Publication Signup – Beneath Article / In Web page
“*” signifies required fields
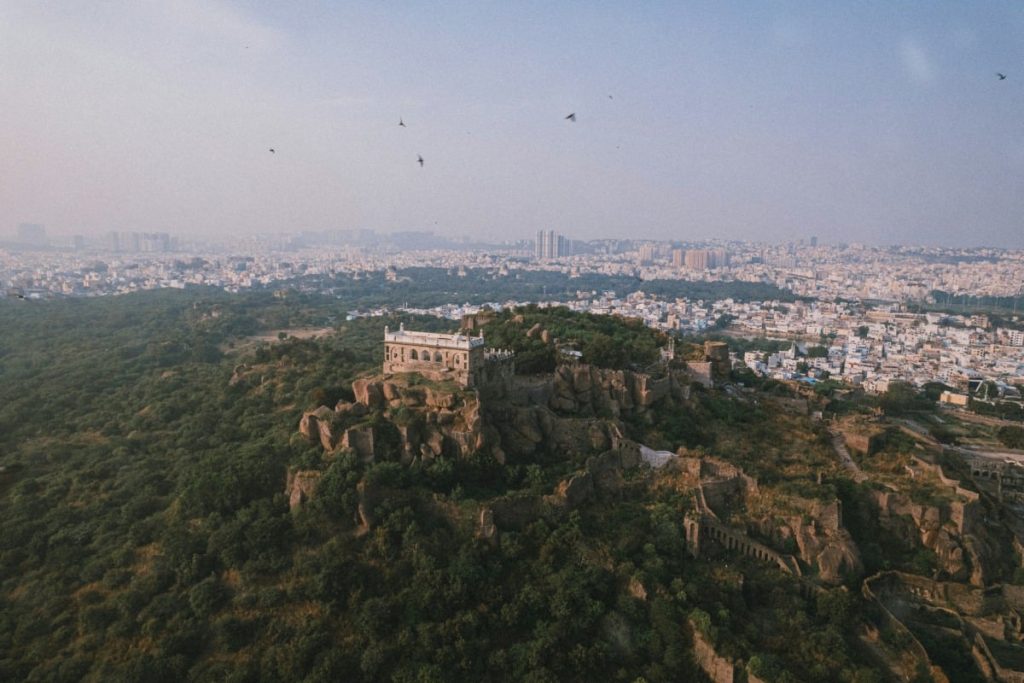
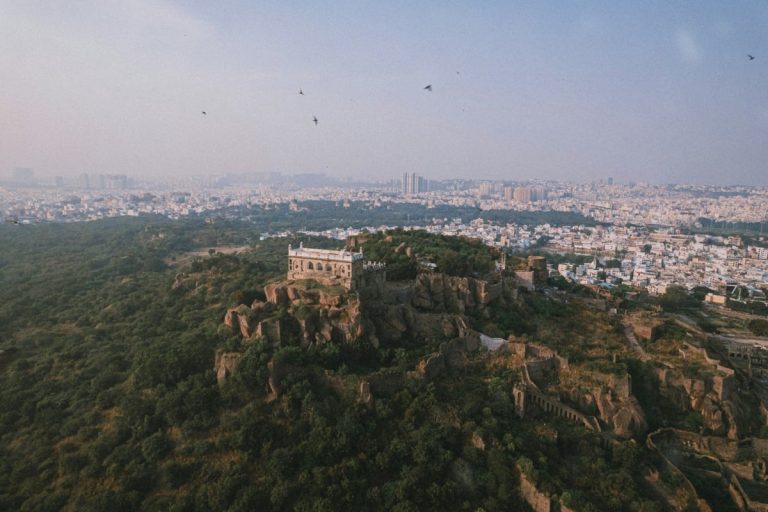
Genome Valley, the two,000-acre life sciences cluster simply outdoors Hyderabad, is on the coronary heart of Telangana’s declare to being the “vaccine capital of the world.” Knowledge present the area produces round one‑third of world vaccine doses, an output that confirms India’s repute because the pharmacy of the world. Past vaccines, Hyderabad accounts for roughly 35% of India’s pharmaceutical and bulk drug manufacturing.
But, whilst Genome Valley strengthens its standing as a producing powerhouse, a query arises: Can it transcend its identification as India’s manufacturing bedrock and emerge as a real innovation hub?
