In silico modelling and molecular dynamics simulations of quenchbodies
Preliminary coordinates to tell quenchbody design had been obtained from PDB ID: 1ZVH32 and 5M1430, similar to the X-ray buildings of lysozyme and MBP-binding nanobodies, respectively. N-terminal Cys-tags had been modelled utilizing Modeller (model 10.2)48,49. Techniques had been arrange utilizing CHARMM-GUI50. The CHARMM36m protein drive subject was used for proteins. The CHARMM Basic Pressure Discipline (CGenFF) generated utilizing the CGenFF interface at parachem.org (https://cgenff.umaryland.edu)51 was used for the fluorophore, TAMRA. The TIP3P mannequin was used for water52. Simulations had been carried out utilizing NAMD 3.0 (Nanoscale Molecular Dynamics, model 3 alpha)53.
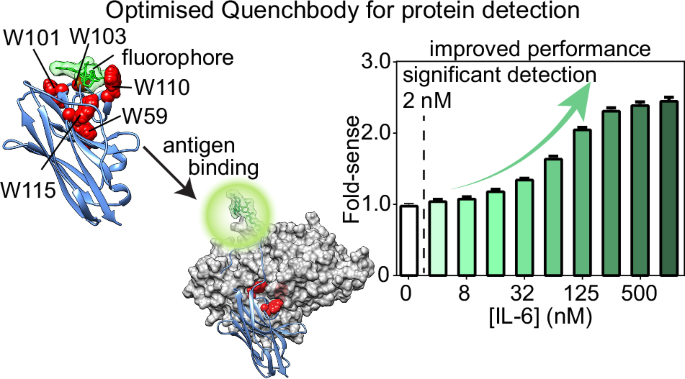
Simulations had been carried out after solvating the system in an octahedral field that prolonged at the very least 12 Å from the solute interface. Na+ and Cl− counter ions had been added to neutralise the system and obtain a salt focus of 0.15 M. pKa calculations had been carried out utilizing PROPKA54 to assign protonation states of ionisable residues. Simulations had been carried out utilizing periodic boundary situations (PBC) at fixed temperature (303.15 Ok) with the Langevin algorithm (a damping coefficient of 1/ps)55 and at a strain of 1.0 bar utilizing the Nostril-Hoover Langevin Piston methodology56. Hydrogen mass repartitioning57 was utilized with the time step set to 4.0 fs, and all covalent bonds involving hydrogens had been stored inflexible with the RATTLE algorithm58. Quick-range electrostatics had been calculated along with long-range electrostatics particle mesh Ewald (PME)59 with a cut-off of 9.0 Å and a PME grid measurement of 1.0 Å. For all techniques, power minimisation (10,000 steps) and 125 ps equilibration had been carried out first with positional restraints positioned on all of the protein-heavy atoms (with a drive fixed of 1.0 kcal/mol/Å2 on the spine atoms and 0.5 kcal/mol/Å2 on the facet chain atoms) and TAMRA heavy atoms (with a drive fixed of 0.5 kcal/mol/Å2). This was adopted by 12 and 6 μs manufacturing runs for the apo and antigen-bound quenchbodies, respectively. Six impartial replicates for every system had been simulated, with a complete of 72 μs for the apo state and 36 μs for the antigen-bound states. Preliminary buildings for the simulations had been the highest 3 modelled Cys-tag buildings primarily based on DOPE scores with hooked up TAMRA(R) or TAMRA(S). Snapshots had been saved each 100 ps. VMD (Visible Molecular Dynamics)60, LOOS (Light-weight Object-Oriented Construction Evaluation)61, MDAnalysis62 and UCSF Chimera63,64,65 had been used to analyse and visualise the trajectories. Quenching distances had been measured between the centres of lots of every of the tryptophans and TAMRA. FoldX was used to foretell the results of residue mutations on quenchbody stability and antigen binding35.
