Supplies
All chemical substances and reagents have been from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. if not in any other case famous. All LC-MS solvents have been Optima LC-MS-grade solvents (Fisher Scientific Inc.). All artificial gene fragments have been from Twist Biosciences Inc. Deoxynucleotide primers have been from Built-in DNA Applied sciences Inc. LC-MS evaluation was carried out on a Thermo QExactive Orbitrap mass spectrometer coupled to a Vanquish Extremely excessive efficiency liquid chromatography instrument. LC-MS information was analyzed with QualBrowser from Thermo Xcalibur software program package deal (v4.3.73.11, Thermo Scientific). Preparative and semi-preparative excessive efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC) was carried out on a Shimadzu HPLC with two binary LC20-AP pumps, a DGU-403 Degasser, an SPD-20A ultraviolet-visible mild detector, and a FRC-10A fraction collector. NMR evaluation was performed on a Bruker Ascend 800 MHz NMR spectrometer with a 5 mm Triple Resonance Inverse Detection TCI CryoProbe. NMR information was analyzed with MestReNova (v14.0.0, Mestrelab Analysis).
Plant cultivation
Nicotiana benthamiana and Glechoma hederacea have been grown from seeds in Premier Horticulture Professional Combine HP Excessive Porosity with Mycorrhizae for plant development below plant development lights with a 16 h mild/8 h darkish cycle for 4–12 weeks at room temperature. N. benthamiana seedlings have been transferred as soon as to bigger pots with the identical soil and added Osmocote fertilizer. G. hederacea seeds have been obtained from the Seed Nook Inc. (Cat #: GROUNDIVYS100). Sacciolepis striata was collected from a pattern within the College of Michigan Herbarium (Cat # 1423220). Glechoma hederacea for glechomanin isolation was collected from the College of Michigan Arboretum (42°16’32.7“N 83°43’27.2“W, June 2022/2023). Stellaria aquatica for moroidin-QLLVWRNH isolation and RNA isolation was collected from Pointe Mouillee State Sport Space (41°59’54.8“N 83°11’47.7“W) with Division of Pure Assets allow 24–25 (June 2024). Mercurialis annua was collected from a pattern within the College of Michigan Herbarium (Cat # 1642848). Orchidantha maxillarioides (accession 1989-4177-1) for peptide chemotyping and RNA isolation was collected from the Missouri Botanical Backyard (June 2024). Bauhinia forticata for stephanotic acid-QLLVW chemotyping was bought from Plant Delights Nursery Inc. Kerria japonica for stephanotic acid-QLLVW chemotyping was bought as a mature plant from Inexperienced Promise FarmsTM.
RNA-seq information obtain and trimming
Paired-end RNA-seq information (Supplementary Desk 4, Supplementary Information 2) have been downloaded from NCBI SRA through fasterq-dump (–split-files) of the SRA Toolkit (v2.10.9)19 to the Nice Lakes Excessive Efficiency Computing (HPC) Cluster on the College of Michigan, Ann Arbor. The datasets have been trimmed through TrimGalore (v0.6.7) with default settings (Phred cutoff: 20, Default pair-cutoff: 20 bp).
Unassembled RNA-seq information seek for stephanotic acid core peptides
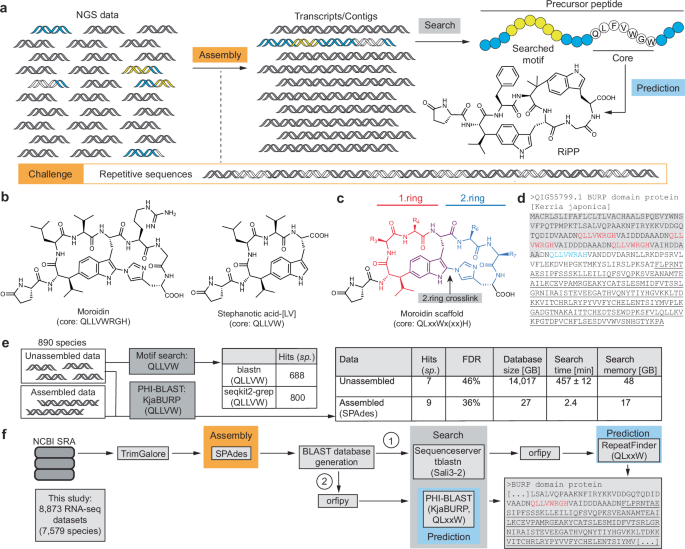
Unassembled RNA-seq datasets of 890 plant species (Supplementary Desk 3, Supplementary Information 1) have been both looked for nucleotide sequence CAACTTCTTGTTTGG encoding stephanotic acid core peptide QLLVW (from the Kerria japonica moroidin cyclase KjaBURP, GenBank ID QIG55799.1) through blastn on the NCBI BLAST webserver (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, default parameters: matrix BLOSUM62, gap-open 11, gap-extended 1, Filter L, e-value 0.05) or for protein sequence of core peptide QLLVW through seqkit2 (v2.3.0)49 on the Nice Lakes HPC cluster. For webserver search, every SRA dataset was searched individually for the goal nucleotide sequence with a most search hit variety of 100. For seqkit2 search, the 890 species datasets have been downloaded and trimmed in batches of 100 datasets. Duplicate reads have been then faraway from every dataset through seqkit2 rmdup command and the ensuing fastq datasets have been transformed to fasta datasets through seqkit2 fq2fa command. The output fasta information have been mixed into one fasta-file for every 100-transcriptomes-batch they usually have been 6-frame translated through orfipy (v0.0.4, parameters: –pep –min 90 –between-stops)94. The orfipy output pep information have been lowered in fasta-header dimension through awk command and the formatted pep file was searched through seqkit2 grep command for the presence of translated reads with the core peptide QLLVW. The recognized reads have been extracted from the seqkit2 grep output file for his or her respective SRA numbers with awk command. Unassembled information was transformed to BLAST databases by makeblastdb and searched by commandline PHI-BLAST (BLAST+ v2.16.0, default settings, E-value 10)50 for the presence of BURP-domain proteins together with stephanotic