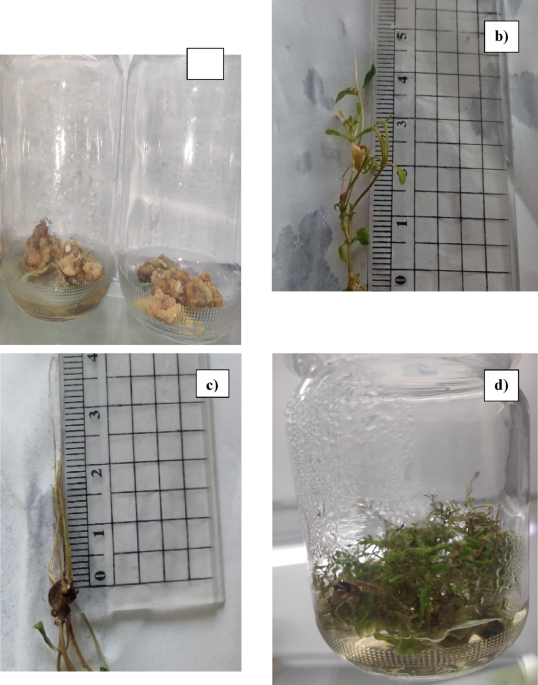
In vitro oblique regeneration and callus formation of S. rebaudiana
Callus induction is the preliminary section of oblique micropropagation within the tissue tradition method20. PGRs, like auxins and cytokinins in various concentrations, are essential for initiating callus formation, selling its progress, and enhancing manufacturing of secondary metabolites20. The sterilized explants of S. rebaudiana stem components have been positioned onto an MS medium fortified with varied focus of PGRs as follows: Kin (1, 2, and three mg/L), and BAP (1 mg/L), and NAA (1 mg/L). After 4 weeks, they have been subcultured in the identical media with the identical combos. The optimum callus formation was achieved after eight weeks of incubation utilizing fortified combos of 1 mg/L of BAP and a couple of mg/L Kin, producing a excessive share of callus capability with a most biomass of 46.5 mg as proven in Fig. 1. The obtained calli is friable and yellowish-brown in shade. Nevertheless, the bottom callus mass was 12.6 mg, fortified by 3 mg/L of n NAA with 70% callus capability. All outcomes are supplied in Desk 1.
Shoot initiation through oblique micropropagation
After 4 weeks of subculturing leaf-derived callus on MS media enriched with various concentrations of PGR reminiscent of BAP, and nutritional vitamins as Myo-Inositol, Thiamine HCl, and Pyridoxine-HCl. The outcomes indicated that MS media fortified with 1.5 mg/L BAP with 15 mg/L Myo-Inositol, 1 mg/L of Thiamine HCl and 0.1 mg/L of Pyridoxine-HCl was the best. This mix resulted within the longest shoot size (1.53 ± 0.09 cm) and the very best variety of shoots (19.8 ± 0.03). Conversely, the MS media enriched with BAP (0.5 mg/L), Myo-Inositol (5 mg/L), produced the shortest shoot size (0.26 ± 0.05 cm) and the bottom variety of shoots (7.6 ± 0.02). An in depth overview of the outcomes is offered in Desk 2.
Shoot multiplication of S. rebaudiana through oblique micropropagation
The shoot multiplication stage was achieved, after 13 weeks, by supplementing MS media with various concentrations of BAP, Myo-inositol, Thiamine HCl (mg/L), and Pyridoxine HCl, that subcultured occurring each 4 weeks. The result indicated that the MS medium enriched with BAP at 2 mg/L, and Myo-Inositol at 10 mg/L, Thiamine HCl at 1 mg/L and Pyridoxine-HCl at mg/L 0.1 was handiest, displaying the longest shoot size (2.90 ± 0.03 cm), and the very best variety of shoots (26.20 ± 0.86) as proven in Fig. 1. Conversely, the media fortified with BAP at 1 mg/L, Myo-Inositol at 5 mg/L, resulted within the shortest shoot size (0.89 ± 0.02 cm) and the bottom variety of shoots (8.60 ± 0.51). All the information are offered in Desk 3.
Root multiplication of S. rebaudiana through oblique micropropagation
To realize the rooting, well-grown shoots measuring 1–1.5 cm have been transmitted to half-strength MS medium (2.2 g) fortified with varied concentrations of IBA (0.5, 1, and a couple of mg/L), thiamine-HCl (0.5 and 1 mg/L), myo-Inositol (5 and 10 mg/L), and pyridoxine-HCl (0.1 mg/L), and cultured for 3 weeks. Probably the most appreciable end result among the many examined media was obtained by including 1 mg/L Thiamine-HCl, 10 mg/L myo-inositol and a couple of mg/L IBA to MS medium as proven in Fig. 1. Nevertheless, the bottom rooting was achieved by MS media fortified with and IBA at 0.5 mg/L and myo-inositol at 5 mg/L. Desk 4 summarizes all of the findings.
