On this examine, now we have meticulously synthesized GNPs by means of two distinct strategies. The physicochemical attributes of the synthesis course of play a pivotal function within the dimension, morphology, and practical properties of those NPs25,26. Subsequently, we employed BA, recognized for its therapeutic potential in addressing neurodegenerative issues, as a conjugation agent with GNPs. Our goal was to reinforce the potential GNP efficacy in neurodegenerative remedy alongside enhancing their stability, biocompatibility, and bioavailability. The outcomes offered on this article discover the intricacies of this modern technique.
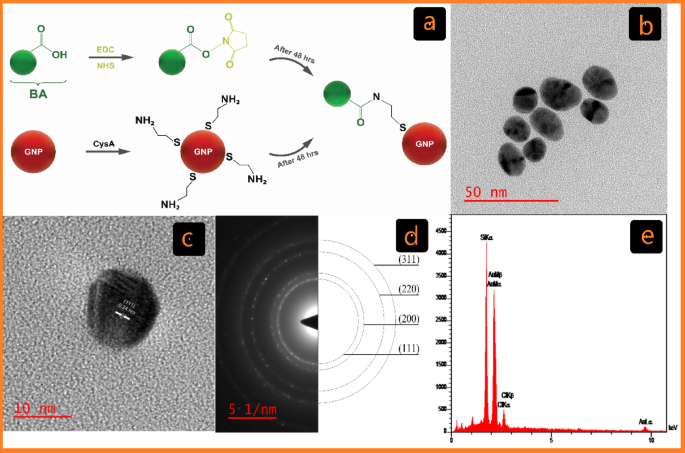
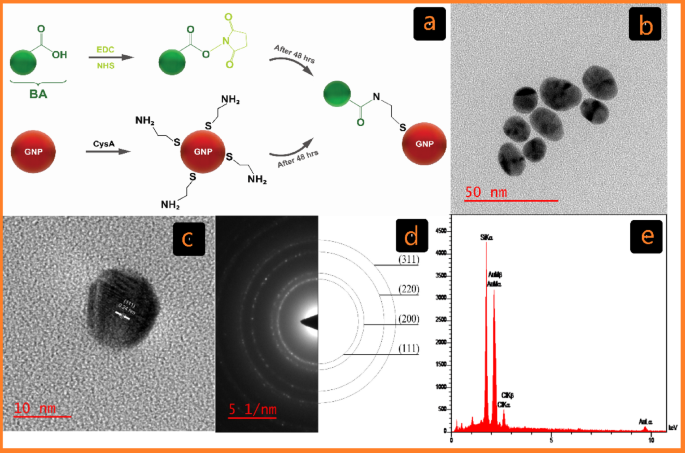
The Turkevich methodology, the most typical chemical methodology for the synthesis of GNPs in organic functions, entails the discount of tetrachloroauric acid (HAuCl4) with trisodium citrate to supply GNPs (C-G)27. Over the previous 20 years, the event of covalent conjugation strategies has considerably superior analysis in biomedicine, supplies science, and nanotechnology28. On this examine, GNPs have been conjugated with BA utilizing cysteamine (CysA) as a linker and EDC/NHS as a cross-linker to ascertain covalent bonds (Fig. 1a)28.
One other efficient methodology for producing GNPs (U-G) is photochemical synthesis29. Whereas every methodology for synthesizing GNPs has its benefits and downsides, chemical strategies are environment friendly however usually contain poisonous lowering brokers, which pose organic dangers. In distinction, photochemical synthesis is a non-toxic, eco-friendly different that’s more and more acknowledged for producing GNPs appropriate for varied organic functions. This methodology makes use of UV irradiation within the presence of Triton X-100 micelles, which play an important function in stabilizing the GNPs and influencing their morphology (U-G)30.
