
Mitochondrial illnesses have an effect on roughly 1 in 5,000 individuals worldwide, inflicting debilitating signs starting from muscle weak point to stroke-like episodes. A few of these circumstances consequence from mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), the genetic materials housed in these organelles. For sufferers with the frequent m.3243A>G mutation, which might trigger MELAS syndrome (mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes) and diabetes mellitus, remedies stay restricted.
A basic problem in mitochondrial illness analysis is that sufferers sometimes have a mixture of each regular and mutated mtDNA inside their cells. This situation, generally known as heteroplasmy, makes focused therapies troublesome to develop, because the normal-to-mutated mtDNA ratios can range drastically from tissue to tissue.
Moreover, present fundamental analysis into mtDNA mutations faces vital obstacles that stem from a scarcity of illness fashions. The advanced relationship between mutation load (the proportion of mutated mtDNA) and illness severity stays poorly understood, partially as a result of there are not any instruments to exactly manipulate heteroplasmy ranges in both route. With out the flexibility to create mobile fashions with totally different mutation masses, scientists can’t successfully research how various percentages of mutated mtDNA relate to illness manifestation.
In opposition to this backdrop, a analysis crew led by Senior Assistant Professor Naoki Yahata from the Division of Developmental Biology, Fujita Well being College Faculty of Drugs, Japan, has developed a expertise that may modify heteroplasmy ranges in cultured cells carrying the m.3243A>G mutation.
Their paper is printed within the journal Molecular Remedy Nucleic Acids. It was co-authored by Dr. Yu-ichi Goto from the Nationwide Middle of Neurology and Psychiatry and Dr. Ryuji Hata from Osaka Prefectural Hospital Group. In it, they element the engineering and use of optimized mtDNA-targeted platinum transcription activator-like effector nucleases (mpTALENs)—specialised enzymes that may selectively goal and cleave particular DNA sequences.
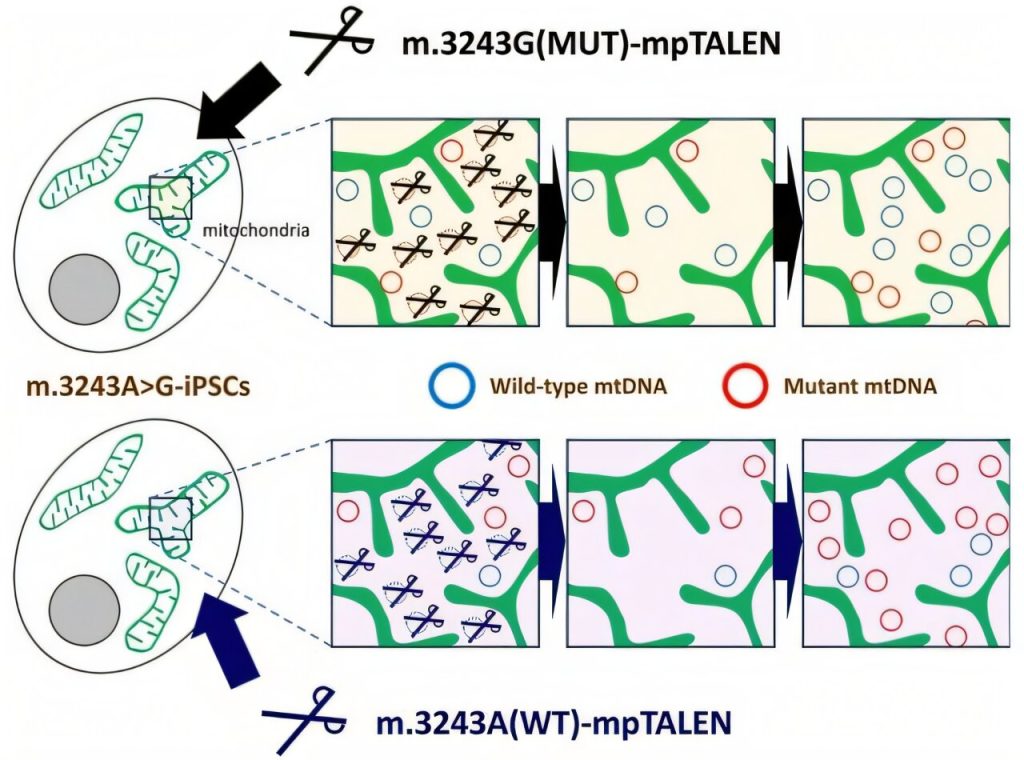
The researchers first established cultures of patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) containing the m.3243A>G mutation after which designed two variations of their mpTALEN methods: one which targets mutant mtDNA for destruction and one other that targets regular mtDNA. This bi-directional strategy allowed them to generate cells with mutation masses starting from as little as 11% to as excessive as 97%, whereas nonetheless sustaining the cells’ means to distinguish into varied tissue sorts.
“Our research is the primary to show a rise within the proportion of pathogenic mutant mtDNA by programmable nuclease,” notes Dr. Yahata.
Key improvements of their strategy included using novel non-conventional repeat-variable di-residues and obligate heterodimeric FokI nuclease domains, which enhanced the expertise’s specificity and diminished undesirable degradation of off-target mtDNA. The crew additionally employed further methods, corresponding to uridine supplementation, to determine secure cell traces with totally different mutation masses, even those who may sometimes have a progress drawback.
“Our outcomes show that our mpTALEN optimization course of created a great tool for altering heteroplasmy ranges in m.3243A>G-iPSCs, bettering their potential for finding out mutation pathology. This enhanced effectivity additionally holds promise for utilizing mpTALENs in therapeutic methods for treating sufferers affected by m.3243A>G mitochondrial illnesses,” says Dr. Yahata.
General, the research represents a big development in mitochondrial drugs for a number of causes. First, it gives researchers with a number of isogenic—in any other case genetically an identical—cell traces that differ solely of their stage of heteroplasmy. This permits for a exact research of how mutation load impacts illness manifestation. Second, it means that mpTALEN expertise could grow to be therapeutically priceless for decreasing mutant mtDNA load in sufferers.
“Our proposed methodology could possibly be tailored for different mutant mtDNAs and will contribute to understanding their related pathologies and growing new remedies, doubtlessly benefiting sufferers with varied types of mitochondrial illness,” concludes Dr. Yahata.
Extra data:
Naoki Yahata et al, Optimization of mtDNA-targeted platinum TALENs for bi-directionally modifying heteroplasmy ranges in patient-derived m.3243A>G-iPSCs, Molecular Remedy Nucleic Acids (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102521
Supplied by
Fujita Well being College
Quotation:
Engineered enzymes allow exact management of mitochondrial DNA mutation ranges in cells (2025, Might 2)
retrieved 2 Might 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-05-enzymes-enable-precise-mitochondrial-dna.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.