acid core peptide QLLVW with KjaBURP GenBank accession QIG55799.1) as a question sequence. For comparability to assembled information, the identical datasets have been assembled de novo by SPAdes (v3.15.5, rnaSPAdes), mixed and 6-frame translated by orfipy (v0.0.4, parameters: –pep –min 450 –between-stops), transformed to BLAST databases by makeblastdb and searched by commandline PHI-BLAST (BLAST+ v2.16.0, default settings, E-value 10) for the presence of BURP-domain proteins together with stephanotic acid core peptide QLLVW with KjaBURP. The ORF size of 90 bp was chosen for unassembled information 6-frame translation attributable to really useful PHI-BLAST database size minimal of 30 amino acids and a typical RNA-seq learn size of 90 bp. For benchmarking of stephanotic acid prediction through unassembled or assembled RNA-seq information searches, a deposited stephanotic acid-[LV] tandem mass spectrum (GNPS: CCMSLIB00006709935) was searched through plantMASST48 (v2025.3.25, parameters: PM Tolerance (Da) 0.05, Fragment Tolerance (Da) 0.05, Cosine Threshold 0.7, Minimal Matched Peaks 3) in a metabolomic database together with all 890 plant species searched of their RNA-seq information. False discovery fee was calculated as [(number of false positives)/((number of false positives) + (number of true positives))].
Transcriptome meeting
For de novo meeting benchmarking, datasets (Desk 1) have been trimmed through TrimGalore (v0.6.7) with default settings (Phred cutoff: 20, Default pair-cutoff: 20 bp) and assembled de novo with Trinity (v2.15.1)23, SPAdes (v3.15.5)24,25, or MEGAHIT (v1.2.9)31 with the parameters in scripts specified on a GitHub repository (https://github.com/UM-KerstenLab4009/Moroidin-Transcriptomics). The working reminiscence for all benchmarking datasets was 48 GB aside from Trinity meeting of SRR7440026 information (80 GB reminiscence), which failed at 48 GB reminiscence. For big-scale de novo meeting, the datasets have been assembled with SPAdes on the Nice Lakes HPC cluster with the identical parameters as for benchmarking. Assemblies which failed at 48 GB reminiscence have been assembled at 180 GB reminiscence (Supplementary Desk 4, Supplementary Information 2). For genome-guided meeting benchmarking, datasets (Desk 2) have been trimmed through TrimGalore (v0.6.7) with default settings. For every RNA-seq dataset, reads have been aligned and mapped to the genome meeting fasta file with STAR (v2.7.11a) utilizing the genome-specific gtf/gff3 annotation file. STAR alignment of a genome was performed with the parameter –sjdbOverhang RNA-seq read-length minus 1. The ensuing sam file was transformed to bam file through samtools (v1.21). The transcriptome was assembled from the bam file both by StringTie (v2.2.1) or Trinity (v2.15.1). For genome-guided transcriptome meeting with Trinity, the parameter genome_guided_max_intron 50,000 was used. For StringTie transcriptome meeting, the ultimate gtf file was transformed with gffread (v0.12.7) to a fasta file.
Transcriptome evaluation
For BLAST library preparation, fasta headers of all de novo assemblies and genome-guided assemblies have been added with their SRA quantity and lowered in size under 51 letters. Precursor meeting benchmarking was performed through Sequenceserver-based BLAST search: De novo assembled transcriptomes have been searched for his or her corresponding precursor peptides through tblastn (v2.16.0 + )71 on Sequenceserver (v3.1.0)72 with the next BLAST parameters: e-value 1e-5, matrix BLOSUM62, gap-open 11, gap-extend 1, filter L. The highest hit of every search was translated into protein sequence and aligned by Needle95 pairwise alignment with the goal precursor peptide. The ensuing similarity and id scores of all 36 precursor peptides have been recorded (Desk 1), added and in comparison with the utmost rating (3600 = 36*100%) (Desk 1). Giant-scale search of BURP-domain transcripts was carried out both through Sequenceserver BLAST and subsequent RepeatFinder evaluation or through commandline PHI-BLAST and subsequent RepeatFinder evaluation. For Sequenceserver-based BLAST search, all SPAdes de novo assembled transcriptomes (Supplementary Desk 4, Supplementary Information 2) have been mixed into 100 transcriptome-databases and searched through tblastn (BLAST+ v2.16.0 + ) for homologs of Sali3-2 as a BURP-domain-containing protein question (GenBank ID AAB66369) on Sequenceserver (v3.1.0) with the next BLAST parameters: E-value 1e-05, matrix BLOSUM62, gap-open 11, gap-extend 1, filter L, max, max_target_seqs 5000. tblastn hits from all databases have been mixed right into a fasta-file and translated into protein sequences through orfipy (v0.0.4)94 with the next parameters: –pep –min 450 –between-stops. The ensuing protein sequence pep file was transformed to a fasta file and analyzed by standalone RepeatFinder36 on the Nice Lakes HPC Cluster on the College of Michigan, Ann Arbor (see GitHub repository for RepeatFinder