The oblique micropropagation of S. rebaudiana, (a) Induced Callus was regenerated in MS media supplemented with 1 mg/L of BAP and a couple of mg/L Kin. (b) In vitro shoot of S. rebaudiana was regenerated on MS media (3.3 mg/L) fortified by 2 mg/L BAP, and 0.1 mg/L thiamine HCl, and 10 mg/L myo-inositol through oblique micropropagation. (c) In vitro root of S. rebaudiana was regenerated on MS media (2.2 mg/L) fortified by 2 mg/L IBA, and 0.5 mg/L thiamine HCl, and 10 mg/L myo-inositol through oblique micropropagation. (d) The regenerated plant of S. rebaudiana through oblique micropropagation of 28 weeks previous.
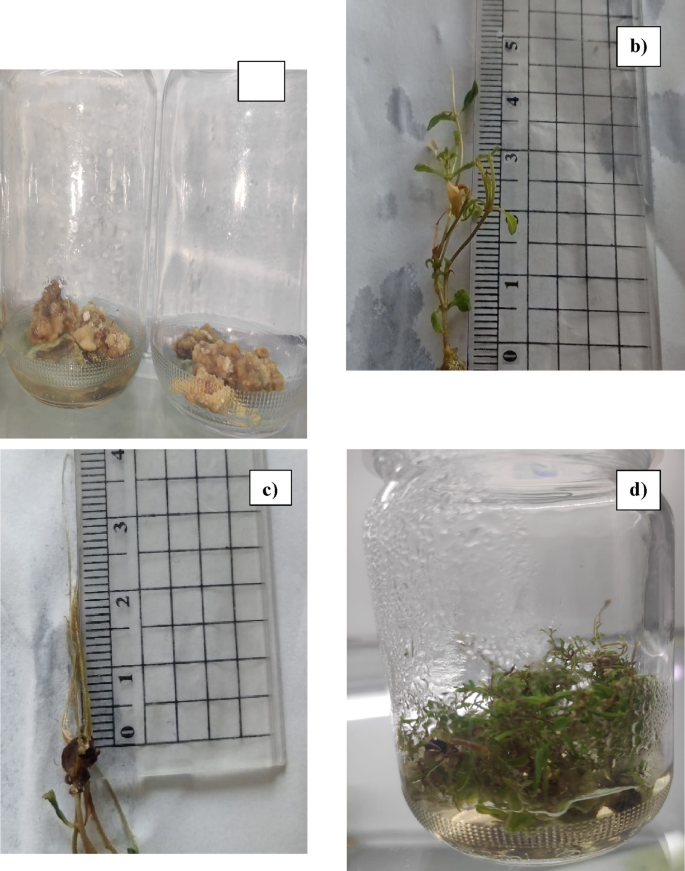
Shoot initiation of S. rebaudiana by means of direct micropropagation
The shoot initiation stage was extremely achieved, after 28 days, by including the explant to full-strength MS medium (4.4 g/L), enriched with 1.5 mg/ml BAP, and plant nutritional vitamins 0.5 mg/L Thiamine HCl, and 15 mg/L myo-Inositol. This mix confirmed the very best shoot quantity with (23.4) with the best root size with (1.9 cm). The bottom variety of shoots (11.20) with the shortest size of shoots (0.5 cm) was achieved by MS medium fortified with 0.5 mg/mL BAP, and 5 mg/L myo-Inositol with the bottom size of shoots (1.9 cm). A abstract of the outcomes is supplied in Desk 5.
Shoot multiplication for S. rebaudiana through direct micropropagation
The lateral bud segments exhibited shoot multiplication after 13 weeks in several media containing various concentrations of BAP, thiamine HCl, myo-Inositol, and pyridoxine-HCl (mg/L) with subculturing each 21 days. The variety of Shoots shaped per explant and the imply shoot size have been recorded amongst all therapies. The optimum taking pictures was obtained by including 2 mg/mL BAP, and 1 mg/L thiamine-HCl, and 10 mg/L myo-inositol in MS medium (3.3 g/L). This mix resulted within the highest shoot quantity per explant (32) and the best shoot size (1.73 cm) as proven in Fig. 2. In distinction, the bottom shoot multiplication was achieved by MS medium supplemented with 1 mg/mL BAP, and 5 mg/L myo-inositol, ensuing within the lowest variety of shoots per explant (11.60) and the shortest shoot size (1.10 cm). Desk 6 supplies a summery for all the outcomes.
