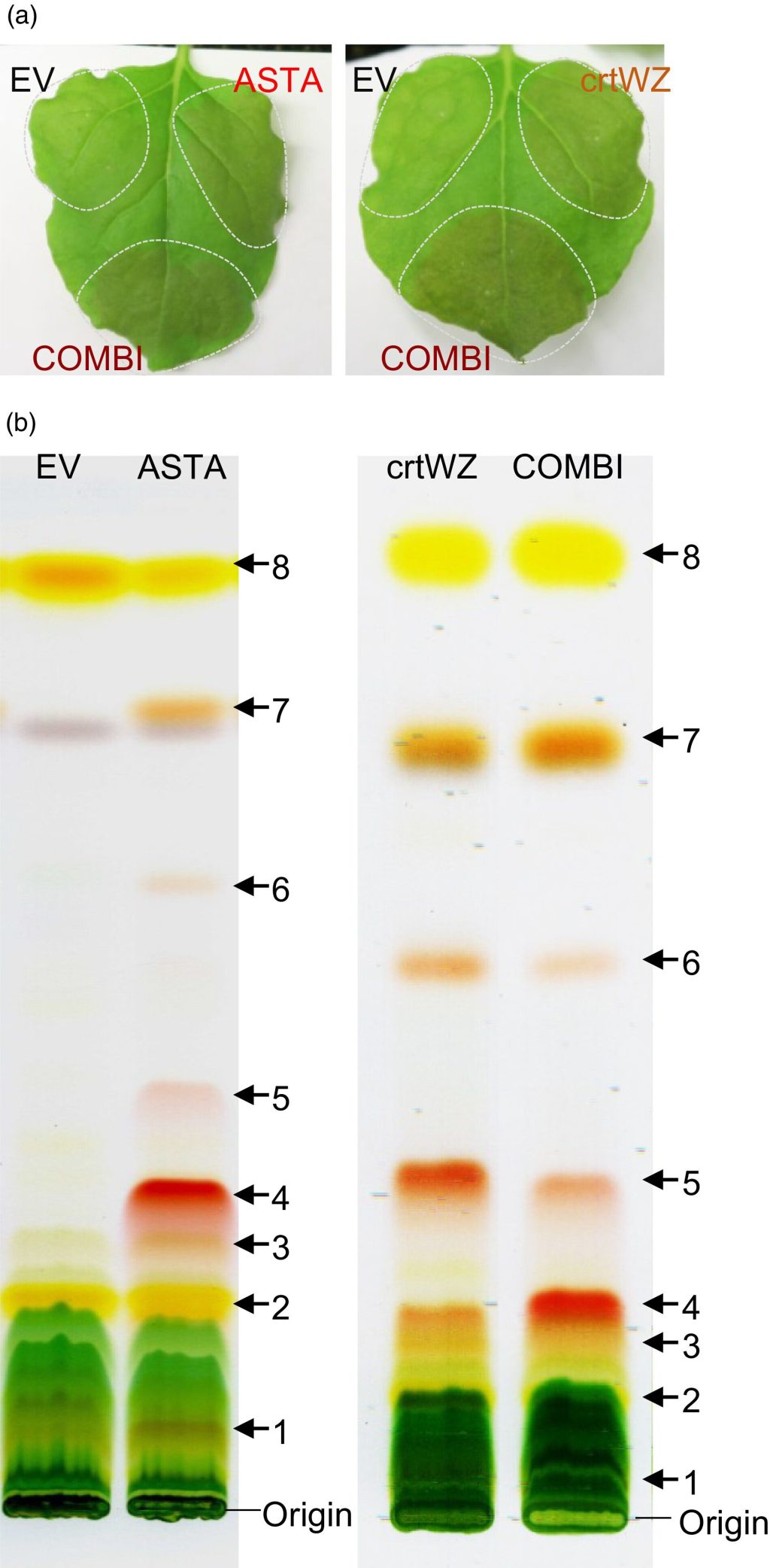

In a significant step ahead for sustainable pigment manufacturing, scientists have efficiently engineered the oilseed crop Camelina sativa to supply excessive ranges of astaxanthin—a invaluable purple antioxidant used to paint farmed salmon and shrimp—utilizing plant-derived genes somewhat than bacterial pathways.
The findings, from a joint US/UK analysis group of biotechnologists led by Prof. Edgar Cahoon, director of the Middle for Plant Science Innovation on the College of Nebraska-Lincoln (UNL), may provide a commercially viable different to artificial astaxanthin, which is presently produced by means of pricey chemical synthesis or from restricted pure sources like algae.
The work is printed within the Plant Biotechnology Journal.
Astaxanthin belongs to a gaggle of purple pigments generally known as ketocarotenoids, that are prized not just for their coloring properties but additionally for his or her distinctive antioxidant capability. These pigments do not happen naturally in most crops, however by borrowing genes from the scarlet flax flower (Adonis aestivalis), researchers launched a brand new ketocarotenoid biosynthesis pathway into Camelina seeds.
In contrast to earlier efforts that used bacterial genes, this plant-derived pathway proved extra environment friendly and cleaner. It transformed almost all of the precursor β-carotene into ketocarotenoids, with astaxanthin making up over a 3rd of the entire—reaching round 47 micrograms per gram of seed.
Importantly, the extracted oil was notably extra immune to oxidation—a trait that will enchantment to the meals business for makes use of similar to oleogels in plant-based merchandise.
Crucially, the modified vegetation confirmed no stunting or seen indicators of stress within the area, and the outcomes have been replicated throughout a number of rising seasons in each the US and UK.
“With rising stress to seek out pure, scalable alternate options to artificial components, we imagine this method may pave the way in which for a brand new technology of sustainable pigment-rich oilseeds,” stated Rothamsted’s Dr. Richard Haslam, one of many co-authors of the analysis paper.
Professor Johnathan Napier commented, “The Rothamsted group was more than happy to be a part of this extremely profitable collaboration leading to crops with enhanced traits. It is also nice to check our prototype vegetation below real-world situations within the area”
UNL’s Professor Cahoon added, “Rothamsted’s world-class experience in GM camelina area trials and lipidomics was important to the success of this analysis. We look ahead to working with Rothamsted investigators to commercialize this know-how.”
Extra info:
Hyojin Kim et al, Oilseed‐primarily based metabolic engineering of astaxanthin and associated ketocarotenoids utilizing a plant‐derived pathway: Lab‐to‐area‐to‐utility, Plant Biotechnology Journal (2025). DOI: 10.1111/pbi.70148
Supplied by
Rothamsted Analysis
Quotation:
Engineered oilseed crop produces excessive ranges of {powerful} antioxidant (2025, June 6)
retrieved 8 June 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-06-oilseed-crop-high-powerful-antioxidant.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