settings). Candidate stephanotic acid-type burpitide cyclases have been characterised in RepeatFinder output as core QLxxW, the place x is any proteinogenic amino acid, and presence in an open studying body, which encoded a BURP-domain motif. For commandline BLAST search, all SPAdes de novo assemblies (Desk 1) have been mixed right into a fasta file after which translated into protein sequences through orfipy (v0.0.4)94 with the next parameters: –pep –min 450 –between-stops. The ensuing pep file was searched through PHI-BLAST (BLAST+ v2.16.0 + ) with phi_pattern QQL-(x)2-W and KjaBURP (GenBank ID QIG55799.1) on default settings (E-value 10). The ensuing hits have been analyzed by RepeatFinder. In our searches, a BURP-domain motif was outlined by the presence of a minimum of half the BURP-domain-conserved residues (i.e., FF/Fx-C-C-CH of FF/Fx-C-C-CH-CH-CH-CH)37. Hits with a single QLxxW core peptide on the first N-terminal α-helix of BURP-domain proteins74 have been eliminated. PHI-BLAST outcomes (Supplementary Desk 4, Supplementary Information 2) additionally included predicted stephanotic acid-type core peptides from transcripts with out or incomplete BURP-domain sequence. Discount of the PHI-BLAST E-value 10 to 1e-5 had no impact on search outcomes from fused burpitide cyclases but it surely lowered hits from incomplete or non-BURP-domain transcripts (Supplementary Desk 5, Supplementary Information 3). With a view to seek for different core peptide motifs inside BURP-domain proteins, the phi_pattern ought to be modified accordingly and a question BURP-domain protein sequence ought to be chosen which incorporates the goal motif, e.g., for a moroidin (core: QLLVWRGH) PHI-BLAST search, use the phi_pattern QQLLVWRGH and KjaBURP (GenBank ID QIG55799.1) which features a QLLVWRGH motif in its sequence.
Peptide chemotyping
Leaf and stem plant materials (0.2 g recent weight) was collected from aerial tissues, frozen and floor with a MP Biomedicals FastPrep-24-5G Tissuelyser in 2-mL MP Biomedicals tubes with 2.3-mm Zirconia beads for 60 s at 6 m/s. 1 mL of 80% methanol was added to floor tissue and floor for 20 s at 6 m/s. The methanolic extract was incubated for 10 min in a 60 °C water bathtub, centrifuged for five min at 16,000 × g at room temperature, and filtered by way of Whatman 0.2 µm syringeless LC-MS filters (UN503NPEORG) earlier than LC-MS evaluation. Filtered extracts have been transferred to LC-MS vials and analyzed by LC-MS/MS with the next settings: LC-Phenomenex Kinetex® 2.6 μm C18 reverse section 100 Å 150 × 3 mm LC column; LC gradient, solvent A, 0.1% formic acid; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0 min, 10% B; 5 min, 60% B; 5.1 min, 95% B; 6 min, 95% B; 6.1 min, 10% B; 9.9 min, 10% B; 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; MS, optimistic ion mode; full MS, decision 70,000; mass vary 400–1200 m/z; dd-MS2 (data-dependent MS/MS), decision 17,500; AGC goal 1 × 105, loop rely 5, isolation width 1.0 m/z, collision vitality 25 eV and dynamic exclusion 0.5 s. Pattern numbers have been n = 3 (organic replicates) for every supply plant extraction and every transient gene expression experiment in N. benthamiana and n = 1 for Mercurialis annua chemotyping from Herbarium specimen. The unfavourable management of transient gene expression experiment in N. benthamiana was an empty pEAQ-HT vector infiltration experiment.
Glechomanin isolation
Mature Glechoma hederacea (root, leaves, stem, flowers, 10 kg complete) was collected and frozen at −80 °C and floor with dry ice in a meals processor to a advantageous powder. The plant powder was extracted with 1 L methanol (HPLC grade) per 500 g plant powder for 16 h at 37 °C at 160 rpm. The crude extract was vacuum-filtered by way of a silica filter after which dried in vacuo. The dried methanol extract was resuspended in 2 L of water. The resuspension was partitioned 1:1 (v/v) with hexanes (3x) and ethyl acetate (2x) after which extracted with n-butanol (1:1, v/v, 2x). The n-butanol extract was dried in vacuo, resuspended in 20% methanol and utilized to a Sephadex LH20 (Sigma-Aldrich, LH20100) liquid chromatography (LC) stable section column (60 × 8 cm) with a cellular section gradient of 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% methanol (500 mL every). LH20 LC fractions have been analyzed for the presence of the goal analyte with the next LC-MS settings: injection quantity 2 µL; LC, Phenomenex Kinetex 2.6 μm C18 reverse section 100 Å 50 × 3 mm LC column; LC gradient. solvent A, 0.1% formic acid; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0 min, 5% B; 2.5 min, 95% B; 3.0 min, 95% B; 3.1 min, 5% B; 5.0 min, 5% B, 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; MS, optimistic ion mode; full MS, decision 35,000, mass vary 400–1200 m/z; dd-MS2, decision 17,500; loop rely 5, collision vitality 25 eV and dynamic exclusion 0.5 s. LH20 LC fractions with glechomanin have been mixed and dried in vacuo.