Root multiplication of S. rebaudiana through direct micropropagation
Effectively-grown shoots, measuring 1.5–2 cm, have been transferred to half-strength MS medium (2.2 g/L) fortified with totally different concentrations of IBA (0.5, 1, and a couple of mg/L). Probably the most important end result among the many examined media was achieved by including 0.1 mg/L of pyridoxine-HCl, 1 mg/L of thiamine-HCl, and 10 mg/L of myo-inositol and a couple of mg/L of IBA, with subculturing for simply 21 days, as proven in Fig. 2. However, the bottom rooting was achieved with the MS medium fortified with 5 mg/L of myo-inositol and 0.5 mg/L of IBA. The outcomes are supplied in Desk 7.
Our findings on shoot induction and callus regeneration align with beforehand reported protocols in S. rebaudiana and associated medicinal species. For example, using BAP and myo-inositol for shoot proliferation has additionally been proven to considerably improve shoot numbers in S. rebaudiana beneath in vitro situations28. The very best shoot induction in our examine was achieved utilizing 1.5–2.0 mg/L BAP, which is in step with the cytokinin concentrations reported to be handiest in prior micropropagation research.
We additionally noticed variability in callus induction charges and shoot growth throughout differing types, which seemingly displays intrinsic metabolic and hormonal variations. Rodriguéz-Páez et al. (2024) reported that variations in endogenous auxin and cytokinin ranges amongst S. rebaudiana sorts affect morphogenic responses, a pattern that was evident in our examine as effectively, particularly throughout oblique micropropagation25.
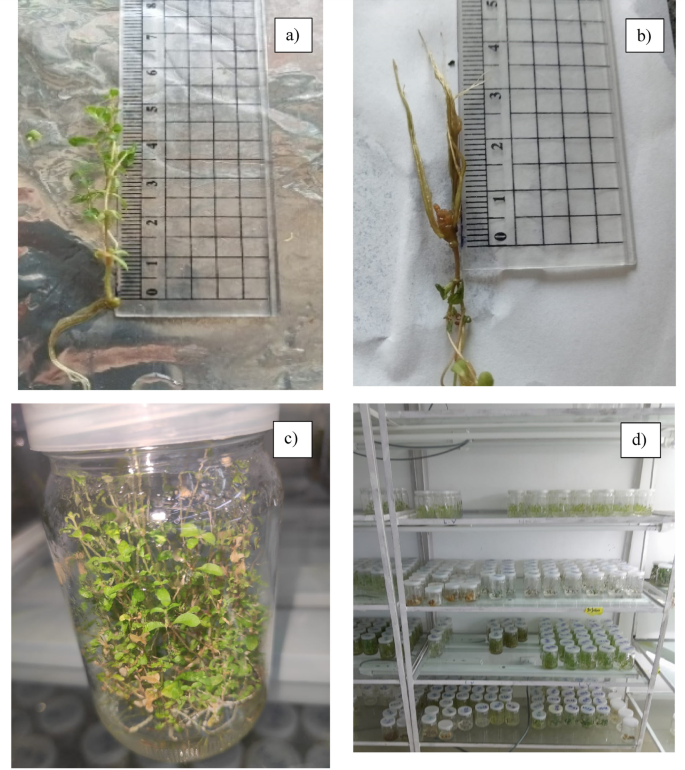
The direct micropropagation of S. rebaudiana, (a) In vitro shoot of S. rebaudiana regenerated on MS media (3.3 mg/L) fortified by 2 mg/L BAP, and 0.1 mg/L thiamine HCl, and 10 mg/L myo-inositol through direct micropropagation, (b) In vitro root of S. rebaudiana regenerated on MS media (2.2 mg/L) fortified by 2 mg/L IBA, and 0.5 mg/L thiamine HCl, and 10 mg/L myo-inositol through direct micropropagation, (c) The regenerated plant of S. rebaudiana through direct micropropagation of 20 weeks previous, (d) The regenerated S. rebaudiana through direct and oblique micropropagation.
