Hey buddies 👋
Immediately’s publish was impressed by a query I at all times hear:
Why are we growing AI within the first place?
I made a decision to go deep down the rabbit gap of AI’s 70-year historical past. I needed to know its origins and founding concepts, why it virtually obtained defunded into oblivion (twice), and its exponential rise in our instances.
I attempted my greatest to summarize 70 years of historical past right into a concise 10-minute learn but it surely was unattainable with out leaving out essential particulars. So, I made a decision to separate it up into 3 smaller components to make it simpler to learn along with your morning espresso:
-
Half 1: Sparks of Intelligence
-
Half 2: AI’s Darkish Winter Rollercoaster
-
Half 3: The Exponential Renaissance
I’m sharing Half 1 in the present day. Half 2 and three will comply with quickly.
Keep curious,
– Fawzi
“They study to talk, write, and do calculations. They’ve an outstanding reminiscence. Should you had been to learn them a twenty-volume encyclopedia they may repeat the contents so as, however they by no means suppose up something authentic.”
– Domin to Helena, Rossum’s Common Robots by Karel Čapek (1920)
Our fascination with creating clever beings is something however new.
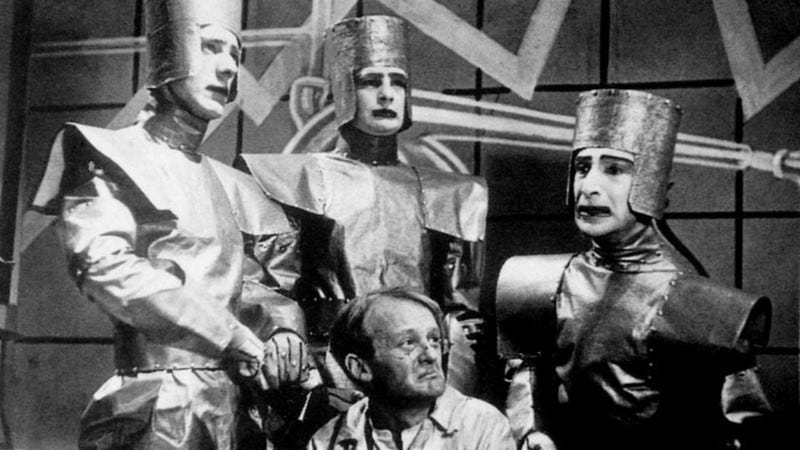
Karel Čapek’s 1920 play, Rossum’s Common Robots (R.U.R.), precisely foreshadows the AI trade that may begin blooming 30 years later.

Younger Rossum, an engineer, decides to design and create the proper employee. He invents the Robotic, and his manufacturing facility begins manufacturing hundreds of them whereas promoting them everywhere in the world:
DOMIN: What do you suppose? From a sensible standpoint, what’s the greatest type of employee?
HELENA: One of the best? In all probability one who—who—who’s sincere—and devoted.
DOMIN: No, it’s the one which’s the most affordable. The one with the fewest wants. Younger Rossum efficiently invented a employee with the smallest variety of wants, however to take action he needed to simplify him. He chucked every part indirectly associated to work, and in so doing he just about discarded the human being and created the Robotic. My pricey Miss Glory, Robots aren’t folks. They’re mechanically extra good than we’re, they’ve an astounding mental capability, however they haven’t any soul. Oh, Miss Glory, the creation of an engineer is technically extra refined than the product of nature.
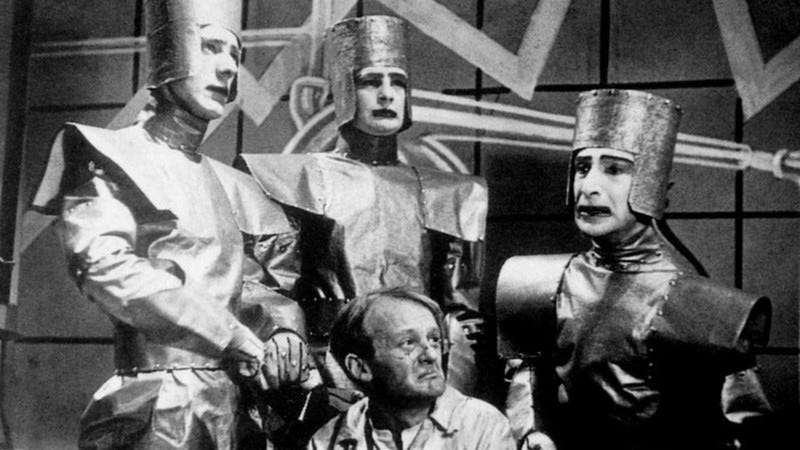
This play launched the world to the time period “robotic”. The phrase was created by Čapek’s older brother Josef, and was derived from the Czech phrase “robota” which means “compelled labour”. In R.U.R., robots regarded precisely like people on the floor however operated fully in another way.