Glechomanin extracts have been separated by preparative HPLC with the next LC circumstances in two rounds: 1. separation: Phenomenex Kinetex® 5 µm C18 100 Å LC Column 150 × 21.2 mm, LC gradients: solvent A – 0.1% TFA, solvent B – acetonitrile (0.1% TFA), 7.5 mL/min, 1. separation: 0 min: 10% B, 1 min: 10% B, 36 min: 50% B, 39 min: 95% B, 42 min: 95% B, 42.5 min: 10% B, 60.1 min: 10% B. 2. separation: Phenomenex Kinetex® 5 µm C18 100 Å LC Column 150 × 21.2 mm, 7.5 mL/min, 0 min: 15% B, 1 min: 15% B, 36 min: 35% B, 39 min: 95% B, 42 min: 95% B, 42.5 min: 15% B, 60.1 min: 15% B. Preparative HPLC fractions have been analyzed for glechomanin described above. Subsequently, glechomanin fractions have been mixed, dried in vacuo and dissolved in 20% acetonitrile. The glechomanin fraction was separated by semipreparative HPLC with the next circumstances: 1. separation: Kinetex® 5 μm C18 100 Å 250 × 10 mm column, solvent A – 0.1% TFA, solvent B – acetonitrile (0.1% TFA), 1.5 mL/min, 0 min – 20% B, 1 min – 20% B, 21 min – 30% B, 22 min – 95% B, 25 min – 95% B, 25.1 min – 20% B, 45 min – 20% B. 2. separation: solvent A – 0.1% TFA, solvent B – methanol (0.1% TFA), 1.5 mL/min, 0 min – 65% B, 1 min – 65% B, 30 min – 85% B, 31 min – 100% B, 36 min – 100% B, 37 min – 65% B, 47 min – 65% B. Subsequently, glechomanin fractions have been mixed and dried in vacuo. Glechomanin (2 mg) was a white powder.
Moroidin-QLLVWRNH isolation
Stellaria aquatica aerial tissue (1.5 kg) was frozen at −80 °C and floor in a meals processor with dry ice and extracted in 6 L of methanol for 16 h at 37 °C with agitation (160 rpm). The methanol extract was filtered over silica and dried below lowered strain. The dried extract was resuspended in 2 L of water and partitioned sequentially with 2 L of hexanes (3x), ethyl acetate (2x), and n-butanol (2x). The n-butanol fraction was dried, resuspended in 10% methanol, and subjected to Sephadex LH20 chromatography (60 × 8 cm) utilizing a methanol gradient (10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%; 500 mL every). Fractions have been analyzed by LC-MS with the next parameters: injection quantity, 2 µL; column, Phenomenex Kinetex® 2.6 µm C18 100 Å (50 × 3 mm); solvent A, 0.1% formic acid in water; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; gradient: 0 min, 5% B; 2.5 min, 95% B; 3.0 min, 95% B; 3.1 min, 5% B; 5.0 min, 5% B. MS settings: optimistic ion mode; full MS decision, 35,000; mass vary, 400–1200 m/z; dd-MS2 decision, 17,500; collision vitality, 25 eV; dynamic exclusion, 0.5 s. Moroidin-QLLVWRNH-containing fractions have been mixed, dried in vacuo, after which separated by preparative HPLC with the next LC circumstances in two rounds: Phenomenex Kinetex® 5 µm C18 100 Å LC column 150 × 21.2 mm; 1. separation: LC gradients: solvent A – 0.1% TFA in water, solvent B – acetonitrile (0.1% TFA), 7.5 mL/min, 1. separation: 0 min: 10% B, 1 min: 10% B, 36 min: 50% B, 39 min: 95% B, 42 min: 95% B, 42.5 min: 10% B, 60.1 min: 10% B. 2. separation: 7.5 mL/min, 0 min: 15% B, 1 min: 15% B, 36 min: 35% B, 39 min: 95% B, 42 min: 95% B, 42.5 min: 15% B, 60.1 min: 15% B. Fractions have been analyzed for moroidin-QLLVWRNH by LC-MS as for LH20 LC and mixed. Closing purification was achieved by semipreparative HPLC (Kinetex® 5 μm C18 100 Å 250 × 10 mm, solvent A: 0.1% TFA in water, solvent B: acetonitrile, 0.1% TFA, 1.5 mL/min: 1. Separation: 0 min – 20% B, 1 min – 23% B, 45 min – 23% B), 2. Separation: 0 min – 23% B, 30 min – 23% B. Moroidin-QLLVWRNH (32 mg) was obtained as a white powder.
Mercurialin isolation
Transgenic tobacco leaves expressing ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY (1.3 kg) have been frozen at −80 °C and floor in a meals processor with dry ice and extracted in 8 L of methanol for 16 h at 37 °C with agitation (160 rpm). The methanol extract was filtered over silica and dried in vacuo. The dried extract was resuspended in 2 L of water and partitioned sequentially with 2 L of hexane (3x), ethyl acetate (2x), and n-butanol (2x). The n-butanol fraction was dried, resuspended in 10% methanol, and subjected to Sephadex LH20 chromatography (60 × 8 cm) utilizing a methanol gradient (20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100%; 500 mL every). Fractions have been analyzed by LC-MS with the next parameters: injection quantity, 2 µL; column, Phenomenex Kinetex® 2.6 µm C18 100 Å (50 × 3 mm); solvent A, 0.1% formic acid in water; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; gradient: 0 min, 5% B; 2.5 min, 95% B; 3.0 min, 95% B; 3.1 min, 5% B; 5.0 min, 5% B. MS settings: optimistic ion mode; full MS decision, 35,000; mass vary, 400–1200 m/z; dd-MS2 decision, 17,500; collision vitality, 25 eV; dynamic exclusion, 0.5 s. Mercurialin-containing fractions have been mixed, dried in vacuo, after which separated by preparative HPLC with the next LC circumstances in two rounds: Phenomenex Kinetex® 5 µm C18 100 Å LC Column 150 × 21.2 mm, solvent A – 0.1% TFA in water, solvent B – acetonitrile (0.1% TFA); 1. separation: LC gradients:, 7.5 mL/min, 1. separation: 0 min: 10% B, 1 min: 10% B, 36 min: 50% B, 39 min: 95% B, 42 min: 95% B, 42.5 min: 10% B, 60.1 min: 10% B. 2. separation: 7.5 mL/min, 0 min: 20% B, 1 min: 20% B, 36 min: 40% B, 39 min: 95% B, 42 min: 95% B, 42.5 min: 20% B, 60.1 min: 20% B. Fractions have been analyzed for mercurialin by LC-MS and mixed. Closing purification was achieved by 2 rounds of semi-preparative HPLC (Kinetex® 5 μm C18 100 Å 250 x 10 mm column, solvent A: 0.1% TFA in water, solvent B: acetonitrile, 0.1% TFA, 1.5 mL/min; 1. and a pair of. separation: 0 min – 38% B, 35 min – 38% B. Mercurialin (5 mg) was obtained as a white powder.
