
Many proteins are able to spontaneously rearranging themselves inside cells to type molecular condensates—membraneless intracellular constructions fashioned by one or a number of proteins—by a course of generally known as liquid–liquid part separation (LLPS). This organic course of is vital, because it permits proteins to arrange, work together and performance in an environment friendly and controlled method inside the mobile atmosphere. When this mechanism fails, neurodegenerative ailments, cancers or developmental issues can seem.
A analysis group from the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine (IBB) of the Autonomous College of Barcelona (UAB) has now created essentially the most complete and dependable dataset of proteins collaborating in LLPS. Their proposal presents a protocol that overcomes the constraints of the algorithms developed to this point to acquire predictive fashions, by which they establish shortcomings that forestall a joint and correct evaluation of the info. The assets generated can be found on an open and on-line platform.
The examine, revealed within the journal Genome Biology, was led by Salvador Ventura, professor of the Division of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of the UAB and director of the Parc Taulí Analysis and Innovation Institute (I3PT-CERCA); Michał Burdukiewicz, Maria Zambrano researcher on the IBB and head of the bioinformatics group on the Medical College of Białystok (Poland); and Carlos Pintado Grima, researcher on the IBB and first writer of the examine.
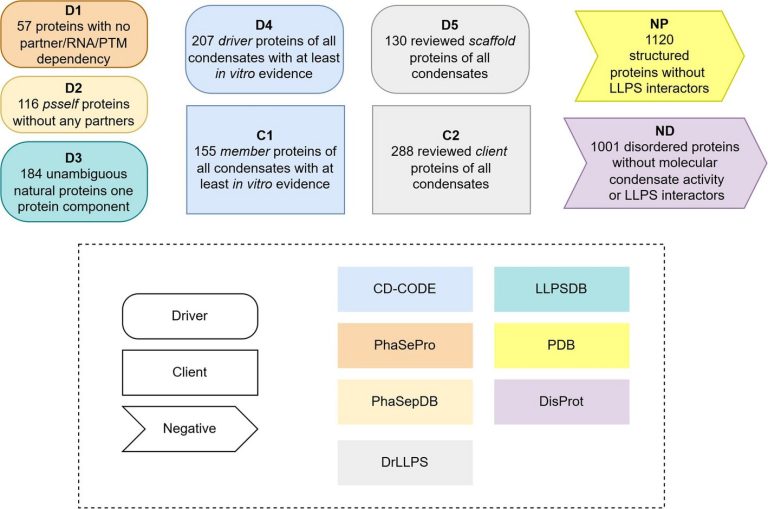
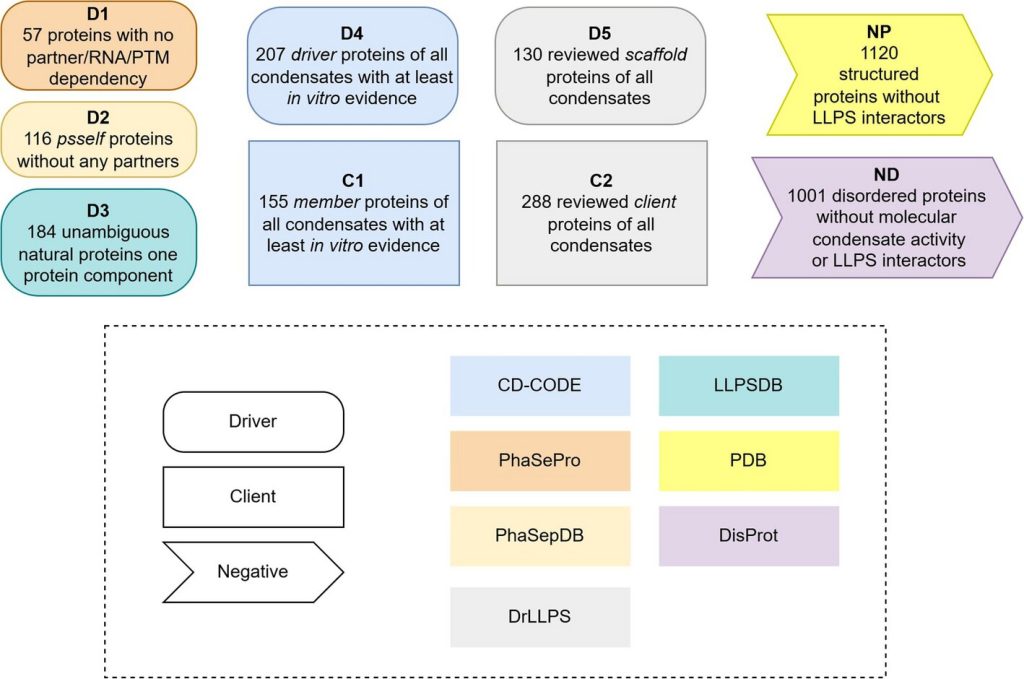
The analysis group categorized exactly the 2 foremost kinds of proteins concerned in LLPS, these that may type condensates by themselves (drivers) and people who solely type a part of them (purchasers). As well as, they developed the primary customary set of proteins that don’t take part on this course of, which incorporates each proteins with outlined constructions and disordered proteins, “a key ingredient for coaching synthetic intelligence techniques pretty and effectively,” says Ventura, who additionally coordinates the Protein Folding and Conformational Ailments analysis group on the IBB.
To validate their work, the scientists investigated particular physicochemical traits concerned in LLPS in numerous subsets of protein sequences, figuring out important variations amongst them. Furthermore, they evaluated the prediction of LLPS in sixteen present bioinformatics instruments, which is essentially the most complete comparability made to this point.
The dataset generated within the examine permits associating the function of a given protein in LLPS precisely. In complete, the researchers categorized 2,876 totally different proteins. “The info we’ve got generated was created to ensure reliability and interoperability amongst them, primarily based on standardized standards for his or her choice and categorization. Till now, we didn’t have sufficient dependable knowledge to make rigorous predictions. With this new useful resource, we open the door to the event of latest, extra exact computational instruments,” says Ventura.
Extra info:
Carlos Pintado-Grima et al, Complete protein datasets and benchmarking for liquid–liquid part separation research, Genome Biology (2025). DOI: 10.1186/s13059-025-03668-6
Offered by
Autonomous College of Barcelona
Quotation:
Extra dependable bioinformatics instruments for the examine of proteins (2025, July 18)
retrieved 20 July 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-07-reliable-bioinformatics-tools-proteins.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.