UPLC-MS evaluation of soil grown, callus, direct and oblique micropropagation of Stevia rebaudiana
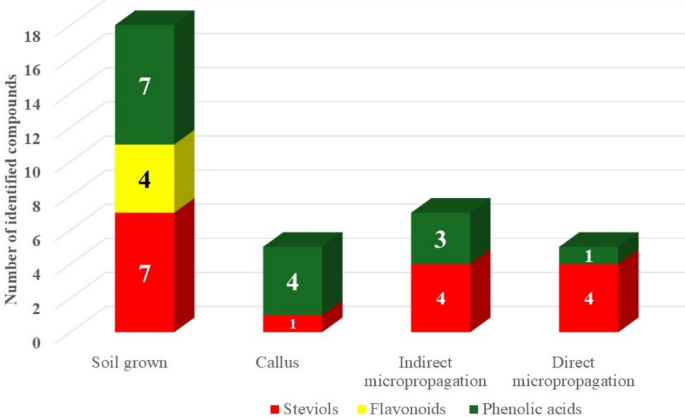
The regeneration route—direct vs. oblique—impacted not solely progress charges but in addition the buildup of secondary metabolites, notably steviol glycosides. Qualitative and quantitative UPLC-MS evaluation revealed that instantly regenerated crops exhibited whole steviol glycoside profile extra corresponding to that derived from soil-grown crops, suggesting that direct regeneration preserves metabolic constancy extra successfully than callus-mediated regeneration. This discovering helps the applying of direct micropropagation for commercial-scale manufacturing of high-glycoside-content stevia (soil-grown, RDM, RINM, and callus with whole space 35.95%, 23.87%, 8.58% and three.18% respectively), providing each time effectivity and metabolic consistency. About 18 compounds have been recognized, comprising phenolics (seven phenolic acids, and 4 flavonoids), and 7 terpenoids in all examined varieties of stevia. The variety of tentatively recognized compounds in all examined varieties of stevia are proven in Fig. 3.
Qualitative profiling
Phenolic acids
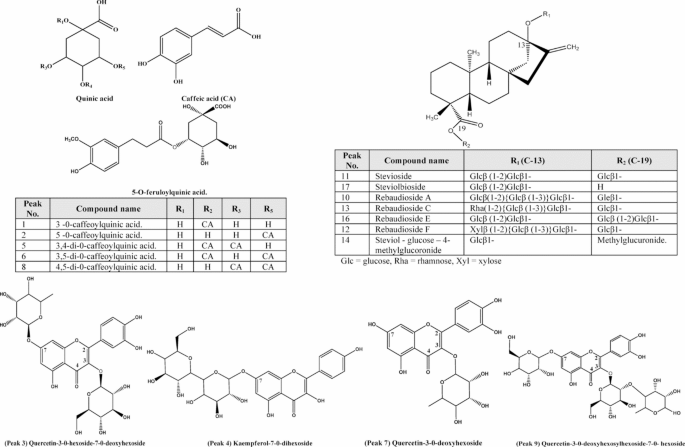
Phenolic acids are thought-about the second most prevalent subclass of phenolic compounds, that are widespread in varied components of crops and thought to be a significant human dietary part29. A number of pharmacological research have highlighted the potential of phenolic acids as free radical scavengers and their subsequent helpful impacts on human well being29reminiscent of safety towards the event of ailments like most cancers, in addition to antimicrobial, antiviral, antiallergic, antithrombotic, and anti inflammatory properties29. Caffeoylquinic acids are a phenolic acid instance with excessive scavenging exercise important antioxidant, thought-about robust metallic chelators, and displayed robust inhibitory results on lipid oxidation30. The UPLC-MS/MS evaluation led to identification of six phenolic acids. Within the 4 varieties of studied stevia Peak (6) with molecular ion peak at m/z 515 31, was detected. The bottom peak at m/z 353 corresponds to the molecular ion peak, representing the lack of a caffeoyl moiety [M-162] −. The fragment ion at m/z 191 similar to the bottom peak, represents the lack of one other caffeoyl by breakage of the bond between quinic acid and caffeoyl moiety [M-162]−. As well as, it confirmed the presence of distinctive fragments ions at m/z 173 and 155, representing the consecutive lack of water moiety [M-18]− 32. This sample of fragmentation is attribute for 3,5-isomer evaluate to different di-caffeoylquinic acids32. It might be tentatively recognized as 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid in comparison with the literature33. A number of pharmacological research report the helpful impact of the compound. It reveals a number of organic actions, together with being a big neuroprotective agent34antioxidant, anti-prostate most cancers35 and wound therapeutic exercise36. Furthermore, its antioxidant exercise is mostly secure in varied cooking strategies, making it a greater choice for utilization as a pure antioxidant37. Peak (1) is current in all studied stevia, aside from the direct micropropagated stevia, which gave molecular ion peak at m/z 353 31−. The bottom peak at m/z 191 signifies lack of caffeoyl moiety [M-162]− by cleavage of the bond between quinic acid and caffeoyl moiety. A standard fragment ion at m/z 179 with larger depth, corresponds to the lack of quinic moiety. primarily based on the literature, peak (1) was annotated as 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid32.Beforehand, reported with a potent antioxidant38 and administration of collagen-induced arthritis39. Peak (8) at m/z 515 31−, has been present in all studied stevia besides the regenerated with direct micropropagated. Fragment ion at m/z 353 corresponds to the lack of caffeoyl moiety [M-162]−. Different fragments at m/z 179 and 135 correspond to the detachment of the quinic acid moiety [M-162]− and additional lack of the moiety (CO2) from caffeoyl fragment. It displayed a base peak at m/z 173, that’s attribute for 4-acylated isomers of caffeoyl quinic acids. Earlier outcomes advised that, peak (8) is annotated as 4, 5- di-O-caffeoylquinic acid40. Peak (5) at m/z 515 31−, offered solely on soil-grown and callus, exhibited