Genome Valley: Main scale-up hub and vaccine powerhouse
Whereas Genome Valley’s ambitions now attain into areas like cell and gene remedy, its basis stays firmly industrial. The current debacles between the U.S. and China following the WuXi AppTec controversy additionally despatched extra enterprise alternatives to Indian contract improvement and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) as they witnessed extra web site visits from firms following the BIOSECURE Act discussions.
The cluster’s function in international provide chains just isn’t a matter of aspiration however of scale: the area produces roughly one-third of the world’s vaccine doses. Shakthi M. Nagappan, CEO of Telangana Life Sciences, confirmed that the hub has firmly established itself because the vaccine capital of the world.
“As of mid-2025, Hyderabad provides over 11 billion vaccine doses yearly, with projections indicating an increase to 14 billion doses by the tip of the 12 months or early subsequent 12 months. This accounts for roughly 65% of India’s complete vaccine manufacturing. Vaccines manufactured in Telangana are exported to over 140 international locations, typically by way of World Well being Group (WHO)-backed applications, and supported by WHO-prequalified and U.S. Meals and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved services.”
To again this declare, Nagappan cited among the vaccine contributions of the area: Hyderabad’s Bharat Biotech’s manufacturing of India’s first indigenous COVID vaccine throughout the pandemic, or Organic E. Restricted’s partnership with Takeda to provide 50 million dengue vaccine doses per 12 months in Genome Valley.
Genome Valley, launched in 1999, was initially designed to consolidate and formalize the Telangana state’s manufacturing energy. Over the previous twenty years, it has advanced into one in every of India’s largest organized biotech and pharmaceutical clusters. In the present day, Genome Valley brings collectively greater than 200 firms from 18 international locations, using round 25,000 individuals.
Whereas international names like Novartis, GSK, and Thermo Fisher have a presence within the area, many native producers and contract improvement corporations drive the cluster’s exercise. Nagappan cited just a few contract analysis organizations (CROs) and CDMOs implanted within the hub, together with Syngene, Sai Life Sciences, Aurigene, and Cohance.
In essence, Genome Valley’s power is density. It combines firms concerned in large-scale vaccine manufacturing, lively pharmaceutical elements (API) manufacturing, and contract manufacturing right into a single area.
One other power Nagappan claims the hub presents is pace. “Genome Valley helps all the spectrum from discovery to international supply. It affords ready-to-occupy lab area, together with plug-and-play services that allow firms to turn out to be operational in three to 5 months.”
Hyderabad Pharma Metropolis, a definite initiative from Genome Valley in improvement close by, is ready to develop the area’s manufacturing focus additional, however at what price? Certainly, you will need to be aware that the Hyderabad Pharma Metropolis challenge is very controversial and sparked native protests, notably amongst farmers, concerning the environmental and societal influence of the area’s pharma manufacturing capabilities growth.
Resulting from these considerations, the challenge was rebranded into Inexperienced Pharma Metropolis and comes with zero liquid discharge insurance policies, however the real-world utility of those greener practices stays to be seen. Turning into the world’s pharmacy comes at a value that the native populations are presently paying by way of polluted water and critical well being considerations.
In 2023, Arte.television requested the query whether or not Hyderabad Pharma Metropolis was curing the world at the price of creating tomorrow’s ailments within the identify of financial development. Whereas Genome Valley was not talked about in Arte’s investigation because it operates in accordance with tighter worldwide rules and follows Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), the broader pharma industrial belt round Hyderabad was designated as answerable for critical environmental influence within the area.
Whereas Genome Valley itself operates below tighter rules, its place inside Hyderabad’s broader pharmaceutical belt inevitably hyperlinks it to wider environmental considerations affecting the area.
The profile of Genome Valley additionally raises a key strategic level: Genome Valley is above all a hub of manufacturing. Whereas manufacturing capability is indispensable to international healthcare, it doesn’t routinely translate into the type of early-stage innovation that defines hubs like Boston or Singapore. In Genome Valley, the query just isn’t whether or not the cluster can produce; it already does at a world scale, however whether or not it will possibly shift its weight in direction of discovery and the event of proprietary therapies.
From manufacturing to innovation: Is the shift actual?