Construction elucidation of glechomanin and mercurialin
For 1D and 2D NMR evaluation, glechomanin was dissolved in DMSO-d6 or methanol-d4 (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc.), whereas mercurialin and moroidin-QLLVWRNH have been ready in DMSO-d6. All information have been acquired utilizing corresponding Shigemi NMR tubes (Wilson Glass). To match ROESY/NOESY information with geometry-optimized buildings of glechomanin and mercurialin, geometry optimizations have been carried out for the Trp7-Cα stereoisomers of glechomanin and the Phe-Cβ stereoisomers of mercurialin. Initially, the 4 stereoisomer buildings have been energy-minimized utilizing MM2 adopted by MMFF94 calculations in Chem3D (v.22.2.0, Revvity Alerts, most iterations set to 10,000). The ensuing conformers have been subsequently geometry-optimized utilizing the B3LYP-D3/6-31 + G(d,p) technique in Gaussian 16 (revision A.03)96 on the Nice Lakes HPC cluster and analyzed in Chem3D.
For Marfey’s evaluation, ~400 μg of purified glechomanin or mercurialin have been hydrolyzed in 600 μL of 6 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) in a sealed thick-walled response vessel. The pattern was heated at 110 °C and stirred in a single day for 12 h. Subsequently, the hydrolysate was concentrated to dryness below nitrogen gasoline and redissolved in 100 μL water. Then, 100 μL of 1 M sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and 100 μL of a 1% acetone resolution of Marfey’s reagent, 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-l-alanine amide (l-FDAA), have been added to the answer. The response combination was incubated at 40 °C for 1 h after which quenched by including 100 μL of 1 M HCl. For the preparation of l-FDAA-amino acid customary derivatives, 50 mM of every amino acid (d/l-Phe, d/l-Glu, d/l-Leu, d/l-Trp, d/l-Val, d/l-Phe, d/l-Arg and d/l-Tyr) dissolved in water (50 μL) was handled with 1 M NaHCO3 (20 μL) and 1% l-FDAA (100 μL) at 40 °C for 1 h, respectively. After the response, the answer was quenched with 1 M HCl (20 μL) and diluted with acetonitrile (810 μL) for LC-MS evaluation. LC-MS/MS evaluation parameters have been as follows: injection quantity 2 µL; LC, Phenomenex Kinetex 2.6 μm C18 reverse section 100 Å 150 × 3 mm LC column; LC gradient: solvent A, 0.1% formic acid; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0 min, 10% B; 40 min, 60% B; 41 min, 95% B; 44 min, 95% B; 45 min, 10% B, 50 min, 10% B, 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; MS, optimistic ion mode; full MS, decision 70,000, mass vary 100–1000 m/z. For the willpower of d/l-Arg, the next LC-MS/MS parameters have been employed: injection quantity 5 µL; LC, Higgins Analytical PROTO300 C4 5 µm 250 × 4.6 mm LC column; LC gradient: solvent A, 0.1% formic acid; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0 min, 10% B; 38 min, 20% B; 39 min, 95% B; 45 min, 95% B; 46 min, 10% B, 56 min, 10% B, 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; MS, optimistic ion mode; full MS, decision 70,000, mass vary 100–1000 m/z. The configurations of the amino acid residues have been decided by evaluating their retention occasions and elution orders with these of FDAA derivatives of amino acid requirements.
BURP-domain gene cloning
Leaves of 10-week-old Glechoma hederacea, stem tissue of Stellaria aquatica, and leaves of Orchidantha maxillarioides have been collected and complete RNA was extracted from every plant with QIAGEN RNeasy Plant Mini Equipment. Complementary DNA was ready from G. hederacea leaf complete RNA, S. aquatica stem complete RNA, and O. maxillarioides leaf complete RNA with Thermo Scientific™ Maxima H Minus First Strand cDNA Synthesis Equipment. Cloning primers for GheBURP, SaqBURP, and OmaBURP1/2 have been designed from candidate GheBURP transcripts, SaqBURP transcripts, and OmaBURP1/2 transcripts, respectively (Supplementary Desk 16). GheBURP and OmaBURP1/2 have been amplified with Phusion Excessive-Constancy DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs) and cloned by Gibson cloning meeting97 (New England Biolabs) into pEAQ-HT73 linearized by restriction enzymes AgeI and XhoI. Cloned GheBURP have been sequenced by Sanger sequencing. Equally, SaqBURP was cloned into pHis8 (pET28a with N-terminal 8xHis-tag) linearized by restriction enzyme NcoI. Cloned SaqBURP was sequenced by Nanopore sequencing (Plasmidsaurus Inc).