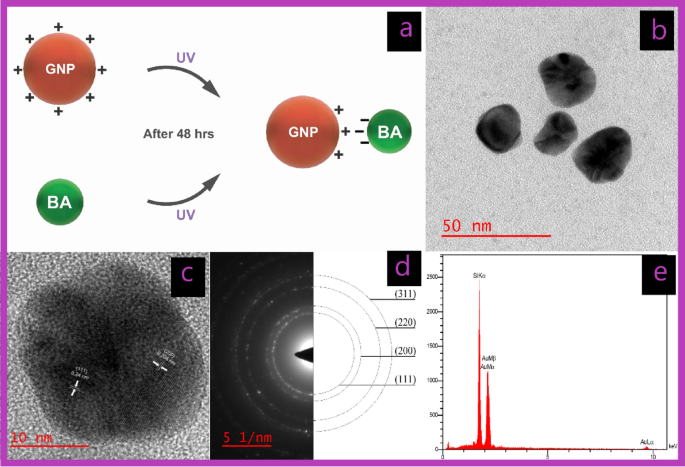
Covalent interactions result in the creation of latest molecules with distinct properties and are usually stronger than noncovalent interactions31,32. Nonetheless, for smaller drug molecules certain to NP surfaces by way of covalent bonds, these bonds should be damaged for the drug launch to operate successfully. Subsequently, for focused remedy, utilizing non-covalent interactions to create nanoconjugates could also be more practical. Such nanoconjugates are steady sufficient to succeed in the meant web site within the physique after administration33. This method ensures each stability and performance, thereby enhancing drug supply efficacy. Accordingly, on this examine, the GNPs have been additionally coated with BA utilizing noncovalent electrostatic interactions (U-G-BA) (Fig. 2a).
Characterization of C-G. (a) Schematic of the cross-linking GNP reactions with BA Functionalized by EDC/NHS in covalent conjugation (C-G-BA). (b) TEM picture displaying C-G and its related dimension distribution. (c) HR-TEM picture of C-G. (d) Chosen space electron diffraction (SAED) sample. (e) EDX evaluation of C-G by way of FE-SEM.
Fabrication and traits of C-G-BA and U-G-BA
The chemical and bodily properties of the synthesized GNPs have been characterised utilizing a mix of UV-Vis spectroscopy, DLS, ζ potential, FT-IR, and HR-TEM. The formation of GNPs was additional confirmed by EDX evaluation by way of FE-SEM. Visible inspection was used to trace the formation of C-G-BA and U-G-BA, with a change from light-yellow colour to wine pink confirming the synthesis. This colour transformation corresponds to the floor plasmon resonance (SPR) characteristic of the produced GNPs34. After three rounds of centrifugation and washing with deionized water, the GNP samples have been examined with UV–Vis spectroscopy. SPR band of C-G was noticed at 522 nm, and after conjugation with BA (C-G-BA), a redshift to 524 nm was famous. To optimize BA focus for conjugation with C-G, varied concentrations (1, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25) have been examined, with the outcomes indicating {that a} BA focus of 5 was the best. Equally, the floor plasmon band of U-G-BA exhibited a slight redshift, shifting from 530 nm to 536 nm in comparison with U-G (Determine S1a). This redshift is because of a change within the dielectric setting of the GNPs, confirming the efficient conjugation of BA to GNPs in each circumstances.
HR-TEM analyses have been carried out to guage the dimensions and morphology of the GNPs. The photographs depicted in Figs. 1b and 2b present spherical-shaped GNPs with a median diameter of 16.48 ± 2.13 and 31.23 ± 6.21 for C-G and U-G respectively. The chosen space electron diffraction (SAED) sample confirmed the crystalline nature of the GNPs, revealing shiny round rings (Figs. 1d and 2d). These rings corresponded to reflections from the usual Bragg planes (111), (200), (220), and (311), indicating that the GNPs had a cubic crystal construction (Figs. 1c and 2c)35. Vitality-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) revealed robust peaks at 2.15 keV, typical of metallic gold nanocrystallites, attributable to floor plasmon resonance (Figs. 1e and 2e)36. We’ve got beforehand demonstrated and characterised the profitable synthesis of leveraged GNPs22. Functionalization and BA conjugation have been additionally confirmed by utilizing DLA, ζ potential, and FTIR. Moreover, these NPs are negatively charged and exhibit important colloidal stability (Desk 1).
