Hey associates 👋
That is Half 3 of three of my mini-series on the historical past of AI till as we speak. Writing these has been a great deal of enjoyable and I hope you’ve been having fun with them.
Additionally, I’ve added a fast nameless ballot on the finish of the story to gauge curiosity on an thought I had. Make sure that to vote! 👀
Keep curious,
– Fawzi
Learn Half 1: Sparks of Intelligence
Learn Half 2: The Darkish Winter Rollercoaster
The darkest hour is simply earlier than daybreak.
After AI funding got here crashing down within the early 90s and the {industry} entered its second winter, researchers wished to distance themselves from the 2 phrases that carried a lot baggage and failed expectations.
“Pc scientists and software program engineers prevented the time period synthetic intelligence for worry of being seen as wild-eyed dreamers.”
– John Markoff, New York Instances in 2005 (Supply)
40 years after the Dartmouth Faculty workshop that birthed the AI area, researchers have been at rock-bottom once more. Confidence in AI was at an all-time low. Hundreds of thousands of {dollars} of funding bought pulled and redirected to different areas of analysis. On paper, there have been some fruitful developments and breakthroughs. However none had the revolutionary influence or scale that was promised.
Within the darkness, the right technological convergence was slowly approaching. The endurance and perseverance of AI believers was about to be rewarded.
Three revolutions have been slowly converging to create the right storm for AI’s success:
#1: The Computational Energy Revolution
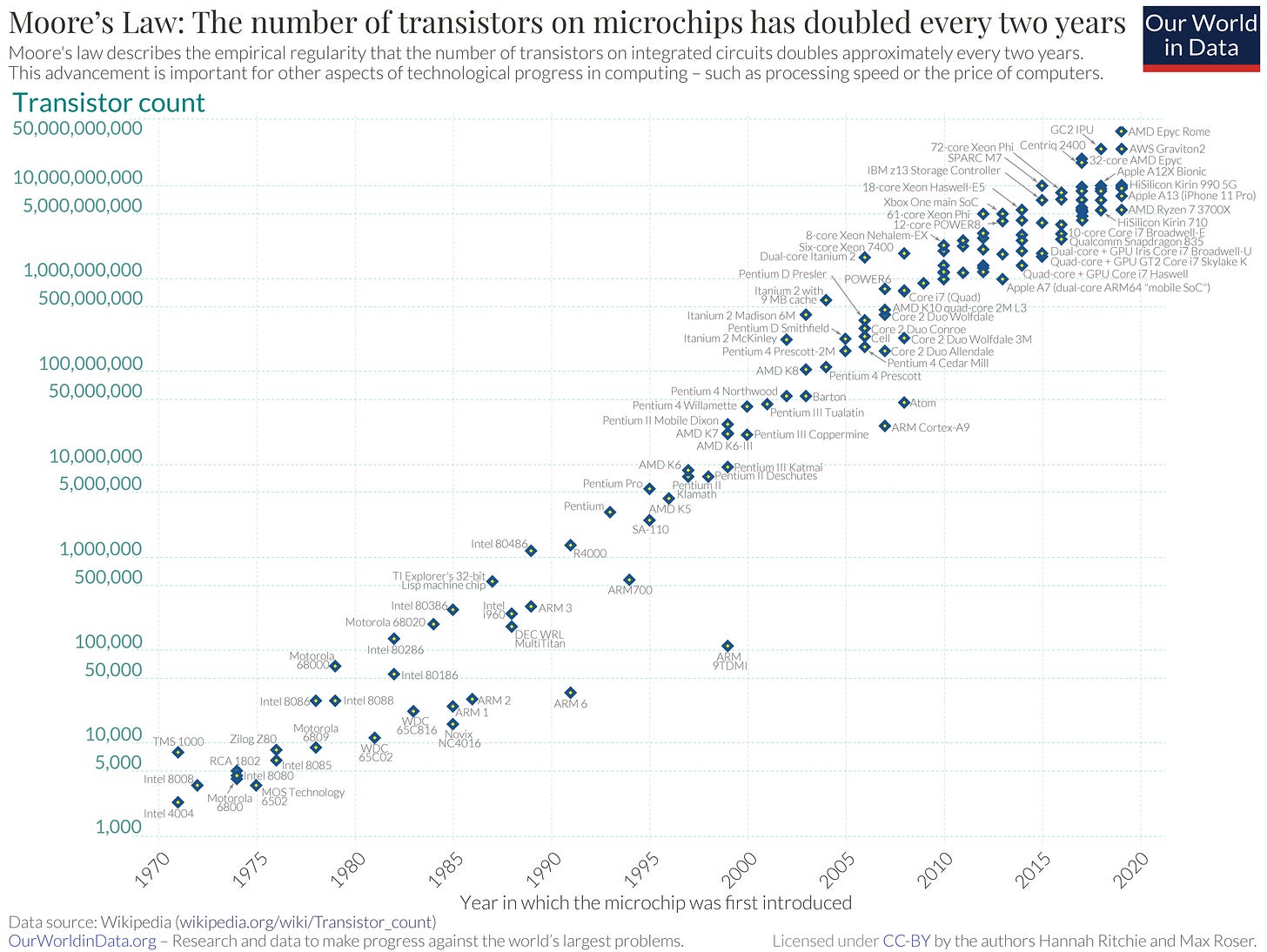
Moore’s Legislation, proposed by Gordon Moore in 1965, is an commentary (and prediction) that the variety of transistors on a microchip would double roughly each two years, resulting in exponential progress in computational energy. It has held true because it was declared.
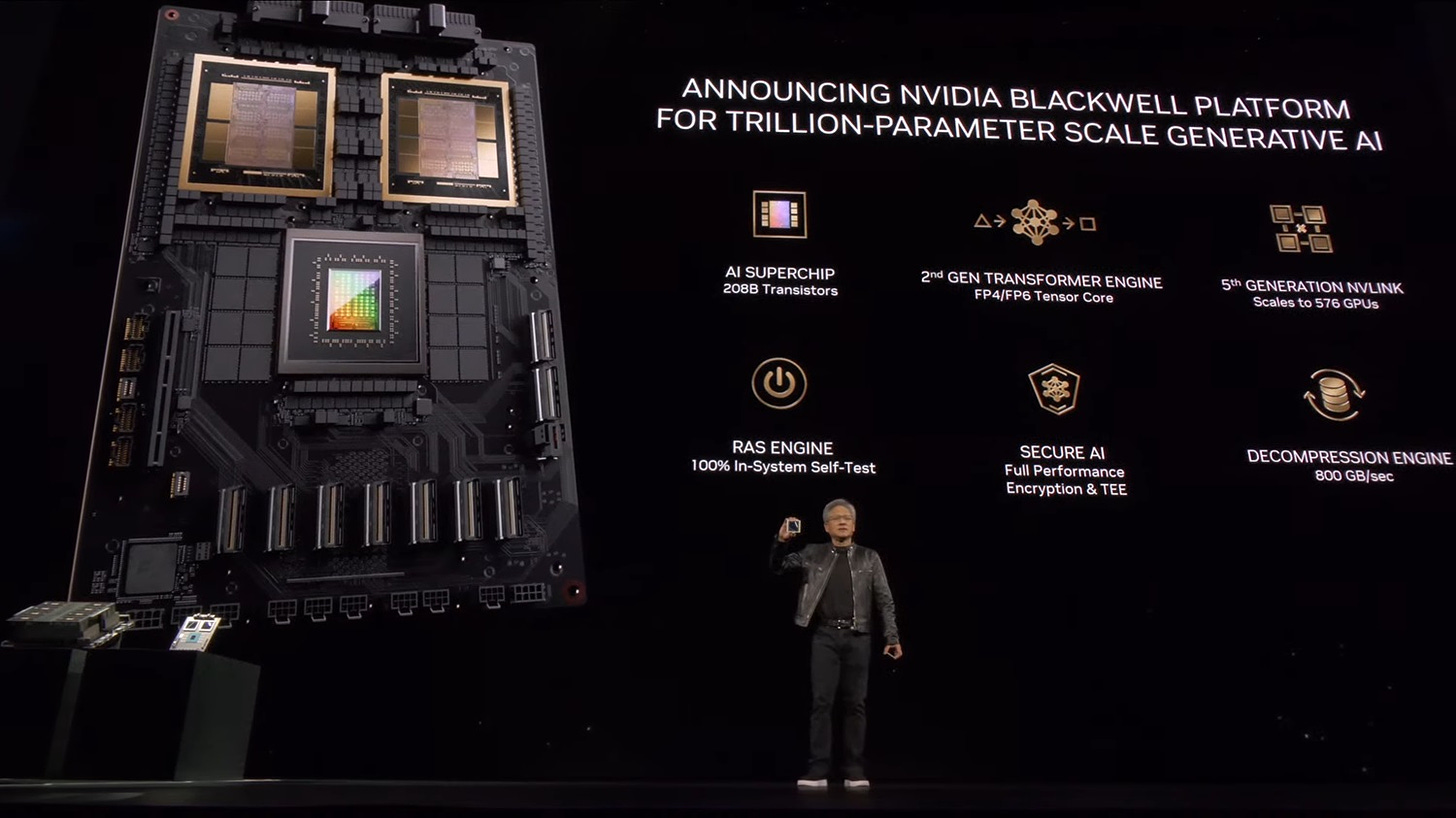
To present you an instance, NVIDIA’s newest Blackwell GPU has 200 billion transistors and is essentially the most highly effective GPU as we speak. In comparison with different microchips from the previous few many years, Blackwell is:
-
100x extra highly effective than 10 years in the past (~2 billion transistors)
-
1,000x extra highly effective than 20 years in the past (~200 million transistors)
-
70,000x extra highly effective than 30 years in the past (~3 million transistors)
-
1,300,000x extra highly effective than 40 years in the past (~150,000 transistors)
-
40,000,000x extra highly effective than 50 years in the past (~5,000 transistors)
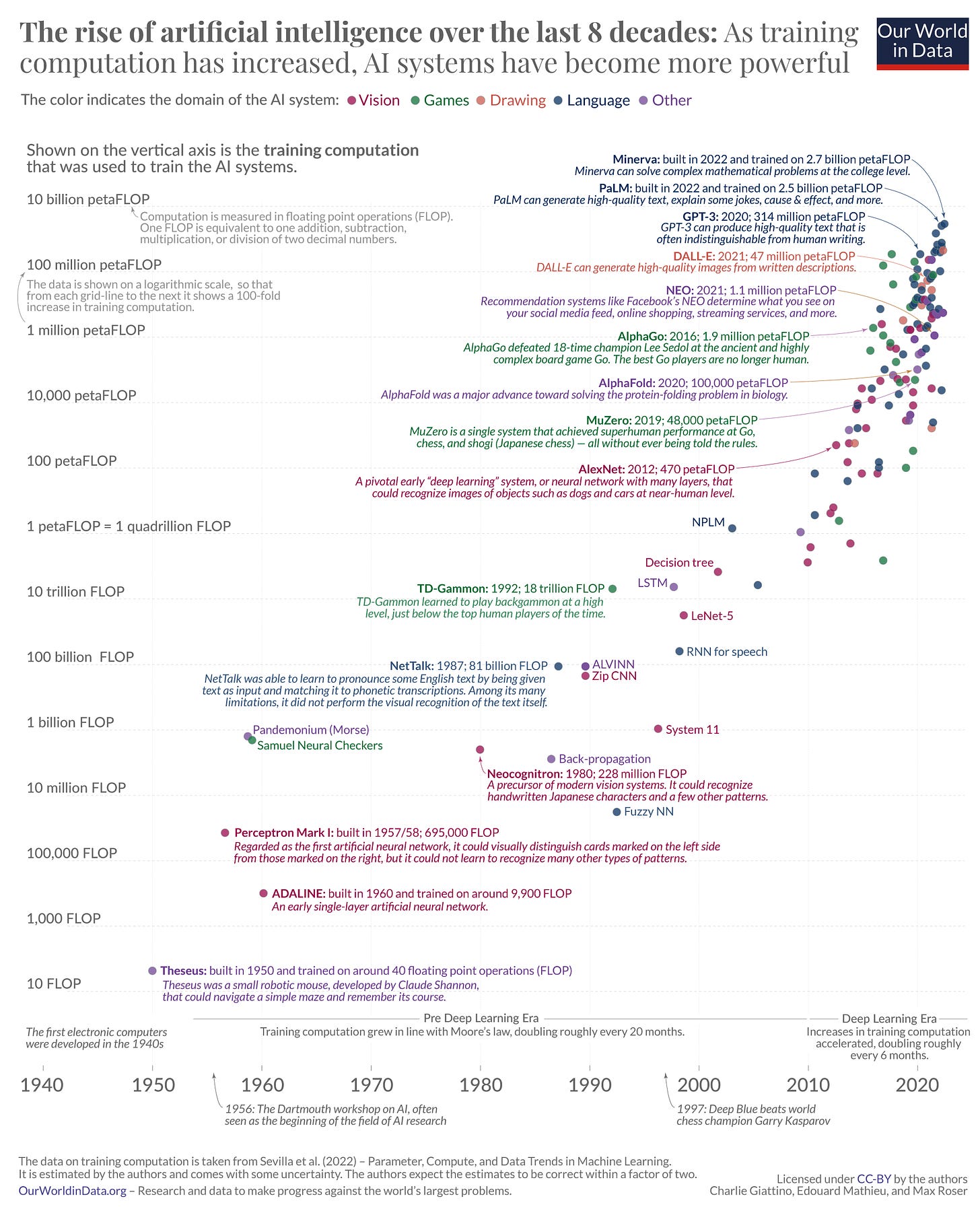
This chart, created by Our World in Knowledge, reveals how this has led to an exponential rise within the energy of AI techniques over the many years.
#2: The Large Knowledge Revolution
The web, social media, and the digitalization of practically all facets of life led to an unprecedented avalanche of information. The web additionally facilitated the availability of that information to researchers all over the world. They may now simply scrape, collect, categorize, and share massive coaching datasets.
This information turned the lifeblood of machine studying algorithms, permitting them to be taught, enhance, and make extra correct predictions. ImageNet, began by Fei-Fei Lee in 2006, is a coaching dataset containing greater than 14 million photos which were hand-annotated throughout 20,000 object classes. Speak about a labour of affection.
#3: The Connectionist AI Revolution
When you recall from Half 2, there was a rift within the AI group between two colleges of thought:
-
Symbolic AI (aka the “top-down strategy”) advocated for using guidelines, symbols, and logic to explicitly program clever techniques. Choice timber and professional techniques are examples of this strategy.
-
Connectionist AI (aka the “bottom-up strategy”) promoted the thought of letting machines be taught from information and establish their very own patterns, as an alternative of express programming. This space was targeted on machine studying, neural networks, and deep studying.
The symbolic philosophy was the “fashionable” one up till the second AI winter and the failure of professional techniques comparable to XCON.
The rise in computational energy and availability of huge dataset gave the connectionist strategy a brand new lifeline.