DNA and protein sequence design of quenchbodies
Protein coding sequences from both the MBP-binding nanobody or the lysozyme-binding nanobody had been designed with (i) an N-terminal Cys-tag as a goal for fluorophore labelling, (ii) a C-terminal Avi-tag to allow biotinylation, and (iii) a 3× FLAG-tag and 10× His-tag to facilitate purification procedures. All the protein coding ingredient was then transformed to DNA and codon optimised utilizing IDT’s Escherichia coli (E. coli) B pressure optimiser. This protein-coding DNA ingredient was then mixed right into a gene expression cassette that includes a flanking T7 promoter and terminator for cell-free in vitro transcription and translation (IVTT) of the protein product and ordered as a Geneblock from IDT. The Geneblock additionally featured flanking DNA components appropriate for polymerase chain response (PCR) replication of the Geneblock, particularly DNA complementary to the ahead primer 5′-ACCCGGCATGACAGGAG-3′ and the reverse primer 5′-TGGCGGCCGCTCTA-3′. PCR replication of Geneblocks was performed utilizing Q5® Scorching Begin Excessive-Constancy Grasp Combine (NEB; as per the producer’s directions) at a scale of 100 μL, utilizing 50 ng of Geneblock as template and 0.5 μM of ahead and reverse primer in a PCR Mastercycler (Eppendorf), with preliminary heating at 98°C for 30 s, adopted by 32 cycles of denaturation (98 °C, 10 s), annealing (60 °C, 30 s), and extension (72 °C, 15 s). Quenchbody PCR merchandise had been purified utilizing Wizard Clear-up kits (Promega; as per the producer’s directions) and had been quantified by A260/A280 absorbance on a Nanodrop 2000C spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher). Quenchbody PCR merchandise had been additional analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis to make sure PCR merchandise had been of the anticipated measurement and purity earlier than they had been used for IVTT. All mutant quenchbodies had been generated by in silico sequence modification of 5M14 and 1ZVH quenchbody constructs and re-ordered as Geneblocks from IDT.
In vitro quenchbody expression, labelling and purification
For every quenchbody, 600 ng of purified PCR product was mixed with NEBExpress® Cell-free E. coli Protein Synthesis System (NEB)66 at 2× the response scale, together with protein disulphide bond enhancer (NEB) and GamS (NEB), as per the producer’s directions, and incubated for 16 h at room temperature with shaking at 1200 rpm in a Thermomixer (Eppendorf; used for all subsequent shaking and incubation steps). Expressed quenchbodies had been then purified from the crude IVTT combination (100 μL) by combining with 12.5 μL of Pierce Anti-DYKD4K (FLAG) Magnetic Agarose beads (equal to 50 μL of unique resuspension) prewashed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) utilizing a MagJET separation magnet (used for all subsequent wash steps). The crude IVTT-FLAG bead combination was then blended at room temperature for 30 min, 1200 rpm, to permit binding of the FLAG-tagged quenchbody to the beads, and subsequently washed with 0.2 mL PBS. In MBP-binding quenchbodies, the beads had been subjected to a further wash with 0.2 mL of 0.5 M maltose dissolved in PBS to take away endogenous MBP (current within the endogenous E. coli cell-free lysate as a contaminant), as maltose competes with the nanobody for MBP-binding30. The beads had been then washed with 100 µL 1 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) in PBS for 10 min at 16°C with shaking at 1200 rpm, adopted by washing with 0.2 mL degassed PBS. Beads had been instantly mixed with 100 μL 250 μM 5(6)-carboxytetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA) maleimide with C6-linker dissolved in degassed PBS at a ultimate focus of 1% (v/v) dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), and incubated for 3 h (room temperature, 1200 rpm). Beads had been then subjected to 9 × 0.2 mL washes with PBS to take away unconjugated dye. Lastly, quenchbodies had been eluted from the beads utilizing 50 μL of 1.5 mg/mL Pierce™ 3× DYKDDDDK Peptide (ThermoFisher).