a base peak at m/z 173 which is typical of 4-acylated isomers. One other attribute fragmentation, at m/z 353 symbolize deprivation of caffeoyl moiety [M-162]− and m/z 335 with excessive depth represents the following lack of water moiety [M-18]−. With evaluating to the literature, it might be tentatively annotated as 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid36. It was reported with a varied organic exercise as, anti-prostate most cancers exercise35α-glucosidase inhibitory exercise41anti-adipogenic42anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, hypotensive, anticancer, hepatoprotective and potent antioxidant exercise43. Peak (2) with molecular ion peak at m/z 353 31, was offered solely at soil-grown stevia. It exhibited a base peak at m/z 191 signifies the quinic acid residue. One other fragment at m/z 179 with decrease depth point out elimination of quinic acid group, and subsequent fragments at m/z 161 point out lack of water moiety [M-18]−. It might be deduced that peak (2) is outlined as 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid in comparison with the literature33. Earlier studied have proven its robust anti-microbial exercise44anti-cancer45and enhancing lipid metabolism issues46. Peak (15) and (18) with molecular ion peaks at m/z 359, and 367 31− current solely on soil-grown stevia. Peak (15) confirmed a base peak at m/z 197, indicating the detachment of a hexosyl moiety [M-162]− and different fragments at m/z 182, 167, and 153 consist with the fragmentation sample of syringic acid. With Evaluating to the literature, it was acknowledged as Syringic acid-O-hexoside47. Peak (18) with base peak at m/z 191 represents removing of quinic acid moiety [M-162]− and different fragments at m/z 173 represents removing of water fragment [M-18]− 48. Primarily based on earlier knowledge it was assigned as 5- O-feruloylquinic acid49. All outcomes are summarized in Desk 8.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are probably the most considerable pure polyphenolic compounds, which current in several components of the crops organs, with a broad vary of reported organic actions50. Their consumption is said with a wide range of health-promoting advantages to the human being50. On this work all of the recognized flavonoids utilizing UPLC-MS evaluation methodology, have been detected solely in soil grown stevia. Peaks (3), (7), and (9) with molecular ion peak at m/z 609, 447, and 771 respectively, confirmed a particular fragment of quercetin aglycone at m/z 300, similar to quercetin aglycone skeleton. Different fragments at m/z 271 correspond to the detachment of (–CH2O), m/z 255 is said to the lack of a (–CH2O2) fragment, and m/z 179 produced by Retro Diels-Alder Fragmentation (RDA) breakage between (O-C2) and (C2-C3), enabling the deprivation of a (–C7H6O2) fragment (Fig. 4). The final distinctive fragment was at m/z 151, which was additionally a results of RDA cleavage, however this time, between (O-C2) and (C3–C4), adopted by the lack of (–C8H6O3) (Fig. 4). Peak (3) with molecular ion peak at m/z 462 31 confirmed that the deoxyhexose fragment was situated on the 7-O place because the detachment of a glycosyl unit on the 7-O place is extra most popular than the hexose unit was situated on the (3-O) place. From earlier outcomes, evaluating to literature it was tentatively recognized as Quercetin-3-O-hexoside-7-O-deoxyhexoside in comparison with literature51. Peaks (7) confirmed the lack of deoxyhexose [M-146]−, which when in comparison with literature it was acknowledged as Quercetin-3-O-deoxyhexoside52which beforehand reported with antiviral exercise53. Peak (9) with a fraction at m/z 609 [M-162]−, demonstrated the connection of a hexose unit at (7-O). A further lack of fragment at m/z 301 [M-308]− confirmed the exitance of a deoxy-hexosylhexose unit within the compound. Primarily based on the earlier knowledge, it was assigned as Quercetin-3-O-deoxyhexosylhexoside-7-O-hexoside52. Peak (4) with molecular ion peak at m/z 609 31, confirmed a particular fragment at m/z 447, that resembles the lack of hexose fragment. In the meantime it confirmed a lack of [M-162] – owing to the hexose moiety, producing the bottom peak at m/z 285 corresponds to Kaempferol aglycone half. Primarily based on these outcomes it may be deduced that compound (4) assigned as Kaempferol-7-O-dihexoside as in comparison with literature54. All outcomes are summarized in Desk 8.