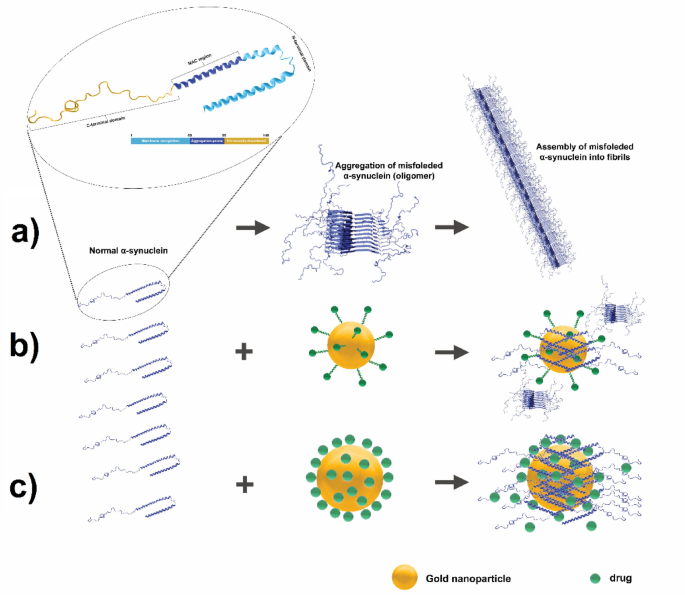
NPs hydrophobicity, dimension, and floor cost are physicochemical properties which can be recognized to have an effect on protein aggregation37,38. It’s effectively documented that floor modifications of NPs can alter protein aggregation pathways, both slowing down or accelerating aggregation, and doubtlessly even reversing preformed aggregates39,40. As an example, modifying the iron oxide NPs’ floor with leucine made them extra hydrophobic and considerably blocked mTTR’s aggregation and fibrillation pathways41. Moreover, these modifications have the potential to sequester misfolded states and even right their conformation. GNPs have been extensively studied for his or her interactions with amyloidogenic proteins, that are related to neurodegenerative ailments39. Particularly, GNPs-BA could work together with α-Syn and result in inhibiting its aggregation and fibrillation processes.
Mechanistic illustration of α-Syn aggregation and its inhibition by GNPs conjugated with BA. (a) Native α-Syn undergoes misfolding, resulting in the formation of oligomers that combination into fibrils. (b) Interplay of α-Syn with C-G-BA partially inhibits fibrillation. (c) Enhanced inhibition of α-Syn aggregation utilizing U-G-BA, successfully stopping fibril formation.
The presence of C-G-BA & U-G-BA NPs alters the aggregation kinetics of α-Syn
The kinetics of α-Syn fibril formation have been studied within the absence and presence of accelerating concentrations of naked GNPs, GNP-BA, and pure BA (Fig. 3). This course of was monitored by monitoring the attribute enhance in Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence depth42,43. Usually, amyloid aggregation kinetics are characterised by a sigmoidal curve, which features a lag part, a development part, and a remaining equilibrium part44. The affect of GNP-BA on each the nucleation (lag time) and elongation (exponential part) processes was quantified utilizing kinetic parameters derived from information becoming. Whatever the particular amyloid protein being studied, experimental information are usually fitted to this sigmoidal mannequin45 (Eq. 1):
$$:F=:frac{{F}_{remaining}-:{F}_{0}}{1+exp(-{okay}_{app}(t-:{t}_{1/2}left)proper)}$$
(1)
On this equation, F represents the fluorescence depth at time t, Fremaining denotes the utmost fluorescence depth, (:{t}_{raisebox{1ex}{$1$}!left/:!raisebox{-1ex}{$2$}proper.}) is the time required to succeed in half of the utmost fluorescence depth (similar to the midpoint between nuclei formation and fibril development), and okayapp stands for the obvious first-order aggregation fixed. The lag time is outlined as the purpose the place the tangent on the most fibrillation price intersects the abscissa, as given by46 (Eq. 2):
$$:{t}_{lag}=:{t}_{1/2}-:{2k}^{-1}$$
(2)
.
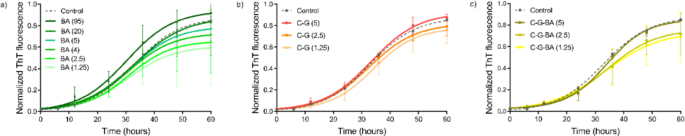
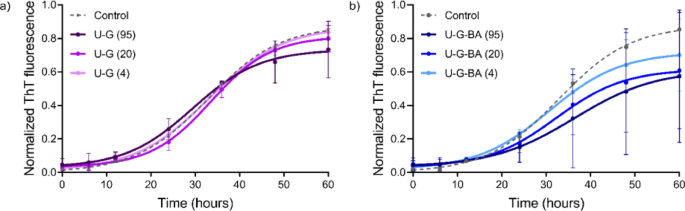
In a number of research, BA has been utilized to deal with neurodegenerative ailments at concentrations starting from 1 to 100 µM47,48. In our experiments, we investigated concentrations from 1.25 to 95 µM. In step with earlier reviews, we discovered that concentrations as much as 20 µM inhibit aggregation (Desk 2; Fig. 4). Nonetheless, at greater concentrations, BA seems to advertise fibril formation by lowering the lag time and rising the plateau part magnitude (Fig. 4a), thereby accelerating the formation of fibril seeds and shortening the lag time. This habits signifies that BA not solely impacts nucleation processes but additionally performs a task within the availability of monomers for subsequent fibril elongation and development49.