DOMIN: Good. You may inform them no matter you need. You may learn them the Bible, logarithms, or no matter you please. You may even preach to them about human rights.
HELENA: Oh, I believed that . . . if somebody had been to point out them a bit of affection—
FABRY: Not possible, Miss Glory. Nothing is farther from being human than a Robotic.
HELENA: Why do you make them then?
BUSMAN: Hahaha, that’s a great one! Why will we make Robots!
FABRY: For work, Miss. One Robotic can do the work of two and a half human laborers. The human machine, Miss Glory, was hopelessly imperfect. It wanted to be performed away with as soon as and for all.
The rise of digital computer systems within the Nineteen Forties marked the start of sensible experiments in synthetic intelligence. In 1950, Alan Turing proposed his well-known Turing Check (initially referred to as the Imitation Sport) to find out whether or not a machine was demonstrating human-level intelligence.
The query “Can machines suppose?” was flawed in response to Turing. The phrases “machine” and “suppose” don’t have clear definitions which makes the query an insufficient measure of intelligence. As an alternative, the Imitation Sport is predicated on the premise that an clever machine ought to be indistinguishable from a human.

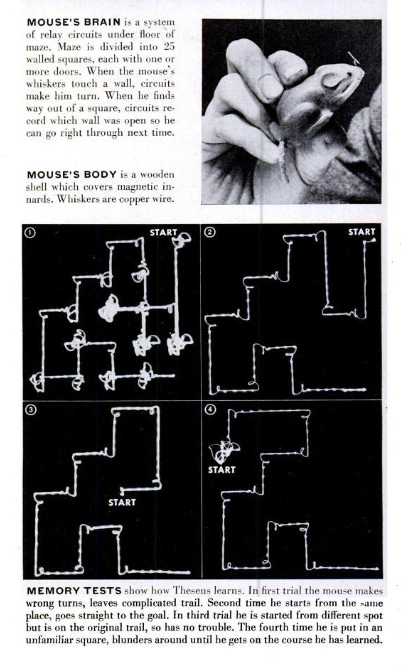
One of many earliest examples of clever methods was the mechanical mouse Theseus constructed by Claude Shannon at Bell Laboratories in 1952. Theseus navigated a maze by itself by way of trial and error, and was spectacular sufficient to be featured in LIFE Journal’s July 1952 version:
The actual canon occasion for AI got here in 1956, when Claude Shannon spent the summer time at Dartmouth School with fellow pc scientists John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky from MIT, and Nathaniel Rochester from IBM.
The time period “Synthetic Intelligence” was formally adopted then, and the AI area was formally born.
The aim was easy:
The examine is to proceed on the premise of the conjecture that each facet of studying or some other characteristic of intelligence can in precept be so exactly described {that a} machine may be made to simulate it.
An try shall be made to search out tips on how to make machines use language, kind abstractions and ideas, clear up sorts of issues now reserved for people, and enhance themselves.
(Learn the complete proposal right here)
The Fifties and Sixties had been a interval of nice pleasure and speedy progress in AI.
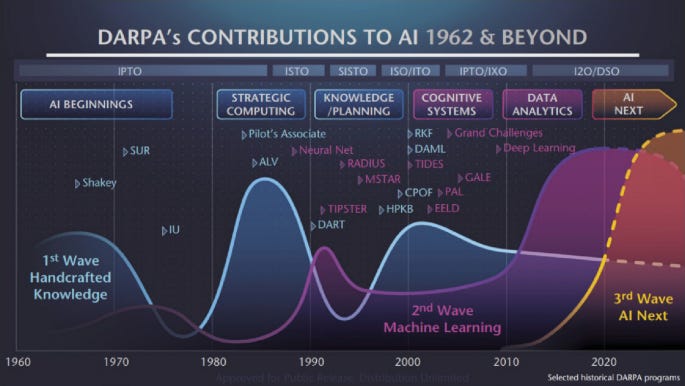
With substantial funding from the U.S. Division of Protection by way of DARPA, researchers developed all kinds of clever methods:
-
1956: Allen Newell, Herbert A. Simon, and Cliff Shaw constructed Logic Theorist, a reasoning program that would show mathematical theorems.
-
1958: John McCarthy created LISP, a programming language that may grow to be basic to AI analysis.
-
1959: Arthur Samuel, who developed the the primary self-learning checkers program, coined the time period “machine studying”.
-
1965: Edward Feigenbaum and Joshua Lederberg created the primary “professional system” referred to as DENDRAL designed to copy human decision-making.