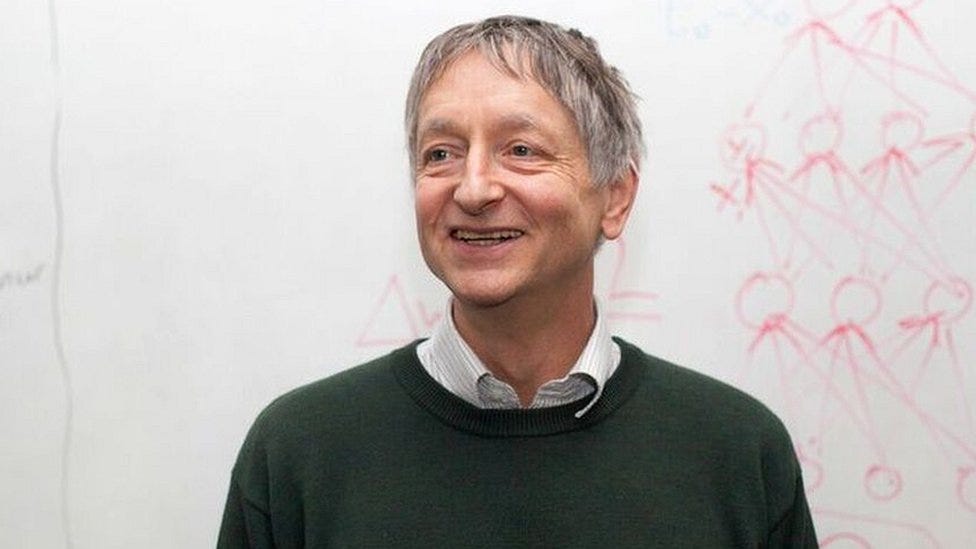
Geoffrey Hinton, who received the Nobel Prize in Physics this week, was one of many few early believers within the connectionist philosophy and neural networks. Hinton, together with fellow researchers David Rumelhart and Ronald J. Williams had developed the backpropagation algorithm in 1982, which turned a vital part of machine studying analysis and growth efforts for the many years that adopted.
The AI area discovered the results of overpromising. Up till the second AI winter, many researchers got down to create techniques with normal intelligence that may be as good (or smarter) than people.
This time, they determined to maintain their toes on the bottom and shifted their focus to slender intelligence (or slender AI). As a substitute of attempting to construct and replicate the complexities of normal intelligence, they constructed specialised techniques to carry out particular duties successfully.
An early success of this strategy was Deep Blue, a chess-playing pc developed by IBM, which famously defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997. This victory demonstrated the ability and potential of slender AI.

Researchers now mixed:
Highly effective Computer systems + Massive Datasets + Improved Studying Algorithms + Particular Duties
It was the right recipe.
By specializing in slender AI, researchers have been in a position to tackle fast wants. Totally different AI methods have been on the basis of main purposes on the time like fraud detection in on-line banking and spam detection in electronic mail.
Nevertheless, the AI area didn’t obtain credit score for these contributions. Researchers have been attempting to rebrand AI due to its previous failures, and the success of fraud and spam detection have been usually seen as industry-specific developments quite than AI particularly.
AI was working laborious behind-the-scenes in incognito mode.
A variety of cutting-edge AI has filtered into normal purposes, usually with out being known as AI as a result of as soon as one thing turns into helpful sufficient and customary sufficient it isn’t labeled AI anymore.
– Nick Bostrom, in 2006
The breakthrough that marked a significant turning level in AI historical past got here in 2012 with the event of AlexNet, created by Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey Hinton, who was their supervisor.
AlexNet was a picture recognition mannequin that received the 2012 ImageNet competitors. AlexNet outperformed its opponents by a big margin, and solely had an error fee of 15% which was 10% decrease than the runner-up.
Check out the leap in efficiency between AlexNet and its opponents from the identical 12 months and the winners from the 2 previous years.
The AlexNet workforce did one thing otherwise than different groups: they used two NVIDIA GPUs to coach their mannequin on thousands and thousands of photos. This was a lot sooner than the everyday strategy of utilizing a CPU, as a result of they’d slower processing speeds and will solely run duties in sequence. GPUs are designed for parallel processing, making them way more environment friendly for coaching deep neural networks on massive quantities of information.