SDS-PAGE and in-gel fluorescence evaluation
Proteins had been diluted in 2× denaturing Tris-glycine pattern buffer to a ultimate focus of 63 mM Tris-HCl, 10% (v/v) glycerol, 5% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol, 2% (w/v) sodium dodecysulfate (SDS), 0.0025% (w/v) bromophenol blue, pH 6.8, and subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) at 150 V for 30 min utilizing Mini-PROTEAN TGX precast gels in a Tetra electrophoresis system full of Tris-glycine working buffer (25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, 0.1% (v/v) SDS, pH 8.3), based on the producer’s directions (BIO-RAD, Gladesville, Australia). Protein measurement was estimated utilizing Precision Plus Twin Color Protein Requirements (BIO-RAD). All gels had been stained in a single day with Instantaneous Blue (Expedeon, Cambridge, UK) and subsequently destained in MilliQ H2O in a single day earlier than being imaged on a Gel Doc XR+ Molecular Imager (BIO-RAD). In-gel TAMRA fluorescence of quenchbodies following SDS-PAGE was analysed on an Amersham Hurricane Biomolecular Imager (Cytiva), utilizing the preset acquisition settings for Cy3 imaging (excitation = 532 nm, emission filter = 570 ± 20 nm).
Pulldown binding assays
To evaluate their antigen binding, quenchbodies had been expressed as above and had been purified from the crude IVTT combination (100 μL) by combining with 12.5 μL beads/50 μL suspension of Pierce Anti-DYKD4K (FLAG) Magnetic Agarose (30 min, 1200 rpm). The crude IVTT-FLAG bead combination was then blended at room temperature for 30 min, 1200 rpm, to permit binding of the FLAG-tagged quenchbody to the beads, and subsequently mixed with 100 μL of (i) 1 μM MBP for MBP-binding quenchbodies, or (ii) 10 μM lysozyme for lysozyme-binding quenchbodies, and incubated for 30 min (room temperature, 1200 rpm). Beads had been then subjected to six ×0.2 mL washes with PBS to take away any unconjugated or non-specifically certain antigen, and at last eluted with 50 μL of 1.5 mg/mL Pierce™ 3× DYKDDDDK Peptide. The eluted quenchbody-antigen complicated obtained by FLAG-pulldown was subjected to lowering SDS-PAGE, and the impact of mutations on antigen binding was semi-quantitatively analysed by comparability to the binding of the wild-type (WT) management.
Protein:TAMRA quantification
Protein focus of TAMRA-labelled quenchbodies was quantified by A280 absorbance on a Nanodrop 2000C spectrophotometer and was corrected towards a FLAG peptide commonplace in PBS, subjected to the identical elution procedures to appropriate for background absorbance related to the FLAG peptide. Protein focus was additional calculated by together with the correction issue for TAMRA (A280 = 0.178) and assuming an extinction coefficient primarily based on the polypeptide sequence properties calculated in ExPaSy ProtParam67; (roughly ε = 47,000 cm−1 M−1 for quenchbodies). TAMRA focus of TAMRA-labelled quenchbodies was decided by additional A555 quantification, assuming an extinction coefficient of 90,000 cm−1 M−1 for TAMRA.
Fluorescence spectrophotometry plate assays
Quenchbodies had been diluted to twenty nM in PBS/0.05% (v/v) Tween-20 (PBST) within the absence or presence of 8000, 4000, 2000, 1000, 500, 250, 125, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, or 1 nM cognate antigens (lysozyme, MBP, or IL-6), or 2% (w/v) SDS with 5% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol as denaturant, and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Samples had been subsequently distributed (n = 3, 40 μL/effectively) into black 384-well Griener microplates and analysed by fluorescence spectrophotometry in a CLARIOstar microplate reader with excitation = 535 ± 20 nm and emission = 585 ± 30 nm, utilizing a dichroic filter of 557.5 nm. To match fluorescence will increase that happen within the presence of varied concentrations of antigen (“fold-sense”), all uncooked fluorescence values had been normalised as a ratio to the 0 nM quenchbody management missing any antigen or denaturant. To derive a quenchbody binding affinity, the fluorescence sign of quenchbody with 0 nM antigen was subtracted from all different samples containing antigen and the information had been fitted to an equation describing a single site-specific binding mode with Hill slope to derive an equilibrium dissociation fixed (OkD) in GraphPad Prism 9.4.0. The WT Qb-MBP was expressed and examined on three separate events, together with temporal separation between replicates, and confirmed basically an identical outcomes throughout replicates, indicating organic replicates had been redundant when finding out any of the opposite mutants within the examine.