Transient gene expression in Nicotiana benthamiana
SstBURP-1xQLLVWRNH, SstBURP-4xQLLVWRNH, SaqBURP-1xQLLVWRNH, OmaBURP1-1xQLFVWGW, ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY, ManBURP-1xQLLVWRY, GheBURP-1xQLLVW, KjaBURP-1xQLLVWRGH, KjaBURP-1xQLLVWRNH, KjaBURP-1xQLLVWRSH, and KjaBURP-1xQLLVWPKH (Supplementary Information 4) have been synthesized with N-terminal overhang TGCCCAAATTCGCGACCGGT and C-terminal overhang CTCGAGGCCTTTAACTCTGG for Gibson cloning into pEAQ-HT73 linearized with AgeI and XhoI. Agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404 was reworked with pEAQ-HT-GheBURP wildtype or artificial constructs (GheBURP-1xQLLVW), pEAQ-HT-KjaBURP artificial constructs (KjaBURP-1xQLLVWRNH, KjaBURP-1xQLLVWRSH, KjaBURP-1xQLLVWPKH), pEAQ-HT-SstBURP artificial constructs (SstBURP-1xQLLVWRNH, SstBURP-4xQLLVWRNH), pEAQ-HT-SaqBURP artificial assemble (SaqBURP-1xQLLVWRNH), pEAQ-HT-OmaBURP1 wild-type and artificial constructs (OmaBURP1-1xQLFVWGW), pEAQ-HT-OmaBURP2 wildtype assemble and pEAQ-HT-ManBURP wildtype and artificial constructs (ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY, ManBURP-1xQLLVWRY) by electroporation (2.5 kV) after which plated on YM agar plates (0.4 g of yeast extract, 10 g of d-mannitol, 0.1 g of sodium chloride (NaCl), 0.2 g of magnesium sulfate (heptahydrate), 0.5 g of potassium phosphate (dibasic, trihydrate), 15 g of agar, and 1 L of deionized water, adjusted to pH 7) with 100 μg/mL rifampicin, 50 μg/mL kanamycin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and incubated for two days at 30 °C. A 5 mL starter tradition of the YM medium with 100 μg/mL rifampicin, 50 μg/mL kanamycin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin was inoculated with a clone of A. tumefaciens LBA4404 pEAQ-HT-GheBURP or different precursor gene constructs and incubated for twenty-four–36 h at 30 °C in a shaking incubator at 220 rpm. Subsequently, the starter tradition was used to inoculate a 25 mL tradition of the YM medium with 100 μg/mL rifampicin, 50 μg/mL kanamycin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin, which was incubated for twenty-four h at 30 °C in a shaking incubator at 220 rpm. The cells from the 25 mL tradition have been centrifuged for 30 min at 3000 × g, the YM medium was discarded, and cells have been resuspended in MMA medium (10 mM MES KOH buffer (pH 5.6), 10 mM magnesium chloride (MgCl2), 100 μM acetosyringone) to provide a last optical density (OD600) of 0.8. The Agrobacterium suspension was infiltrated into the underside of the leaves of N. benthamiana vegetation (6-8 weeks previous) utilizing 1 mL plastic syringes. N. benthamiana vegetation have been positioned within the shade 2 h earlier than syringe infiltration. After infiltration, N. benthamiana vegetation have been grown as described above for six days. Subsequently, infiltrated leaves have been collected and subjected to peptide chemotyping. For peptide purification, infiltrated leaves have been collected after 7 days and saved at -80 °C till purification.
Protein purification
E. coli-codon-optimized GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW and ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY (Supplementary Information 4) have been cloned through Gibson cloning into NcoI-linearized pHis8 expression vector (pET28a with an N-terminal 8xHis-tag) with 5’-overhang GAAAACTTGTACTTCCAGGCCCATGGC and three’-overhang CCATGGCGGATCCGAATTCGAG. They have been reworked into E. coli BL21(DE3) respectively. Every colony of E. coli BL21(DE3) was inoculated to a ten mL Luria-Bertani medium with 50 µg/mL kanamycin for 16 h incubation at 37 °C and 200 rpm. The starter tradition was used to inoculate 1 L Terrific Broth liquid medium with 50 µg/mL kanamycin and the tradition was incubated at 37 °C and 200 rpm till OD600 reached 0.7-1. The tradition was then added with Isopropyl-β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside to a last focus of fifty µg/mL and cooled to 18 °C for incubation at 200 rpm for 16 h.
Cells have been centrifugated at 3500 × g and 4 °C. The cell pellet was resuspended in resolution buffer (50 mM Tris-hydrochloride (Tris-HCl) (pH 8), 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, pH 8), 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 25% sucrose (w/v)) with 5 mL per g moist cell pellet. Resuspended cells have been sonicated on ice to interrupt cells open for two min 57 sec at 80% amplitude (59 s on, 59 s off). Subsequently, 1 mg lysozyme and 1 mg DNAse I is added per mL lysate and 25 µL divalent cation resolution (400 mM MgCl2, 400 mM calcium chloride (CaCl2)) is added per mL lysate. The lysate was then stirred at room temperature for 20 min. Subsequent, the identical quantity of lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 1 mM EDTA (pH 8), 1 mM DTT, 200 mM NaCl, 1.0 % Triton X-100 was added to the lysate and combined for 1 h at 4 °C. The lysate was sonicated once more on ice for two min 57 sec and 60% amplitude (59 s on, 59 s off) after which added with EDTA resolution (pH 8, last focus 20 mM). The inclusion our bodies have been subsequently checked for full resuspension. The ensuing lysate was centrifugated for 30 min at 6000 × g and 4 °C. The supernatant was discarded and the inclusion our bodies have been resuspended in the identical quantity because the discarded supernatant of Wash Buffer with Triton X-100 (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 1 mM EDTA (pH 8), 1 mM DTT, 100 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100). The inclusion physique resuspension was sonicated on ice for two min 57 sec and 60% amplitude (59 s on, 59 s off). The inclusion our bodies are checked for full resuspension and centrifugated for 30 min at 6000 × g and 4 °C. The inclusion our bodies have been washed yet another time with Wash Buffer with Triton X-100, earlier than the inclusion our bodies have been washed twice with Wash Buffer with out Triton X-100 (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 1 mM EDTA (pH 8), 1 mM DTT, 100 mM NaCl). After the ultimate centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded and the inclusion physique pellet was resuspended in TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 1 mM EDTA (pH 8)) at 5 mL per g moist inclusion our bodies after which aliquoted as 1 mL inclusion physique resuspension for storage at -80 °C earlier than additional protein purification.