-
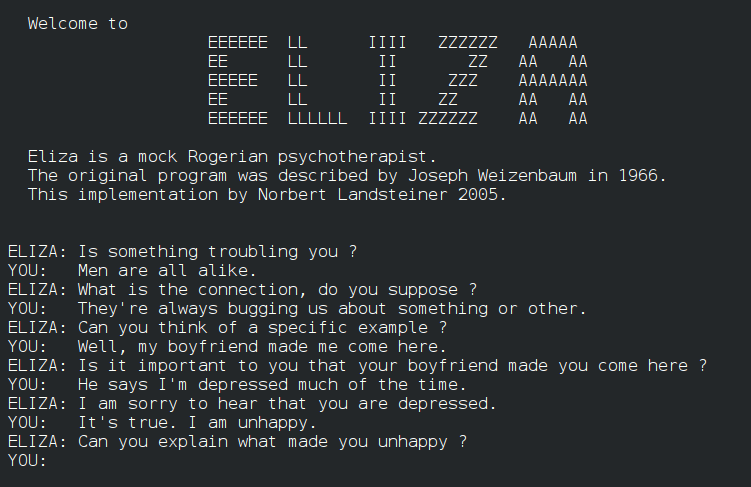
1966: Joseph Weizenbaum launched ELIZA, the primary chatbot, which used pure language processing to converse with people.
-
1968: Alexey Ivakhnenko developed the Group Methodology of Information Dealing with (GMDH) which laid the muse for Deep Studying.
With pleasure, hype, and beneficiant funding comes sky-high expectations.
J.C.R. Licklider, the pinnacle of DARPA’s Info Processing Strategies Workplace on the time, performed a key function in backing AI researchers and their ambitions. Licklider additionally pioneered basic concepts that may form analysis in AI and computing in his 1960 paper Man-Laptop Symbiosis.
Within the anticipated symbiotic partnership, males will set the targets, formulate the hypotheses, decide the factors, and carry out the evaluations. Computing machines will do the routinizable work that should be performed to organize the way in which for insights and selections in technical and scientific pondering.
– J.C.R. Licklider in Man-Laptop Symbiosis (1960)
Hope and optimism shortly reworked into disappointment within the late 60s and early 70s.
Two vital authorities reviews dealt a devastating blow to the AI area and despatched the trade into the first AI winter:
-
The ALPAC Report: In 1966, a committee of scientists chosen by the U.S. authorities evaluated the progress in machine translation and concluded that it was dearer, much less correct, and slower than people. Machine translation was a prime precedence for the U.S. to translate Russian communications throughout the Chilly Warfare.
-
The Lighthill Report: Throughout the Atlantic Ocean in 1973, Sir James Lighthill delivered an identical report back to the British Authorities. He concluded that AI failed to realize its “grandiose” aims and was unlikely to take action within the foreseeable future.
“Most staff in AI analysis and in associated fields confess to a pronounced feeling of disappointment in what has been achieved previously twenty-five years. […] In no a part of the sector have the discoveries made up to now produced the key impression that was then promised.”
– Sir James Lighthill, Synthetic Intelligence: A Normal Survey (1972)
Funding was considerably down, however the AI area’s coronary heart was nonetheless beating slowly… and it might rise once more.
Learn Half 2:
🤬 LinkedIn faces a serious AI opt-in backlash
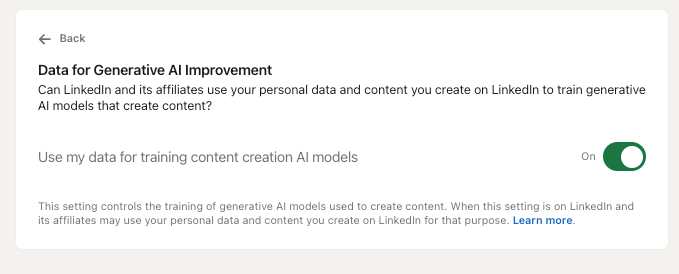
For no matter motive, LinkedIn thought it might be a good suggestion to routinely opt-in all its customers in permitting their content material for use for AI coaching. It’s shocking to see LinkedIn, owned by Microsoft, undertake such an strategy after the same backlash that Adobe obtained earlier this 12 months for doing the identical factor.
The excellent news is you could simply opt-out by following this hyperlink.
🤖 OpenAI launched a preview of its highly-anticipated o1 mannequin
OpenAI lastly launched a preview of its highly-anticipated o1 mannequin. Not like its earlier fashions, it spends extra time “pondering” by way of an issue earlier than responding which leads to higher outputs.
There’s one caveat, nevertheless. The main points behind the reasoning steps aren’t totally displayed, and the mannequin prices extra to run as a result of it generates extra output tokens for its “pondering” steps. And if you happen to’re questioning why “o1” isn’t referred to as “GPT-5”, right here’s OpenAI’s reply:
[…] However for advanced reasoning duties this can be a vital development and represents a brand new degree of AI functionality. Given this, we’re resetting the counter again to 1 and naming this sequence OpenAI o1.
AI for non-technical folks course: I’m nonetheless engaged on my “What you must find out about AI” course for non-technical folks. I underestimated the time it took to make a nice course, however you’ll be able to be a part of the waitlist to be the primary to listen to about it. The course shall be free FYI.
Share this publish in your group chats with buddies, household, and coworkers.
If this was forwarded to you, subscribe to Yr 2049 without spending a dime.