Quenchbody library meeting
Quenchbody libraries with evolvable CDRs had been assembled utilizing oligonucleotides randomised by trimer phosphoramidite combine (TRIM) as beforehand described30, with the next modifications. CDRs 1–3 had been assembled by PCR meeting utilizing Vent polymerase (NEB), with every response consisting of 1× ThermoPol buffer, 5% (v/v) DMSO, dNTPs (0.4 mM), ahead and reverse outer primers (1 µM), random TRIM oligonucleotide (50 nM), megaprimer (25 nM), meeting primer (25 nM) and Vent polymerase (2 U), with a ultimate quantity to 100 μL. Megaprimers had been bought as 4 nmol ultramers (IDT). Random TRIM oligonucleotides had been bought both from IDT or Ella Biotech GmbH. The CDR 1 response consisted of CDR1_c random TRIM oligonucleotide, megaprimer1_c, FW2_C_rev meeting and FW1_c_for and Link1_c_rev outer primers. CDR2 reactions contained Q_CDR2_c randomised oligonucleotide, megaprimer2_c and Link1_c_for and Link2_c_rev outer primers. CDR3 reactions consisted of Q_CDR3_c randomised oligonucleotide, and Link2_c_for and FW4_c_rev outer primers. PCR meeting reactions had been: 2 min preliminary denature at 94 °C, then 30 cycles of 94 °C 30 s, 60 °C 30 s, 72 °C 30 s, then ultimate extension for five min at 72 °C. Particular person reactions had been purified on Macherey-Nagel Gel clean-up columns. DNA fragments encoding CDRs 1 and a couple of had been digested in a single day with BsaI-HFv2 and BbsI-HFv2, respectively (NEB). Reactions had been cleaned up with Macherey-Nagel Gel cleanup columns. DNA merchandise had been quantified and ligated in equimolar mixtures. The right ligation product was gel extracted earlier than PCR amplification with outer oligos FW1_c_for and Link2_c_rev. CDR1 + 2 fragment was digested with BsaI-HFv2 and CDR3 fragment with BbsI-HFv2 and ligated with T4 ligase. The right ligation product was gel extracted. BbsI restriction websites had been added to the ends of the assembled library with 8 cycles of PCR. PCR merchandise had been then digested with BbsI and ligated to an expression vector utilizing T4 ligase.
SNAP show choice
Genes coding for nanobody variants had been fused to the N-terminus of a SNAP-tag through a Glycine/Serine linker sequence, as a part of an expression cassette underneath the T7 promoter. Genes had been fused to dendrimer-like DNA buildings (DL-DNA), such that every gene displayed eight benzylguanine moieties, as described beforehand36,37. To assemble nanobody library expression cassettes, we ligated 50 ng of BbsI-digested nanobody library to 200 ng of BbsI-digested expression vector with complementary overhangs for 1 h at 16 °C. Ligation merchandise had been then amplified with “outPCR” primers, containing uracil and overhangs appropriate with Thermolabile USER II digestion/ligation (NEB). Following outPCR, DL-DNA had been assembled by simultaneous Thermolabile USER II digestion and T4 ligation to DL-DNA buildings with appropriate cohesive ends. Ligation merchandise had been confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The genes had been diluted to 125 pM in 30 µL PURExpress cell-free expression combine (NEB) containing 0.06% pluronic acid (F-127, ultimate focus) and 1 µL of every disulfide bond enhancer 1 and a couple of (NEB #E6820). We used droplet oil consisting of three M™ Novec™ HFE7500 Engineered Fluid (3 M, 7100025016), filtered with a 2 μm cellulose filter (VWR, #514-0061) and supplemented with 2% fluorinated surfactant FluoSurf neat (Emulseo, #1903) for droplet emulsification. For emulsification, 0.4 mL of droplet oil was loaded right into a 1 mL Luer Lock syringe, and the cell-free expression combination layered on high. A 1 mL syringe full of 0.8 mL of droplet oil related to a 5 µm hydrophobic membrane pumping machine equipped by Shirasu Porous Glass (SPG) (#PC05U). The oil part was pushed by means of the SPG membrane till the oil part was stage with the open facet. The syringe containing the cell-free expression combine was then related to the SPG membrane, and the combination was emulsified by repeatedly alternating the combination from one syringe to the following, for a complete of 10 speedy extrusions by means of the membrane. The emulsification course of produces monodisperse droplets with volumes within the fL vary. At ≈125 pM in PURExpress cell-free