A analysis staff from Skoltech, the Institute of Bodily, Chemical, and Organic Issues of Soil Science of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and different scientific organizations in Russia and the U.S. carried out a examine of microbial communities residing in excessive situations within the fumarolic fields of the Elbrus (Russia), Ushkovsky (Russia), and Fuji (Japan) volcanoes.
The authors found probably the most environment friendly approach for separating DNA from microbial samples and demonstrated that the microbial communities of each volcanic area are distinct and influenced by the geochemical situations of their surroundings.
The findings are printed within the Scientific Studies journal.
Volcanoes are one of the vital mysterious and charming locations on Earth. Cracks or openings in Earth’s crust on their slopes and at their bases result in the discharge of scorching gases and steam. These areas are often called fumarolic fields, forming in zones of volcanic exercise the place magma heats underground water, changing it into vapor.
Regardless of these harsh situations, life exists even there—archaea and micro organism thrive on fumaroles with fascinating adaptational mechanisms that stay largely unexplored.
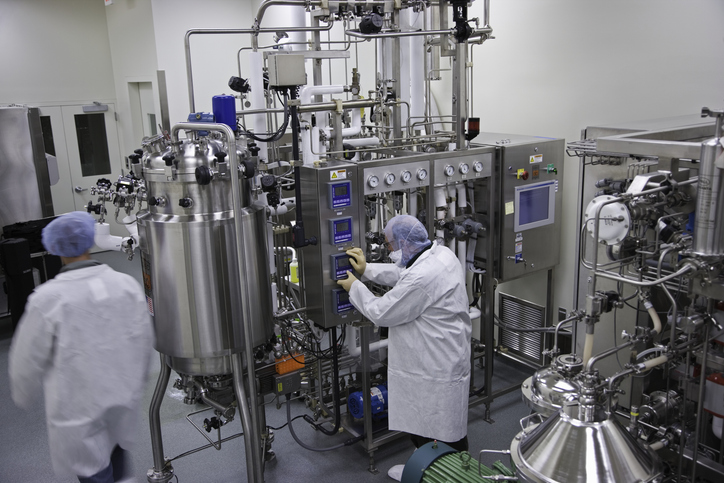
“Samples collected from fumaroles characterize a extremely difficult materials for DNA extraction. In the meantime, thermophilic micro organism able to surviving at excessive temperatures possess intriguing adaptive methods,” defined lead creator Alla Shevchenko, a Ph.D. scholar within the Life Sciences program at Skoltech.
“Our examine offered the primary description of microbial communities inhabiting the fumaroles of Elbrus, Ushkovsky, and Mount Fuji. Samples taken from beneath the snow cowl on Elbrus exhibited a soil floor temperature of roughly +22.5°C.
“Summer season collections from the Ushkovsky Volcano yielded specimens from a fumarolic space with a floor temperature reaching as much as +68.4°C. Fuji samples consisted of frozen sediment deposits. After assortment, all samples had been preserved at -20°C.”
Researchers used totally different strategies of soil pattern pulverization previous to DNA extraction—vertical and horizontal homogenization (mixing). Vertical homogenization proved more practical relating to each DNA yield and detection of archaeal sequences when in comparison with horizontal homogenization.
“The vast majority of DNA was extracted by way of vertical homogenization. Variations in microbial populations correlate with particular options of every volcano. Acidobacteria and Pseudomonas dominate the soils of Elbrus. Ushkovsky fumaroles harbor quite a few members of the Crenarchaeota group. Fuji’s frozen soil harbors fewer microorganisms total however retains Actinomyces and extra species of micro organism,” acknowledged Professor Mikhail Gelfand, a examine co-author and analysis supervisor, the vp for biomedical analysis at Skoltech.
These findings spotlight the importance of choosing an optimum methodology for pattern preparation, significantly beneath excessive situations. Microorganisms residing inside fumaroles function delicate indicators of environmental change.
Their adaptability mirrors ecosystem responses to components like temperature, moisture ranges, pH values, and heavy metallic concentrations.
Modifications within the construction and composition of bacterial and fungal colonies could possibly be an indication of worldwide warming, thermal regime shifts, and anthropogenic impacts.
Extra info:
Alla Yu. Shevchenko et al, Microbial range of high-elevated fumarole fields, low-biomass communities on the boundary between ice and hearth, Scientific Studies (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-99782-3
Supplied by
Skolkovo Institute of Science and Know-how
Quotation:
Volcanic microbes beneath the microscope: Scientists determine optimum DNA extraction methodology (2025, June 17)
retrieved 17 June 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-06-volcanic-microbes-microscope-scientists-optimal.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.