We noticed that negatively charged C-G (citrate-capped), barely accelerated the aggregation of α-Syn at concentrations starting from 1.25 to five µM, as evidenced by a slight discount within the lag time and a small enhance in plateau depth (Desk 2; Fig. 4b). These findings are in step with earlier analysis, which additionally reported that NP floor cost and focus can modulate protein aggregation pathways. This underscores the twin function of NP in both inhibiting or selling fibril formation, relying on their physicochemical properties and the setting20. It’s well-known that fibrillation is a nucleation-dependent mechanism wherein nucleation is triggered by exterior components, together with NP interactions. NPs act as catalysts that facilitate the meeting of peptides into steady fibril aggregates by rising the native focus of these peptides and selling the formation of nucleation websites50.
α-Syn consists of three structural domains: the N-terminal area (residues 1–60), the central non-amyloid part (NAC) area (residues 61–95), and the C-terminal area (residues 96–140). The N-terminal area is predominantly positively charged as a result of presence of 11 lysine residues, whereas the C-terminal area is negatively charged51. C-G seems to work together with the N-terminal area of α-Syn, doubtlessly exposing the NAC area. This publicity could lead to greater native concentrations of the NAC area, thereby facilitating aggregation20.
When finding out C-G-BA at concentrations starting from 1.25 to five µM, fibril formation declined by elevated lag time in comparison with each BA and C-G alone, indicating robust inhibition of nucleation. The speed of fibril formation additionally decreased with rising concentrations of C-G-BA (Desk 2; Fig. 4c). This means that the presence of BA slows down the expansion kinetics of fibril formation. The prolonged lag time means that C-G-BA raises the vitality barrier for nucleation extra successfully than BA or C-G alone. The interactions between the C-G-BA and α-Syn could forestall the formation of fibril nuclei by competing with monomer-monomer interactions. The plateau part depth is decrease than that of C-G, indicating diminished fibril formation (Fig. 7). These outcomes recommend that C-G-BA limits monomer addition to fibril ends20.
We noticed that positively charged U-G Triton (X-100 capped), at concentrations starting from 4 to 95 µM, decreased the aggregation of α-Syn, as indicated by a rise within the lag time, shortening the expansion part, and lowering the plateau part depth. This means that U-G additionally partially inhibits elongation by interfering with monomer addition to fibril ends. The positively charged floor of U-G possible binds to the negatively charged C-terminal area of α-Syn, stopping nucleation and fibril elongation (Desk 2; Fig. 5a). At greater concentrations, the lag time decreased, however the plateau part depth considerably decreased, suggesting that U-G exerts a concentration-dependent impact. The binding of numerous monomers to U-G at greater concentrations could lead to a depletion of free monomers, limiting their availability for elongation and lowering the general fibril content material. Earlier research have proven that positively charged NPs can bind to the C-terminus of α-Syn. The positively charged U-G are anticipated to adsorb/seize numerous α-syn monomers, making them promising candidates to forestall or delay the fibrillation course of52.
The U-G-BAs, studied at concentrations starting from 4 to 95 µM, considerably prolonged the lag part and impacted the elongation part (Desk 2; Fig. 5b), and diminished plateau depth in comparison with each U-G and BA. This inhibitory impact of U-G-BA was concentration-dependent, with essentially the most pronounced enhance within the lag part on the highest focus of 95 µM. The interactions between the U-G-BA floor and α-Syn monomers and/or oligomers would possibly create unfavorable situations for fibril development by obstructing binding websites for the addition of latest monomers53. U-G possible binds to the C-terminal area of α-Syn, whereas BA interacts with different aggregation-prone areas, such because the NAC area, stabilizing α-Syn in its monomeric type and delaying the formation of fibril nuclei. The numerous discount within the plateau depth means that U-G-BA inhibits general fibrillation by limiting each nucleation and elongation.