Terpenoids
Terpenoids are a big class of naturally occurring secondary metabolites, with over 50,000 terpenoids recognized, exhibiting various pharmacological actions and varied medicinal purposes55. Greater than 30 varieties of steviol diterpenoid glycosides have been beforehand reported from S. rebudiana, which is attribute of its sweetness in comparison with pure sweeteners55. The USA Meals and Drug Administration (US-FDA) and the European Meals Security Authority (EFSA) have thought-about stevia leaf extract, with a each day dose 4 mg/kg of physique weight of steviol glycosides equivalents, to be a secure natural product8. This examine employed UPLC-MS evaluation, that led to preliminary identification of seven diterpene glycosides within the 4 stevia samples. Peak (11) with molecular ion peak at m/z 803 31− was detected in 4 varieties of the studied stevia with the diagnostic detachment of a glucose unit showing at m/z 641, because the cleavage of the weaker ester linkage between the glucose unit and the carboxyl group at (C−19) (Fig. 4). Different fragments at m/z 479, and 317 point out detachment of two glucose moieties. Primarily based on these outcomes it might be deduced that with evaluating to literature recognized as stevioside56. An important steviol glycoside is stevioside which is non-toxic, thermally secure, low-calorie pure, and is especially accountable for the sweetness of stevia with ca. 200–300 fold sweetener than sucrose57. Stevioside was reported with different physiological actions as being antihypertensive with intakes of 500 mg/day58antifibrotic59, and exhibited average tuberculostatic exercise60immune regulation61antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, and anticancer58. Peak (10) and (13) have been detected in all varieties of stevia studied besides in callus. The molecular ion peak of (peak 10) at m/z 965 31−, with distinctive fragmentation patterns at m/z 803, ensuing from the removing of a hexosyl group. Additional losses of the hexosyl items gave fragment ions at m/z 641, 479, and 317. It might be deduced that peak (10) was annotated as rebaudioside A in comparison with the literature62. Rebaudioside A is among the most necessary steviol glycoside accountable for the sweetness of stevia with ca. 200–300 occasions extra sweetener than sucrose63. It confirmed a number of organic actions as being antihyperglycemic44hepatoprotective impact64antioxidant65anti-caries66 and anti-obesity58. The presence of each stevioside and rebaudioside A within the plant is accountable for the aftertaste and ensures its efficacy as a sweetening agent11. The molecular ion peak of peak (13) at m/z 949 31− with fragmentation patterns m/z 787, and 625, ensuing from the consecutive lack of a dihexosyl moiety. One other fragmentation sample at m/z 479, resembles the removing of rhamnose moiety. With evaluating these outcomes to the literature it was annotated as rebaudioside C67. Peak (14) with at m/z 935 31−, presents in each soil-grown and direct micropropagation stevia, exhibiting fragment at m/z 687 and base peak at m/z 479, indictive of the detachment of 4-O-methylglucuronide. It implies that the 4-O-methylglucuronide was hooked up to (C−19) of the steviol aglycone, by means of the methyl group, not hydroxyl one, afterward the height at m/z 317 that signifies the removing of hexose unit on the (C-13) place. Primarily based on this data, in comparison with literature knowledge, it was annotated as Steviol glycoside containing hexose and 4-O-methylglucuronide items54. Peaks (12), (16), and (17) have been detected solely in soil-grown stevia. Peak (12) at m/z 935 31−, with fragmentation patterns at m/z 773, in accordance with the detachment of a hexosyl unit [M-162]− from (C-13), confirmed the lack of as much as two hexosyl fragments leading to peak ions at m/z 611, and 479 from (C-19) (Fig. 4). Outcomes with evaluating to literature knowledge annotated as rebaudioside F54. Peak (16) at m/z 965 31− with a base peak at m/z 641 aligned with the lack of a dihexosyl moiety [M-324]− from (C-19) linked to the carboxylic group. Extra fragment ions at m/z 479 and 317 are resulted from sequential losses of hexosyl items from (C-13) (Fig. 4). With evaluating to literature knowledge it was annotated as rebaudioside E54. Peak (17) displayed a molecular ion peak at m/z 641 31 −, with distinctive fragments 479, and 317 corresponds to the successive losses of hexosyl moieties from (C-13). When in comparison with literature knowledge, it was recognized as Steviolbioside68which was beforehand reported to have average tuberculostatic exercise60. All outcomes are summarized in Desk 8.
