contrast microscopy exploits variations in refractive indices inside cells and their surrounding medium to generate distinction, permitting detailed visualization of dwelling cells on plastic petri dishes with out disturbing their motility or viability. This system bypasses the optical distortions or interferences typically encountered when imaging by commonplace tradition dishes, guaranteeing genuine recording of mobile actions.
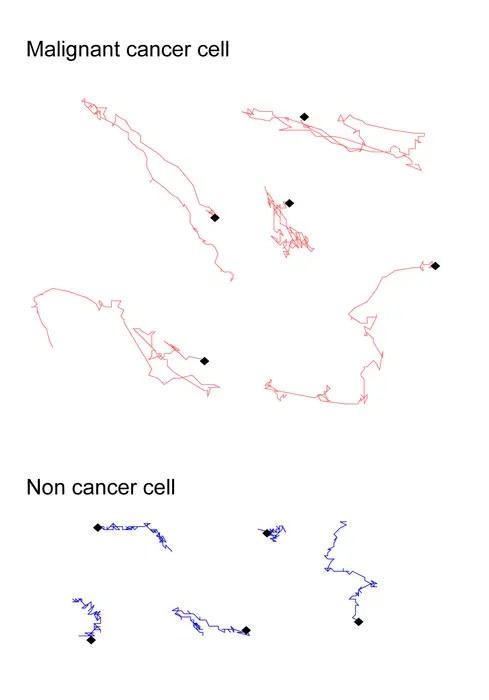
To decode the complicated migratory behaviors of particular person cells, the researchers utilized refined picture evaluation algorithms to extract and reconstruct the trajectories of quite a few single cells from time-lapse phase-contrast movies. They quantitatively characterised the paths utilizing metrics comparable to migration pace and the “sum of flip angles,” which measures how continuously and sharply cells change their path. Notably, the frequency of shallow turns and the general curvature of the trajectories emerged as pivotal parameters encoding refined mechanical and morphological disparities between cancerous and non-cancerous cells.
A direct comparability between wholesome fibroblast cells — important structural cells that type connective tissue and help wound therapeutic — and malignant fibrosarcoma cells — aggressive most cancers cells originating from fibrous connective tissues — underscored the diagnostic potential of this technique. Regardless of their related appearances, the migratory trajectories of those cells revealed distinct fingerprints. Whereas regular fibroblasts tended to observe straighter, slower paths characterised by fewer shallow turns, the most cancers cells exhibited extra erratic and curvilinear actions. Capturing these nuanced variations enabled the analysis workforce to categorise cell sorts with exceptional precision.
The implications of this analysis prolong far past easy most cancers cell discrimination. Since mobile motility underlies quite a few physiological and pathological processes, together with embryogenesis, immune responses, tissue regeneration, and metastatic development, the offered label-free, quantitative monitoring strategy opens new avenues for exploring myriad organic features. By reframing how we analyze cells—from static snapshots to dynamic trajectories—this know-how might remodel not solely diagnostics but additionally our understanding of mobile biomechanics and habits in well being and illness.
Furthermore, the automated, label-free side of this system is especially advantageous for medical translation. Eliminating the necessity for fluorescent or chemical markers reduces prices, processing instances, and dangers of cell perturbation, thereby making real-time monitoring of patient-derived cells extra possible. Such an strategy is invaluable for personalised medication, the place speedy identification of malignant cells in biopsy samples might improve diagnostic accuracy and information therapeutic choices with out in depth pattern manipulation.
The researchers’ findings additionally maintain promise for enhancing most cancers prognosis. Since metastasis stays the deadliest attribute of many cancers, with the ability to detect refined variations in migratory patterns might assist predict the aggressiveness of tumors and their chance to unfold. This perception may facilitate early intervention, enhancing affected person outcomes by well timed and focused remedies. Monitoring cell motility dynamics quantitatively may also function a platform for screening anti-metastatic medication by revealing how candidate compounds modulate most cancers cell motion in actual time.
From a technical standpoint, the success of this examine hinged on integrating superior microscopy with computational picture evaluation. Automated extraction of trajectories from phase-contrast photos demanded algorithms able to noise discount, exact cell segmentation, and correct monitoring over prolonged durations regardless of challenges like cell crowding, overlapping, and morphological adjustments. The researchers’ capability to reliably course of giant datasets with out human intervention underscores the maturity of present bioimage informatics instruments and their pivotal function in advancing biomedical analysis.
Crucially, this strategy adheres carefully to the native habits of cells, avoiding artifacts launched by labeling which may affect motility. Conventional fluorescent strategies typically require genetic or chemical modification, which might alter cell metabolism, cytoskeletal dynamics, and signaling pathways, in the end biasing noticed behaviors. Observing cells of their near-physiological states enhances the organic relevance and translatability of findings, a vital consideration for medical functions.
Moreover, the examine emphasizes that evaluating cell motility in bulk populations gives better diagnostic robustness than analyzing remoted cells. The automated capability to concurrently monitor tons of or 1000’s of cells minimizes sampling bias and enhances statistical confidence in differentiating wholesome versus cancerous cells. This high-throughput paradigm additionally accelerates knowledge acquisition, enabling well timed evaluation that may very well be essential in medical contexts.
As the worldwide scientific group continues to unravel the complexities of most cancers biology, instruments that exploit bodily and dynamic cell traits complement conventional molecular and genetic analyses. The novel methodology offered by the Tokyo Metropolitan College analysis group exemplifies such integrative innovation, marrying classical microscopy with fashionable computational evaluation to yield actionable biomedical insights.
In conclusion, this pioneering analysis marks a considerable leap towards label-free, non-invasive most cancers cell identification based mostly on motility profiles extracted by phase-contrast microscopy. The power to discriminate malignant fibrosarcoma cells from wholesome fibroblasts with 94% accuracy solely by analyzing their migratory paths opens thrilling prospects for diagnostics, drug improvement, and elementary cell biology. As additional refinements and validations ensue, this know-how guarantees to change into a useful asset in each analysis laboratories and medical settings, enhancing our capability to fight most cancers and perceive cell habits in unprecedented element.
—
Topic of Analysis: Cell motility-based discrimination between cancerous and wholesome cells utilizing label-free phase-contrast microscopy.
Article Title: Improvement of label-free cell monitoring for discrimination of the heterogeneous mesenchymal migration
Information Publication Date: 31-Mar-2025
Net References:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0320287
Picture Credit: Tokyo Metropolitan College
Key phrases: Most cancers analysis, Cell migration, Most cancers cells, Picture evaluation, Fibroblasts, Metastasis, Pace, Cell polarity
Tags: accuracy in cell differentiationadvancements in microscopy for cell studycancer cell motion patternscell motility and most cancers metastasiscellular trajectory evaluation for diagnosticsdistinguishing wholesome and cancerous cellsdynamic nature of dwelling cellsfibrosarcoma cell migration behaviorsinnovative most cancers analysis methodslabel-free imaging in cell analysisphase-contrast microscopy techniquesTokyo Metropolitan College analysis