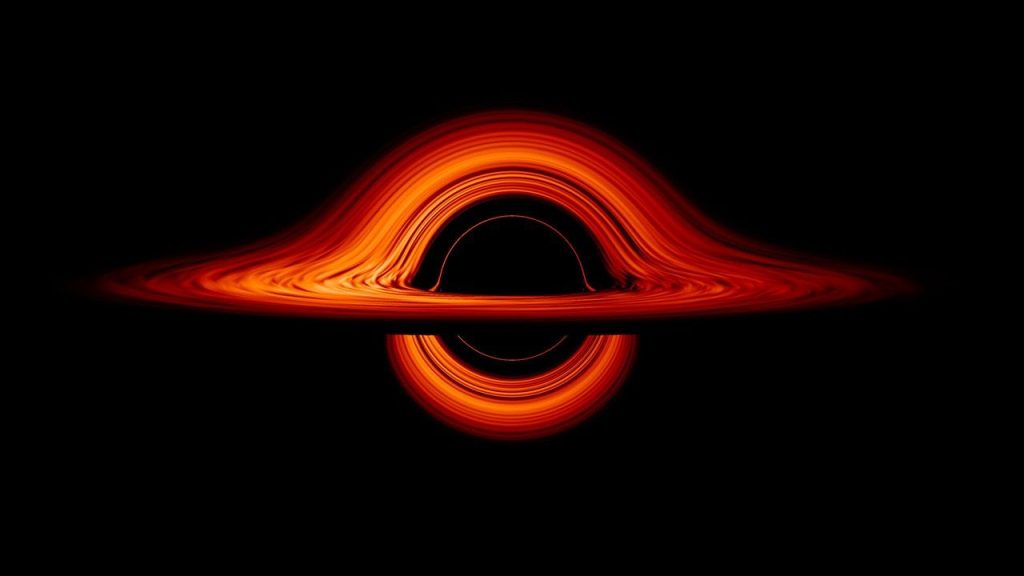
The Huge Bang is usually described because the explosive beginning of the universe—a singular second when house, time, and matter sprang into existence. However what if this was not the start in any respect? What if our universe emerged from one thing else—one thing extra acquainted and radical on the similar time?
In a brand new paper, printed in Bodily Evaluate D (full preprint right here), my colleagues and I suggest a putting various. Our calculations counsel the Huge Bang was not the beginning of every little thing, however fairly the result of a gravitational crunch or collapse that fashioned a really large black gap—adopted by a bounce inside it.
This concept, which we name the black gap universe, presents a radically totally different view of cosmic origins, but it’s grounded fully in recognized physics and observations.
In the present day’s commonplace cosmological mannequin, primarily based on the Huge Bang and cosmic inflation (the concept the early universe quickly blew up in dimension), has been remarkably profitable in explaining the construction and evolution of the universe. Nevertheless it comes at a worth: It leaves a few of the most basic questions unanswered.
For one, the Huge Bang mannequin begins with a singularity—some extent of infinite density the place the legal guidelines of physics break down. This isn’t only a technical glitch; it’s a deep theoretical downside that means we don’t actually perceive the start in any respect.
To clarify the universe’s large-scale construction, physicists launched a quick section of fast enlargement into the early universe referred to as cosmic inflation, powered by an unknown subject with unusual properties. Later, to clarify the accelerating enlargement noticed at present, they added one other “mysterious” part: darkish vitality.
Briefly, the usual mannequin of cosmology works properly—however solely by introducing new substances we have now by no means noticed straight. In the meantime, probably the most primary questions stay open: The place did every little thing come from? Why did it start this manner? And why is the universe so flat, easy, and huge?
New Mannequin
Our new mannequin tackles these questions from a special angle—by trying inward as an alternative of outward. As a substitute of beginning with an increasing universe and making an attempt to hint again the way it started, we think about what occurs when an excessively dense assortment of matter collapses underneath gravity.