Except in any other case specified, all subsequent procedures have been carried out at room temperature. The denaturing resolution was ready in a 15 mL conical tube by mixing stable urea with 4 mL of fifty mM Tris-HCl (pH 8) and 100 mM NaCl, attaining a last focus of seven.5–8.0 M, adopted by the addition of 8 mM β-mercaptoethanol. Thawed inclusion our bodies (1 mL aliquot) have been then added to the denaturing resolution and gently combined. The combination was inverted or pipetted each 10 min for 60 min till full dissolution was achieved. Subsequently, the answer was filtered by way of a 0.45 µm syringe filter right into a conical tube. The dissolved and filtered GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW/ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY was diluted into 500 mL of fifty mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 500 mM NaCl, and a pair of.5 M urea to stop aggregation throughout refolding. Earlier than use, a 4 L inventory of refolding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (GoldBio), 10% glycerol) was cooled to 4 °C. The diluted GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW/ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY (every 500 mL) was then launched into 3.5 kDa molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) dialysis tubing and dialyzed in a single day at 4 °C in 4 L of refolding buffer. Following dialysis, the protein was faraway from the tubing and centrifuged at 4000 × g at 4 °C for 30 min to get rid of aggregates previous to purification. Subsequently, 2.5 mL of Ni-NTA resin was added to a 20 mL column, washed with deionized water, and equilibrated with 10 column volumes (CV) of refolding buffer containing 30 mM imidazole at pH 8. The refolded protein was then utilized onto the resin, and the flow-through was discarded. The resin was washed with 10 CV of refolding buffer containing 30 mM imidazole at pH 8, adopted by elution of the protein with 10 CV of refolding buffer containing 600 mM imidazole at pH 8. A combination containing 1 mg of TEV protease for each 10 mg of eluted protein was subjected to in a single day dialysis in 3.5 kDa MWCO dialysis tubing at 4 °C with stirring in 4 L of TEV protease buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM lowered glutathione (GSH), 0.3 mM oxidized glutathione (GSSG)). Subsequently, GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW/ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY was separated from uncleaved His8-GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW/His8-ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY, respectively, and the His-tagged TEV protease utilizing a second 2.0 mL Ni-NTA column, which had been pre-equilibrated with 10 CV of TEV protease buffer in a disposable 20 mL column. The flow-through was then concentrated utilizing Amicon Extremely-15mL 10 kDa MWCO centrifugal concentrators, subjected to SDS-PAGE evaluation, and utilized for enzyme assays.
Enzyme assays
For core peptide evaluation, enzyme assays have been carried out utilizing 50 µL volumes containing both copper(II) chloride (CuCl2) from JT Baker Chemical Co. or water. Assays for BURP-domain proteins comprised 300 µM GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW/100 µM ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY, 1 mM CuCl2, and a citrate:phosphate buffer (pH 7) with last concentrations of 18 mM citrate and 165 mM Na2HPO4. The enzyme reactions have been incubated for twenty-four h at 20 °C. Subsequently, 1 µg of trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, T7575-1KT) in 20 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8)/1 µg of LysC (NEB, P8109S) in 10 µL of 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8) buffer was added to GheBURP/ManBURP assay, respectively, and additional incubated at 37 °C for twenty-four h. Every digest was centrifuged, added to ChromacolTM LC-MS vial, and subjected to LC–MS/MS evaluation. LC-MS/MS settings: Injection quantity 15 µL, LC-Higgins Analytical PROTO300 C4 5 µm 250 × 4.6 mm, solvent A-0.1% formic acid, solvent B-acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid), 0.7 mL/min, 30 °C, LC gradient: 0 min: 10% B, 10 min: 50% B, 11 min: 95% B, 13 min: 95% B, 13.1 min: 10% B, 20 min: 10% B, MS – Constructive ion mode, Full MS: Decision 35,000, mass vary: 700-1250 m/z for GheBURP digest and 700-1450 m/z for ManBURP digest, dd-MS2: decision 17,500, AGC goal 1e5, loop rely 5, isolation window 0.4 m/z, collision vitality 25 eV, dynamic exclusion 2 s. Scaled enzyme assays for exoproteolytic cyclic peptide formation have been carried out on a 2 mL scale utilizing purified GheBURP-1xQLFVWGW/ManBURP-1xQLFFWRY obtained from a 4 L/2 L expression and purification course of. These assays included 130–350 µM of the BURP area cyclase and 1 mM CuCl2 in a citrate:phosphate buffer at pH 7. The assays have been incubated for twenty-four h at 20 °C. Following incubation, trypsin/LysC was launched into the GheBURP/ManBURP response mixtures at a protease-substrate molar ratio of 1:250/1:100, with the pH adjusted to eight utilizing a 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8) buffer and incubated at 37 °C for twenty-four h. Two digests have been subjected to preparative HPLC, respectively (LC settings, Phenomenex Kinetex 5 µm C18 100 Å LC Column 150 x 21.2 mm, 7.5 mL/min; solvent A, 