Quantitative profiling
Quantitative profiling of S. rebaudiana propagated through callus-induction, direct, in addition to oblique regeneration and soil-grown protocols was performed utilizing UPLC-MS/MS to enhance the qualitative identification of steviol glycoside and phenolic constituents. The evaluation was carried out by evaluating their relative peak areas of the entire ion chromatogram in every pattern, as summarized in Desk 8.
Steviol glycosides
Among the many main candy steviol glycosides recognized in S. rebaudiana, stevioside at peak 11, confirmed the very best abundance in all samples. Its best relative peak space was in RDM, adopted by soil-grown, RINM, and callus-derived samples (13.17, 11.81, 6.69, and three.18%, respectively). Equally, rebaudioside A, peak 10 revealed an space of 5.71% in RDM, which was remarkably larger than that in RINM (1.28%), in the meantime it was unobserved within the callus. Earlier research reported a variety of stevioside content material from 5 to fifteen% of dry leaf weight whereas that of rebaudioside was between 2 and 6% in a soil-grown plant69. Rebaudioside C offered extremely in soil-grown in comparison with RDM, and RINM with whole space 13.82, 4.36, and 0.61 respectively, in the meantime it was absent within the callus. Moreover, rebaudioside C and steviolbioside, peaks 13 and 17 have been considerably denoted in soil-grown and RDM samples, with rebaudioside C accounting for 13.82 and 4.36% respectively, whereas it was absent in callus and RINM samples. These yields method particularly, that of RDM samples, highlighting the shut alignment in sweeteners profiles between the direct regeneration technique and the standard cultivation methodology. Thus, it might be thought-about as a viable propagation method for pure sweetener manufacturing.
Phenolic compounds
Past sweeteners, S. rebaudiana was wealthy in a number of key phenolic acids and flavonods contributing to its medicinal prospectives. UPLC-MS/MS evaluation confirmed substantial variations within the accumulation of these compounds between varied propagation strategies. Remarkably, 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, peak 8 was probably the most considerable in callus (29.62%) and soil-grown crops with peak areas of (29.62 and 15.54%), respectively whereas it was considerably minor or absent in RINM and RDM samples. In distinction, 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, peak 6 was predominant in RINM and callus (28.57 and 13.48%, respectively), however comparatively low in soil-grown and RDM samples (2.86 and a couple of.03%, respectively). Notably, 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid, peak 1 was noticed in all samples aside from RDM, with the best amount in callus accounting for (26.04%). These outcomes have been in step with prior research, which documented excessive phenolic and flavonoid content material in soil-grown stevia and lowered accumulation in RDM70suggesting the promising efficacy of direct micropropagation method to prioritizes the biosynthesis of steviol glycosides, presumably on the expense of that some phenolic constituents.
Metabolic implications for sweetener manufacturing
Qualitative and quantitative phytochemical evaluation of 4 S. rebaudiana samples, together with callus-derived, instantly, in addition to not directly regenerated, soil-grown crops, revealed that metabolite content material diversified considerably in response to totally different propagation strategies. Earlier research have described that progress cycles, transplantation stress, and agroclimatic environments such soil composition could give rise to marked alterations within the accumulation of secondary metabolites, reminiscent of steviol glycosides, flavonoids, and phenolic acids15,71. For instance, the content material of steviol glycoside tends to lower instantly after transplantation on account of metabolic reallocation towards root institution and stress restoration nonetheless improve as soon as stevia stabilizes and re-initiate the energetic state of progress. Persistently, the flavonoid and phenolic biosynthesis may be moderated by stresses both biotic or abiotic, together with salinity, drought, and by cultivation practices reminiscent of typical vs. natural farming16. These fluctuations in metabolic pathways should be taken under consideration throughout phytochemical standardization of stevia-derived merchandise and are necessary consideration upon choosing the proper propagation methodology whether or not for medicinal worth or sweetener consequence.
