
A global group of researchers has developed BiaPy, an open-code synthetic intelligence platform that facilitates the evaluation of biomedical photographs utilizing deep studying methods. The work has been revealed in Nature Strategies.
The group was led by Ignacio Arganda (College of the Basque Nation—UPV/EHU, Ikerbasque, Donostia Worldwide Physics Heart, and the Biofisika Institute) and Arrate Muñoz-Barrutia (College of Madrid Carlos III, Gregorio Marañón Well being Analysis Institute).
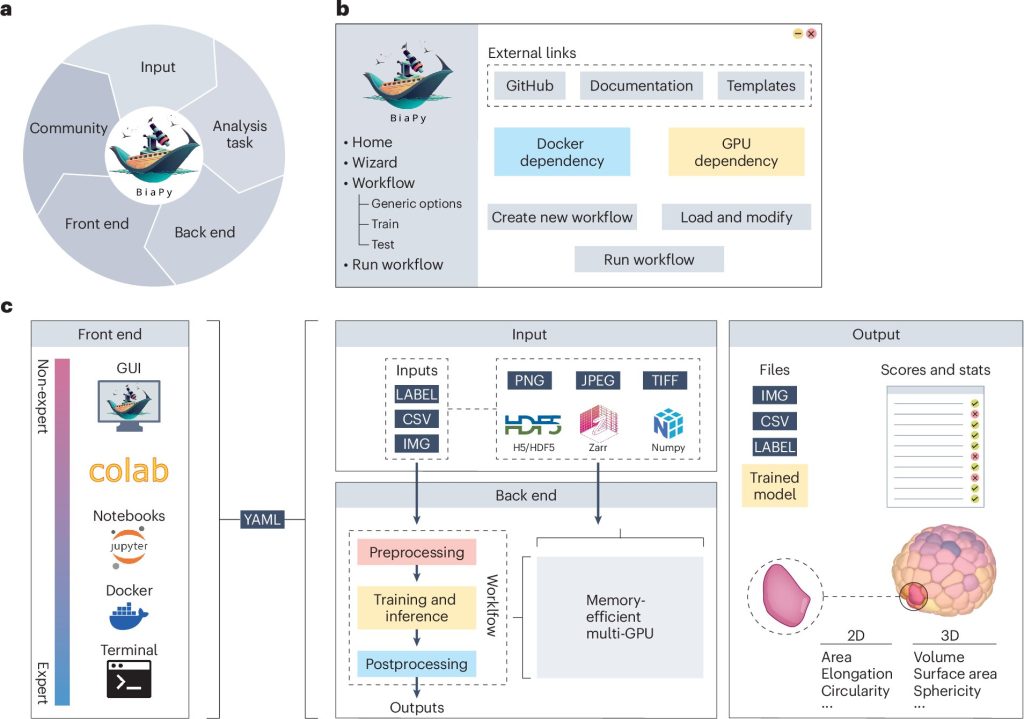
Used to review mobile constructions, tissue, and organs throughout a variety of disciplines, picture evaluation is an important software in biomedicine. Nevertheless, making use of AI to investigate these photographs has historically been the protect of specialists in programming and information science. BiaPy breaks down that barrier by providing an easy-to-use platform that enables superior AI fashions to be utilized with out the necessity for specialised technical information.
“BiaPy goals to democratize entry to synthetic intelligence in bioimaging by enabling extra scientists and well being care professionals to harness its potential with out the necessity for superior programming or machine studying expertise,” defined Daniel Franco, lead creator of the research and presently a postdoctoral researcher on the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Cambridge College (United Kingdom).
BiaPy permits various kinds of evaluation to be carried out on scientific photographs, equivalent to robotically figuring out cells or different organic constructions, counting parts, classifying samples in line with their look, or enhancing picture high quality to see the finer particulars. All this may be performed with two-dimensional photographs in addition to with three-dimensional photographs obtained by the use of varied microscopy methods.
As well as, BiaPy has been designed to be environment friendly and scalable: it could possibly work with a broad number of information volumes, from a number of small photographs to terabytes of knowledge, equivalent to these generated when tissue or total organs are scanned.
The software is predicated on the usage of AI fashions, that are algorithms skilled to acknowledge patterns in photographs, just like the way in which the human eye can establish shapes or colours. Examples are used to create a mannequin: for instance, photographs by which cells have already been tagged manually. With enough coaching, the mannequin learns to carry out these duties robotically, even on new photographs it has by no means seen earlier than.
“BiaPy has additionally been built-in into the BioImage Mannequin Zoo (bioimage.io), a database by which researchers from world wide share pre-trained fashions. Due to this integration, BiaPy customers can reuse current fashions for brand spanking new photographs or practice their very own fashions simply,” defined Arrate Muñoz, senior co-author of the paper and member of the European consortium AI4Life that developed the BioImage Mannequin Zoo.
This software is already being utilized in superior scientific tasks. One instance is CartoCell, a software program answer developed in collaboration with the lab coordinated by Luis M. Escudero (Institute of Biomedicine of Seville [Virgen del Rocío University Hospital/CSIC/University of Seville]). CartoCell analyzes microscopy photographs to disclose hidden patterns within the form and distribution of cells inside 3D epithelial tissue from completely different organisms.
One other case worthy of word is its utility in collaboration with the laboratories of Emmanuel Beaurepaire (École Polytechnique, France) and Jean Livet (Institut de la Imaginative and prescient, Paris). These teams have developed the ChroMS microscopy method, which permits large three-dimensional photographs of total brains to be obtained utilizing fluorescent colours generated by proteins from jellyfish and corals.
BiaPy is used to robotically detect every cell in these large-scale photographs, even in densely populated areas of the mind, permitting mind growth to be studied by reconstructing the lineage of cells based mostly on their colours and three-dimensional positions.
As an open-access software, BiaPy is out there freed from cost to the scientific neighborhood, thereby selling collaboration and the continuing enchancment of the software program. It may be used on PCs or servers with a number of graphics playing cards, in addition to within the cloud. It’s simple to put in and ensures that experiments will be simply repeated in varied environments, thus selling open, reproducible science.
As Arganda, the senior creator of the paper, identified, “The event of BiaPy represents an necessary step in the direction of the democratization of superior synthetic laptop imaginative and prescient in microscopy. Its accessible design and deal with open collaboration scale back technical limitations, making it simpler for extra researchers and well being care professionals to use synthetic imaginative and prescient to their research.
“Its compatibility with varied computing environments and its open-code nature imply that it’s a platform that provides large potential in driving ahead innovation and dashing up scientific discovery.”
Extra data:
Daniel Franco-Barranco et al, BiaPy: accessible deep studying on bioimages, Nature Strategies (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41592-025-02699-y
Offered by
College of the Basque Nation
Quotation:
Open-access AI software makes biomedical picture evaluation accessible to non-experts (2025, April 29)
retrieved 30 April 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-04-access-ai-tool-biomedical-image.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