The success of AlexNet ignited curiosity and investments into deep studying. AI slowly began taking part in an even bigger function in our lives as huge tech firms jumped on the practice:
-
Voice Assistants: Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa turned built-in into each machine round us, enabling us to ask questions and provides instructions utilizing our voice solely.
-
Suggestion Programs: Platforms like Netflix and Amazon utilized AI to research person preferences and supply customized content material, bettering person expertise and engagement.
-
Self-Driving Automobiles: Firms like Tesla and Waymo constructed and skilled vehicles to course of their atmosphere and make autonomous driving choices.
Even throughout this time, AI was a refined layer behind nearly all of these purposes. Folks didn’t care if AI was behind the hood or not. They only wished helpful purposes that solved their fast wants.
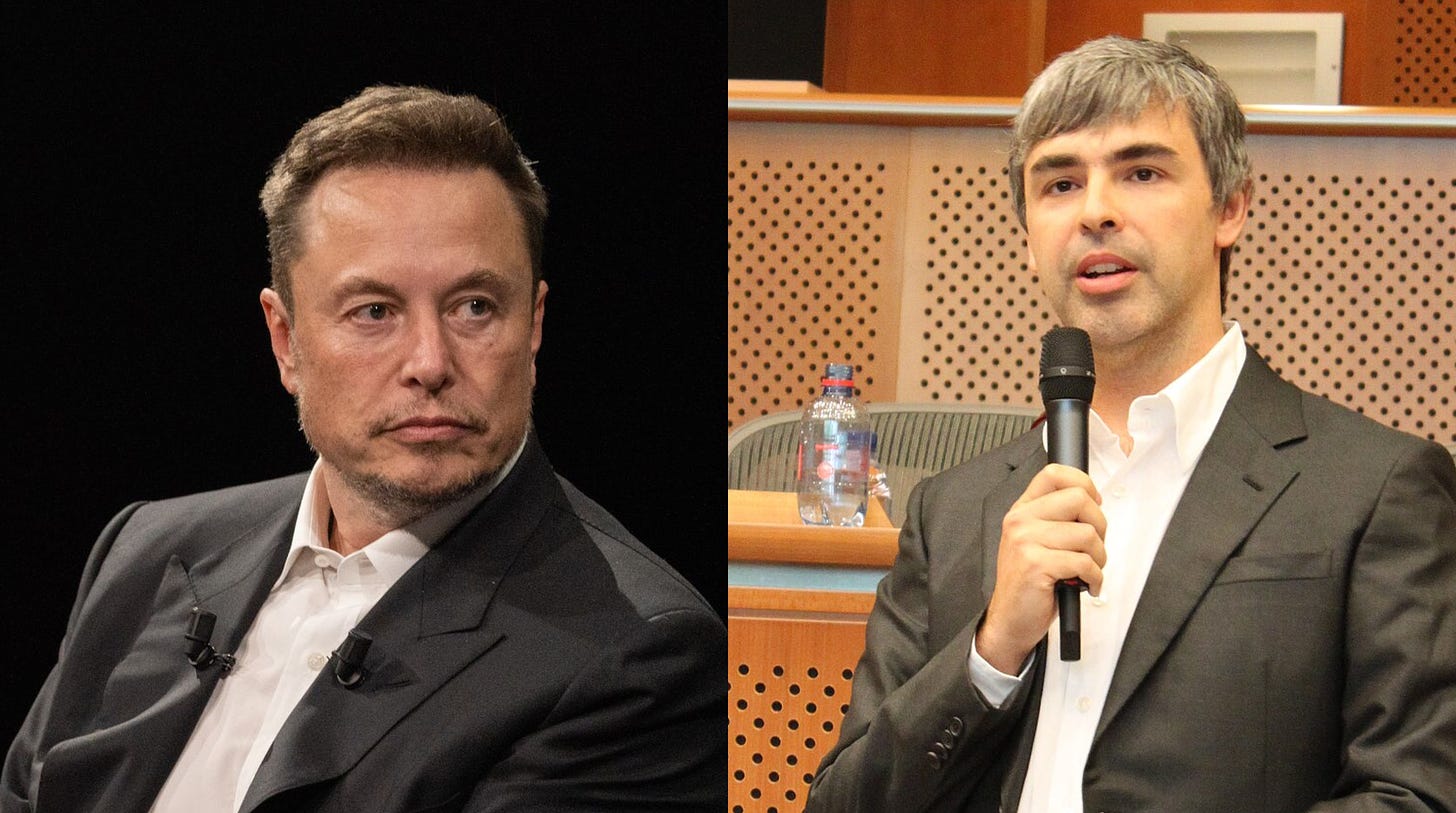
Probably the most consequential occasion in AI’s historical past may’ve occurred at Elon Musk’s forty fourth birthday in 2015.
