
Swarming is likely one of the principal types of bacterial motility facilitated by flagella and surfactants. It performs a particular position in each illness and therapeutic. For instance, in urinary tract infections (UTIs), swarming micro organism can aggressively migrate throughout tissue surfaces, contributing to the unfold and severity of an infection. Conversely, in inflammatory bowel illness (IBD), sure swarming microbes have been proven to advertise intestine lining restore.
These contrasting roles spotlight the potential of the detection of swarming micro organism as a beneficial biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring numerous circumstances.
Though each swarming and swimming are pushed by flagella, they signify essentially totally different behaviors. Swimming entails particular person micro organism transferring independently by means of liquid environments, whereas swarming is a coordinated group motion throughout semi-solid surfaces, aided by surfactants that allow the group of micro organism to maneuver in unison.
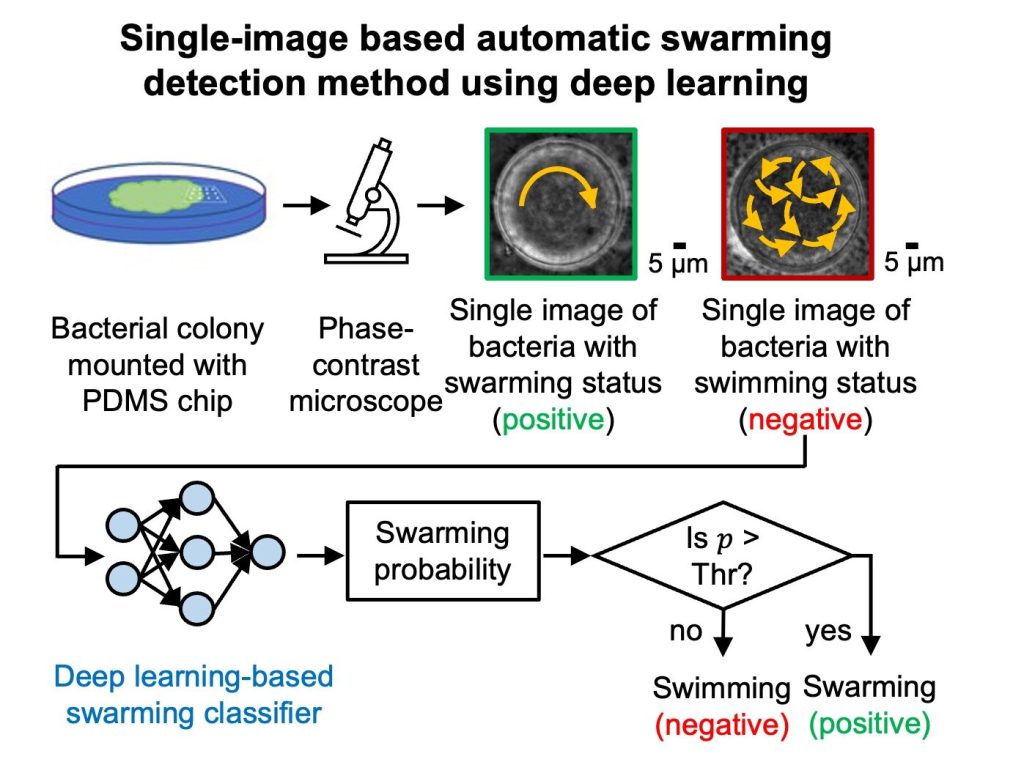
To check these behaviors intimately, researchers typically place tiny round wells fabricated from a comfortable polymer alongside the perimeters of bacterial colonies. Below an optical microscope, swarmers show a big, single swirl that circulates throughout your complete effectively. In distinction, swimmers generate a number of small, disorganized native swirls—like scattered whirlpools transferring in no specific path.
Historically, distinguishing these movement patterns requires video recording and professional visible inspection, limiting its scalability and accuracy.
In a latest examine led by Professor Aydogan Ozcan at UCLA and Professor Sridhar Mani at Albert Einstein School of Drugs, researchers launched a deep learning-based technique for robotically detecting bacterial swarming from a single blurry microscopic picture. The paper is revealed within the journal Intestine Microbes.
This automated method eliminates the necessity for handbook professional video evaluation, making the method quicker and extra correct. That is particularly well-suited for high-throughput functions and supplies goal, quantitative readouts.
Through the use of a single long-exposure picture that encodes time-varying movement into the spatial smear patterns, this technique eliminates the necessity for high-frame-rate video seize, making it extra accessible and sensible to be used in resource-limited settings.
By coaching an AI mannequin on 1000’s of microscopy pictures equivalent to a pressure of micro organism, the workforce developed a neural community able to distinguishing the attribute movement patterns of swarming from swimming with very excessive accuracy—reaching a sensitivity of 97.44% and a specificity of 100%.
Remarkably, the classifier not solely carried out effectively on the bacterial pressure utilized in coaching but in addition generalized successfully to completely various kinds of micro organism with out the necessity for retraining the community, sustaining over 96% sensitivity and specificity.
This AI-powered bacterial swarming detection technique represents a major development for diagnostic microbiology functions. Future work will deal with evaluating the strategy underneath a wide range of circumstances, together with advanced environments with combined bacterial populations.
With its automated readout and easy imaging {hardware}, this method additionally holds sturdy potential for integration with smartphone-based imagers—enabling transportable, on-site, and non-invasive detection of swarming micro organism.
Extra info:
Yuzhu Li et al, Deep learning-based detection of bacterial swarm movement utilizing a single picture, Intestine Microbes (2025). DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2505115
Quotation:
AI predicts bacterial swarming from a single blurry picture, unlocking new diagnostic prospects (2025, Might 19)
retrieved 19 Might 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-05-ai-bacterial-swarming-blurry-image.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.