0.1% TFA; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% TFA); LC gradient, 0 min, 10% B; 1 min, 10% B; 36 min, 50% B; 39 min, 95% B; 42 min, 95% B; 42.5 min, 10% B; 60.1 min, 10% B). HPLC fractions have been analyzed by LC–MS evaluation for goal plenty of modified core peptides with the next LC–MS parameters: injection quantity 2 µL; LC, Phenomenex Kinetex 2.6 μm C18 reverse section 100 Å 50 × 3 mm LC column; LC gradient. solvent A, 0.1% formic acid; solvent B, acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); 0 min, 5% B; 2.5 min, 95% B; 3.0 min, 95% B; 3.1 min, 5% B; 5.0 min, 5% B, 0.5 mL/min, 30 °C; MS, optimistic ion mode; full MS, decision 35,000, mass vary 400–1200 m/z; dd-MS2, decision 17,500; loop rely 5, collision vitality 25 eV and dynamic exclusion 0.5 s. LC fractions containing goal peptides have been dried and resuspended in 30 µL DMSO for additional evaluation. Exopeptidase assays have been carried out with ~25–50 µg of peptides (with 4% DMSO), carboxypeptidase Y (from S. cerevisiae, Sigma-Aldrich), and aminopeptidase N (from Rat, Sigma Aldrich) at a peptidase:peptides ratio of 1:10 (w/w). These assays have been carried out in 100 mM Tris-HCl buffer at pH 7 and 37 °C for twenty-four h. Following incubation, the assays have been centrifuged and analyzed by LC-MS/MS as follows: Injection quantity 15 µL, LC-Higgins Analytical PROTO300 C4 5 µm 250 × 4.6 mm, all gradients: solvent A-0.1% formic acid, solvent B-acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid), 0.7 mL/min, 30 °C, LC gradient: 0 min: 15% B, 60 min: 40% B, 61 min: 95% B, 63 min: 95% B, 63.1 min: 15% B, 80 min: 15% B, MS – Constructive ion mode, Full MS: Decision 35,000, mass vary: 800–1300 m/z for GheBURP and 700–1450 m/z for ManBURP, dd-MS2: decision 17,500, AGC goal 1e5, loop rely 5, isolation width 0.4 m/z, collision vitality 25 eV, dynamic exclusion 0.6 s. The evaluation was in comparison with purified glechomanin or mercurialin requirements.
Bioassay
Most cancers cell strains H1437 (ATCC® CRL-5872), H1299 (ATCC® CRL-5803), A549 (ATCC® CCL-185), U2OS (ATCC® HTB-96), LNCaP (ATCC® CRL-1740), HUH-7 (JCRB® JCRB0403), and noncancerous cell strains IMR-90 (ATCC® CCL-186), HFF (ATCC® CRL-2088), and MEFs have been maintained at 37 °C and 5% CO2 environment. Normal isolation and tradition of main mouse embryonic fibroblasts from pregnant feminine mice on the College of Michigan established the MEF cell line98. H1437, H1299 and LNCaP have been grown in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 Medium (Fisher Scientific, 11875119), U2OS have been grown in McCoy’s 5 A Medium (Thermo Fisher, 16600082), and the remaining strains grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s medium (Fisher Scientific, 11995065). A549 cell media have been supplemented with 15% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS; Thermo Fisher, A5670701), whereas the remaining media have been supplemented with 10% FBS and 1x penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco, 15140122).
384-well plates (Perkin Elmer, 6057300) have been seeded with H1437, H1299, A549, U2OS, LNCaP, HUH-7, IMR-90, HFF, and MEF at 5000 cells per effectively in 50 μL of their respective full media. Cell seeding densities have been optimized such that the cells can be 90–100% confluent in DMSO automobile management wells after 72 h. Cells have been allowed to connect to the wells for twenty-four h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Compounds (10 mM) have been added utilizing the HPD300e digital compound dispenser in randomized, ten-point, two-fold dose response (n = 3) from a beginning focus of 40 μM. Compounds have been normalized to the very best class DMSO quantity of 1%, then incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 48 h. Every cell line had n = 16 optimistic controls (10 μM taxol) and automobile (DMSO). Cells have been mounted with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min, permeabilized with 0.03% Triton X-100 for 20 min and rinsed twice with PBS between every step. Cells have been then stained for 30 min with a 1:1000 PBS dilution of Hoechst 33340 (Thermo Scientific, H1399) for nuclei staining and 1:10,000 PBS dilution of CellMask Orange (Thermo Fisher, H32713) for cell delineation. Fastened and stained plates have been washed twice with PBS, then left in a last quantity of 25 μL per effectively for imaging utilizing a Thermo Fisher CX5 excessive content material imaging microscope with LED excitation (386/23 nm, 560/25 nm) at 10x magnification. Cells have been imaged at a single z-plane as optimized by way of image-based autofocus for every channel, and the publicity occasions have been chosen to maximise the signal-to-background ratio. Cellpose99 was used to section and rely cell nuclei for every cell line, a p.c viability rating for compounds was generated by normalizing the cell rely to the typical well-level cell counts noticed within the unfavourable management (DMSO), and dose-response curves have been match utilizing the GraphPad Prism software program (v10.1.0, Dotmatics).
Phylogenetic tree development
The tree was constructed within the net server Interactive Tree of Life100 displaying angiosperm orders distinguished as ANA grade, Magnolids, Monocots and Eudicots101.
Reporting abstract
Additional data on analysis design is offered within the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract linked to this text.