In the course of the get together, Elon and his shut pal (and Google co-founder) Larry Web page, bought right into a heated argument concerning the future and risks of AI.
Whereas Musk argued that safeguards have been wanted to stop A.I. from doubtlessly eliminating the human race, Web page retorted that machines surpassing people in intelligence was the following stage of evolution
– Alexandra Tremayne-Pengelly in The Observer
The argument adopted Google’s acquisition of the distinguished AI analysis lab/startup DeepMind in 2014. DeepMind’s success and expertise attracted vital consideration, and the sale to Google raised considerations concerning the focus of AI developments inside a tech behemoth that was profit-driven.
In response to those considerations, Elon Musk, Sam Altman, and others based OpenAI in 2015 with the purpose of guaranteeing that “synthetic normal intelligence would profit all of humanity”. OpenAI positioned itself as an open analysis group, dedicated to transparency and collaboration, sharing its findings to advertise the secure growth of AI.
Since 2015, DeepMind and OpenAI have been pioneers in AI analysis and their work has already had a worldwide influence on our lives:
-
DeepMind: AlphaGo defeated the world Go champion in 2016, showcasing the ability of deep reinforcement studying, adopted by AlphaFold, which solved the advanced drawback of protein folding, revolutionizing organic analysis.
-
OpenAI: Developed the GPT collection of huge language fashions, with GPT-3 and GPT-4 revolutionizing pure language processing. Additionally they launched slightly software known as ChatGPT that introduced AI to the mainstream.
AI is just not within the shadows anymore. At this time, it’s within the headlines and on everybody’s minds.
Large tech firms are racing to reap the fruits of shopper pleasure. Startups have noticed a window of alternative to innovate and dethrone the incumbents. Persons are torn between the advantages AI can present, the harms it creates, and most significantly, the existential query:
“If AI can do all of it, what am I good for?”
The Finish.
It appears like the actual story is simply starting.
🚨 Your suggestions is required 🚨
I notice there are lots of totally different phrases, acronyms, and different jargon used when speaking about AI. I’m considering of making a mini-book/glossary explaining what every time period or idea means, why it’s necessary, together with a real-life instance or software. Is that one thing you’re fascinated with?
One remaining be aware
Thanks for following this 3-part collection on the historical past of AI. I feel it’s essential for all of us to grasp historical past, particularly when it’s a couple of know-how that appears to be creeping into extra facets of our lives on daily basis.
This collection is a part of my upcoming “What that you must find out about AI” course. I’m making this course for non-technical individuals who wish to construct a powerful understanding of what AI is and the way it works, and I plan on providing it free of charge.
Information provides us a way of readability and confidence, and eliminates fears and misconceptions that we would’ve had. When you’re , you’ll be able to join the waitlist under.
Share this publish in your group chats with associates, household, and coworkers.
If a pal despatched this to you, subscribe free of charge to obtain sensible insights, case research, and sources that will help you perceive and embrace AI in your life and work.
When you missed Half 1 and Half 2:
You too can take a look at the Yr 2049 archive to browse all earlier case research, insights, and tutorials.