Although S. rebaudiana thrives in comparatively excessive humidity and average temperatures of subtropical climates, Egypt’s arid to semi-arid environments, characterised by low relative humidity and excessive evapotranspiration charges, face agronomic challenges with respect to discipline cultivation. Remarkably, stevia is delicate to water stress, primarily throughout sprouting and early developmental phases, resulting in lowered biomass and steviol glycoside manufacturing. Nevertheless, its general water demand is markedly lesser than that of beet or sugarcane, introducing stevia as a possible sustainable various beneath Egypt’s rising water insufficiency. Upcoming research ought to prioritize methods personalized to Egypt’s agroclimatic constraints together with choosing drought-tolerant genotypes, implementing superior domestication plans, adjusting efficient irrigation buildings, and making use of controlled-environment planting. In vitro tradition, and hydroponic farming may additionally mitigate excessive humidity and temperature fluctuations. The improved regeneration protocol established by this examine, with its improved metabolite manufacturing charges, was deliberate to assist from small to large-scale stevia agriculture. This technique had the power to generate the required transplants for 1–2 hectares/cycle of stevia. Furthermore, centralized tissue tradition amenities can present scaling up, handle nationwide wants for high-quality materials, and assist Egypt’s coverage to condense sugar imports.
Multivariate knowledge evaluation of secondary metabolites recognized through UPLC-MS in Stevia rebaudiana soil grown (s), callus (C), regenerated by direct micropropagation plant (RDM), oblique micropropagation (RIDM)
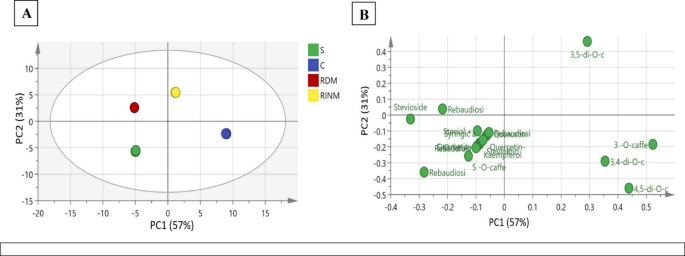
Multivariate evaluation is an efficient statistical used to research knowledge units containing a couple of variable72. It allows the creation of classifications by providing data in type of factual information72. Principal part evaluation (PCA) is among the most used exploratory instruments in multivariate evaluation. It’s employed to establish similarities and uncover hidden patterns amongst samples, notably when relationships inside the knowledge and pattern grouping continues to be unclear. The first use of PCA is to distinguish between UPLC-MS metabolite profiles of the 4 studied plant groups-derived from totally different propagation strategies; RDM, RIDM, callus-derived and soil-grown. The recorded metabolites have been primarily steviol glycosides, phenolic acids and flavonoids. PC1 accounts for 56.9%, whereas, PC2 accounts for 31.2%. The PC1/PC2 rating plot confirmed that the 4 distinct clusters are shaped and distributed throughout the 4 plot areas, similar to the 4 samples. An examination of the loading plot confirmed discrimination between callus and regenerated stevia by oblique micropropagation on the optimistic aspect versus the soil-grown and instantly micropropagated stevia. The higher proper aspect of the loading (Constructive PC1 values) means that the callus of stevia is especially enriched with 3,5 di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (Peak 6). In the meantime, the decrease proper aspect of the loading (Constructive PC1 values) for regenerated stevia by oblique micropropagation, is enriched by 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid (Peak 1), and three, 4 di-O- caffeoylquinic (Peak 5) as proven in determine (5). Quite the opposite, on the plot’s left aspect (damaging PC1 values), steviol glycosides are positioned between the higher and decrease sides of rebaudioside A (Peak 10) and stevioside (Peak 11), and between soil-grown and regenerated stevia by direct micro propagated, each of that are accountable for the sweetness of the stevia. However, on the plot’s decrease left aspect (damaging PC1 values), different steviol glycosides, reminiscent of rebaudioside (F, C, and E) peaks (12, 13, 16), steviolbioside (Peak 17), and different phenolic compounds are considerable in soil-grown stevia as proven in Fig. 5. The present outcomes from UPLC-MS coupled with PCA affirm that the direct micropropagation is intently associated to soil-grown for being to be used as a pure sweetener.
Principal part evaluation (PCA) of secondary metabolites in Stevia rebaudiana soil grown (s), callus (C), regenerated through direct micropropagation plant (RDM), and regenerated oblique micropropagation utilizing UPLC/MS-MS evaluation. (a) PCA rating plot of PC1 vs. PC2 scores, (b) The loading plot for PC1 and PC2. The metabolite clusters are positioned in a two-dimensional house at distinct areas outlined by two principal part PC1 = 57% and PC2 = 31%.