expression combine, droplet loading is 0.1 genes per droplet. The emulsion was then transferred into a brand new 1.5 mL tube and incubated at 37 °C for 4 h, then at 4 °C in a single day in an Eppendorf thermomixer. To interrupt the emulsion, extra HFE oil was eliminated by aspirating with a 23 G needle from the underside of the tube, and Perfluoro-1-Octanol (Sigma-Aldrich/Merck, #370533) was added to the tube in 1:1 ratio with the emulsion quantity. After vortexing for 15 s, the tubes had been centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 min, and the aqueous part was recovered in a clear tube. The recovered emulsion was diluted in 5 x Restoration and Binding Buffer (RBB; 40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 10 mM EDTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5% Tween-20, and 10 μM BG-mPEG12). Magnetic beads displaying recombinant IL-6 protein (BioLegend #570806) had been ready by washing 70 μL of tosyl-activated M-280 magnetic dynabeads (ThermoFisher #14203), 3× with 1 mL of PBS for five min. IL-6 binding buffer was ready by diluting 10 µg of IL-6 in PBS to a complete quantity of 75 μL. Beads had been coupled to 70 μL of IL-6 binding buffer by incubating in a single day with end-over-end mixing at 37 °C. The amount of IL-6 certain to beads was decided by absorbance spectroscopy of pre- and post-binding options on a nanodrop at A280. Following binding, beads had been washed 1× with 1 mL PBS, then with 1 mL 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.5% Tween-20 for 1 h with end-over-end mixing. Lastly, beads had been washed for 1 h in 1 mL of PBS for 1 h earlier than being washed 1× and resuspended in 20 µL 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.5% Tween-20. SNAP-display complexes had been then chosen by affinity panning on IL-6-coated beads (500 nM equal IL-6, until in any other case acknowledged), in a complete quantity of 75 µL (2 µL of answer was retained for qPCR evaluation) for 1 h at room temperature with end-over-end mixing. Alternatives had been washed 5× in 200 μL of RBB. Certain complexes had been then launched from the beads by warmth shock (20 min at 70 °C) in 15 µL of fifty mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.5% Tween-20, and the chosen genes amplified by PCR utilizing Q5® Scorching Begin polymerase (NEB) utilizing ahead primer: GATCACGAAGACATTATGGCGGATCAAGTCCAGCTGGTGGAATCG and reverse primer: GATCACGAAGACATCACCAGAACGGTAACTTGGGTGCCCTG. PCR reactions had been composed of 10 µL Q5 response buffer (NEB), 1 µL 10 mM dNTPs (NEB), 2 µL every 10 µM ahead and reverse primers, 5 µL elution, 24.5 µL nuclease-free water, 5 µL DMSO, and 0.5 µL Scorching-start Q5 excessive constancy polymerase. Biking situations had been 98 °C, 2 min, adopted by 25–30 cycles of 98 °C 30 s, 60 °C 20 s and 72 °C 30 s, with a ultimate extension of 72 °C for two min. Amplification of recovered genes was verified by agarose gel electrophoresis. Chosen genes can then be re-formatted for additional rounds of choice.
Statistics and reproducibility
Statistical analyses had been carried out utilizing GraphPad Prism 9.4.0. Binding curves had been fitted to a single site-specific binding mannequin with a Hill slope to derive equilibrium dissociation constants. Fluorescence spectrophotometry plate assays had been carried out with three technical replicates per situation, and information are reported as imply ± commonplace deviation (SD). For the MBP-targeting quenchbody (Qb-MBP), experiments had been independently repeated on three separate events with temporal separation, yielding basically an identical outcomes. Molecular dynamics simulations had been performed as six impartial replicates per system, with a complete of 72 μs for the apo and 36 μs for the antigen-bound states. For in vitro evolution experiments, two technical replicates of NGS choices had been carried out, and enrichment was assessed throughout 5 choice rounds. The place statistical significance was examined (e.g. IL-6 titration), one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s a number of comparisons was used, and significance was outlined at α = 0.05.
Reporting abstract
Additional info on analysis design is accessible within the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract linked to this text.