It is a acquainted course of: Stars collapse into black holes, that are among the many most well-understood objects in physics. However what occurs inside a black gap, past the occasion horizon from which nothing can escape, stays a thriller.
In 1965, the British physicist Roger Penrose proved that underneath very normal situations, gravitational collapse should result in a singularity. This end result, prolonged by the late British physicist Stephen Hawking and others, underpins the concept singularities—just like the one on the Huge Bang—are unavoidable.
The thought helped win Penrose a share of the 2020 Nobel prize in physics and impressed Hawking’s international bestseller A Temporary Historical past of Time: From the Huge Bang to Black Holes. However there’s a caveat. These “singularity theorems” depend on “classical physics” which describes odd macroscopic objects. If we embody the results of quantum mechanics, which guidelines the tiny microcosmos of atoms and particles, as we should at excessive densities, the story might change.
In our new paper, we present that gravitational collapse doesn’t have to finish in a singularity. We discover a precise analytical answer—a mathematical end result with no approximations. Our math exhibits that as we strategy the potential singularity, the scale of the universe adjustments as a (hyperbolic) operate of cosmic time.
This straightforward mathematical answer describes how a collapsing cloud of matter can attain a high-density state after which bounce, rebounding outward into a brand new increasing section.
However why do Penrose’s theorems forbid such outcomes? It’s all all the way down to a rule referred to as the quantum exclusion precept, which states that no two similar particles generally known as fermions can occupy the identical quantum state (akin to angular momentum, or “spin”).
And we present that this rule prevents the particles within the collapsing matter from being squeezed indefinitely. Because of this, the collapse halts and reverses. The bounce is just not solely attainable—it’s inevitable underneath the fitting situations.
Crucially, this bounce happens fully inside the framework of normal relativity, which applies on giant scales akin to stars and galaxies, mixed with the essential rules of quantum mechanics—no unique fields, additional dimensions, or speculative physics required.
What emerges on the opposite facet of the bounce is a universe remarkably like our personal. Much more surprisingly, the rebound naturally produces the 2 separate phases of accelerated enlargement—inflation and darkish vitality—pushed not by hypothetical fields however by the physics of the bounce itself.
Testable Predictions
One of many strengths of this mannequin is that it makes testable predictions. It predicts a small however non-zero quantity of optimistic spatial curvature—which means the universe is just not precisely flat, however barely curved, just like the floor of the Earth.
That is merely a relic of the preliminary small over-density that triggered the collapse. If future observations, akin to the continued Euclid mission, verify a small optimistic curvature, it could be a powerful trace that our universe did certainly emerge from such a bounce. It additionally makes predictions concerning the present universe’s charge of enlargement, one thing that has already been verified.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying ESA’s Euclid mission on the launch pad in 2023. Picture Credit score: ESA, CC BY-SA
This mannequin does greater than repair technical issues with commonplace cosmology. It might additionally shed new mild on different deep mysteries in our understanding of the early universe—such because the origin of supermassive black holes, the character of darkish matter, or the hierarchical formation and evolution of galaxies.
These questions can be explored by future house missions akin to Arrakihs, which is able to research diffuse options akin to stellar halos (a spherical construction of stars and globular clusters surrounding galaxies) and satellite tv for pc galaxies (smaller galaxies that orbit bigger ones) which can be tough to detect with conventional telescopes from Earth and can assist us perceive darkish matter and galaxy evolution.
These phenomena may additionally be linked to relic compact objects—akin to black holes—that fashioned through the collapsing section and survived the bounce.
The black gap universe additionally presents a brand new perspective on our place within the cosmos. On this framework, our total observable universe lies inside the inside of a black gap fashioned in some bigger “mother or father” universe.
We’re not particular, not more than Earth was within the geocentric worldview that led Galileo (the astronomer who instructed the Earth revolves across the solar within the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries) to be positioned underneath home arrest.
We’re not witnessing the beginning of every little thing from nothing, however fairly the continuation of a cosmic cycle—one formed by gravity, quantum mechanics, and the deep interconnections between them.
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.