The bigger diameter of U-G-BA gives an elevated floor space for stronger interactions with α-Syn, enhancing its capability to dam nucleation and elongation. Its stronger electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged C-terminal area of α-Syn permit more practical sequestration of monomers and oligomers in comparison with C-G-BA. Moreover, its decrease floor passivation ensures larger binding effectivity, making U-G-BA a more practical inhibitor of fibrillation. Furthermore, the habits of U-G-BA in inhibiting fibril formation is paying homage to chaperone-like exercise. Chaperone proteins help within the correct folding of different proteins and stop misfolding and aggregation. U-G-BA, by means of its interactions and enhanced solubility, mimics this chaperone-like operate by stabilizing α-Syn in its non-fibrillar type and stopping the development of aggregation54.
Our outcomes recommend that the noticed modifications within the lag time primarily replicate modulation of nucleation, because the robust inhibition by U-G-BA and C-G-BA signifies that these methods stabilize α-Syn by interacting with aggregation-prone domains, such because the N-terminal or NAC areas. These interactions cut back the native focus of free α-Syn monomers, and the first impact is on early-stage aggregates, stopping the initiation of latest nuclei55.
To handle this challenge, ThT kinetics information have been confirmed by AFM and far-UV round dichroism (CD) analyses, which give precious info on the morphology and extent of α-syn fibrils. These findings present perception into the interactions between GNP-BA and α-Syn, suggesting the potential for concentrating on associated amyloid formations past central nervous system aggregation. Constructing on proof from research the place GNPs modulate microbial amyloid formation and biofilm improvement by means of intestine microbiota transforming, we hypothesize that GNP-BA could equally goal microbial amyloids related to intestine biofilms. Given its demonstrated inhibitory results on α-Syn aggregation by means of ThT fluorescence and AFM imaging, GNP-BA is probably going able to disrupting β-sheet-rich amyloids by means of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. This potential means that GNP-BA may play a task in managing amyloid-related processes inside the intestine, that are hypothesized to contribute to PD development by way of the gut-brain axis56,57,58.
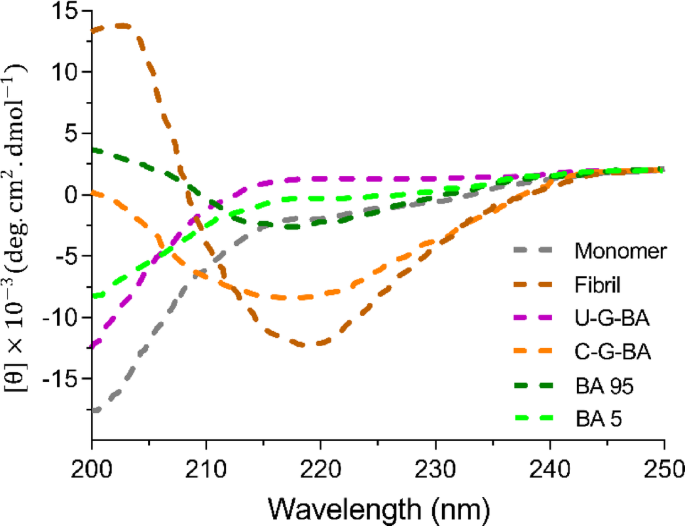
The Far-UV CD spectra of α-Syn (Fig. 6) resemble the classical spectrum of a disordered protein, whereas the β-sheet buildings of fibrils are characterised by a adverse minimal round 218 nm and a optimistic peak at 202 nm respectively59. The Far-UV CD signature grew to become extra complicated within the presence of GNP-BA, suggesting alterations within the α-syn’s secondary construction. Conversely, C-G-BA exhibited a weak band at 218 nm, indicative of diminished fibril formation and the potential emergence of different fibril morphologies. U-G-BA successfully preserved α-Syn’s native secondary construction and inhibited fibril formation, as mirrored by the absence of notable spectral modifications. Moreover, the Far-UV CD spectrum of α-Syn within the presence of BA at 5 µM instructed the protein predominantly remained monomeric, whereas, at 95 µM, a transition to aggregated states was noticed, characterised by a adverse minimal at 216 nm.
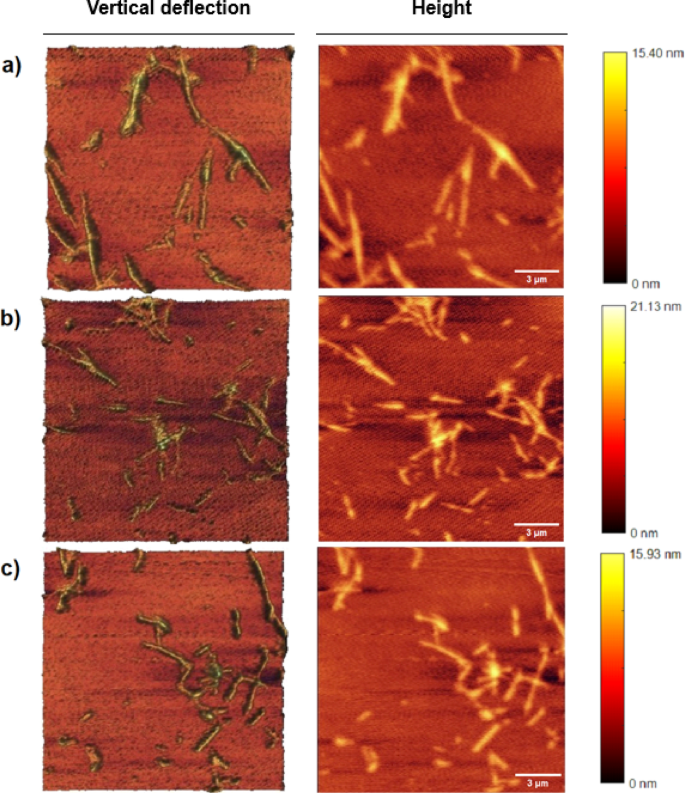
AFM has been utilized as an acceptable software to find out doable rearrangements between the protofibrils producing a fibrillar polymorphism within the mature fibril. AFM within the management pattern, which was untreated, the fibrils exhibited an elongated and intertwined morphology with heights reaching as much as 15.40 nm and common lengths of 1.2 μm. These fibrils have been uniformly structured, indicating a steady morphology with minimal peak variation (Fig. 7a). Therapy with C-G-BA led to extra complicated fibril buildings, with heights extending as much as 21.13 nm and common lengths of 0.54 µm.
The AFM photographs revealed a heterogeneous association of fibrils, together with straight and curved types with various densities amongst handled samples. This means that C-G-BA remedy induced important structural modifications, leading to a extra pronounced and diverse fibril morphology in comparison with the management. The elevated peak vary and numerous structural options indicated a extra intensive aggregation sample (Fig. 7b). In distinction, U-G-BA remedy resulted in fibrils with heights as much as 12.55 nm and common lengths of 0.39 μm. The AFM photographs confirmed elongated, thread-like buildings with much less pronounced peak variation and a extra dispersed distribution. This sample means that U-G-BA remedy is related to diminished aggregation in comparison with C-G-BA, as indicated by the smaller and fewer aggregates. The much less pronounced peak variation within the U-G-BA-treated fibrils additional helps the notion that this remedy results in a much less structured fibril community (Fig. 7c)60. U-G-BA largely determines the polymorphism of fibrils61.
Amongst a number of therapeutic approaches explored for Alzheimer’s and PD lately, efforts have been made to make use of interfering molecules as fibrillation or aggregation inhibitors. In a earlier examine of ours, tau was used as a protein mannequin for fibrillation22, permitting a direct comparability between the beforehand obtained tau information and the present α-Syn information within the presence of GNP-BA. Whereas tau and α-Syn are related to completely different neurodegenerative ailments, their aggregation mechanisms share similarities.
Analyzing the impact of GNP-BA on each α-Syn and tau, the outcomes from ThT, CD, and AFM collectively offered proof that GNP-BA has the potential to forestall fibril formation. Within the ThT assay, α-Syn exhibited a barely extended lag time within the presence of GNP-BA, indicating delayed fibrillation. AFM evaluation revealed that α-Syn fibrils have been fewer in quantity and displayed branched morphological options, whereas tau fibrils appeared shorter and had a straight morphology within the presence of GNP-BA. Far UV-CD spectrum additional supported these findings, displaying that when evaluating each proteins to their respective fibril controls, α-Syn confirmed a decrease β-sheet content material than the tau protein within the presence of GNP-BA. Maybe we are able to conclude that GNP-BA is more practical on α-Syn. A deeper understanding of those mechanisms may contribute to figuring out novel therapeutic targets for varied neurodegenerative ailments.