Nagappan highlighted that Genome Valley was shifting away from a purely manufacturing hub to an innovation-driven ecosystem. “Within the area of drug discovery, Genome Valley hosts top-tier CROs and CDMOs akin to Syngene, Sai Life Sciences, Aurigene, and Cohance. In cell and gene remedy, Genome Valley is pioneering India’s progress with firms akin to Bharat Biotech’s vertically built-in CGT facility, Miltenyi Biotec’s CAR-T manufacturing unit, and Yapan Bio’s viral vector platform. The B-Hub, supported by the Division of Biotechnology (DBT), provides additional power by enabling organic scale-up manufacturing and workforce coaching on this rising area.”
In early 2025, Bharat Biotech launched a cell and gene remedy (CGT) and viral vector manufacturing plant at Genome Valley with a $75 million funding. The power is configured for GMP-grade manufacturing of adeno-associate virus (AAV), lentivirus, and adenovirus vectors, core parts in gene and cell therapies. The corporate studies they’re advancing a pipeline of 5 platform merchandise, together with CAR-T, CAR-NK, and off-the-shelf gene therapies, concentrating on launches by 2028.
The corporate press launch frames this transfer as a strategic pivot from vaccine manufacturing to personalised remedy, aiming to democratize CGT entry by producing human-grade vectors domestically. But, regardless of its vertical integration, the initiative stays rooted in vector manufacturing, a manufacturing-intensive process. Bharat Biotech has not disclosed any late-stage medical trials or proprietary therapeutic candidates in superior improvement, suggesting that proof of medical innovation lies extra sooner or later than the current.
Moreover, international instruments supplier Miltenyi Biotec launched India’s first CGT Middle of Excellence in Genome Valley in early 2024.
Genome Valley has made deliberate investments in cutting-edge CGT infrastructure and coaching, a departure from standard manufacturing, sure, however extra of an incremental shift than a full transformation. These platforms set up the best circumstances for biotech R&D, but the absence of ongoing medical proof factors means the cluster’s evolution into an innovation hub stays aspirational. The subsequent 24 months, when Bharat Biotech’s CGT pipeline information is predicted and startups interact with Miltenyi’s instruments, will probably be decisive in figuring out whether or not the hub has genuinely taken flight past manufacturing.
The B-Hub Nagappan talked about is one other step towards innovation. It’s a public-private accelerator operated collectively by the Authorities of Telangana, the Division of Biotechnology (DBT), and the Telangana State Industrial Infrastructure Company. Whereas the phrase “accelerator” could recommend early-stage analysis help, the B‑Hub’s services are explicitly geared towards GLP/GMP biomolecule manufacturing fairly than discovery.
It affords plug‑and‑play labs and shared gear, serving to startups and mid‑sized corporations to scale manufacturing, which is efficacious, however extra within the realm of tech switch, fairly than novel R&D. With coaching areas and accessible gear, it does deal with the hole of the dearth of hands-on manufacturing and regulatory expertise within the CGT area.
In contrast to conventional accelerators, the B‑Hub doesn’t provide seed funding, mentorship, or drug discovery help. Its mission is to assist corporations convert bench analysis into regulatory‑grade materials, not essentially to information pipeline improvement to medical levels.
So, is the shift actual? The reply won’t be sure or no, however a extra nuanced not but.
Genome Valley’s future: Between coverage push and innovation actuality
Regardless of its manufacturing scale and increasing infrastructure, Genome Valley’s transformation into a real innovation hub stays constrained. Essentially the most urgent of those constraints is expertise. “Expertise improvement is one other space of ongoing focus. Whereas Hyderabad has a powerful technical workforce, rising fields like biologics, digital well being, and regulatory science require new expertise. Upskilling applications and academic-industry partnerships are underway, however continued funding in human capital is important to satisfy future demand,” mentioned Nagappan.
The area additionally faces limitations in its broader innovation ecosystem. In comparison with biotech innovation clusters, Genome Valley lacks a deep base of enterprise capital, early-stage biotech startups, and proprietary drug discovery efforts. A lot of the exercise stays targeted on contract analysis and manufacturing providers for international corporations. Mental property technology, regulatory infrastructure for progressive merchandise, and startup funding mechanisms are nonetheless growing, components that restrict the emergence of homegrown biotech pipelines.
To handle these weaknesses, Telangana’s authorities has rolled out a sequence of coverage initiatives. The TG-iPASS system, providing streamlined approvals and regulatory help, has made it simpler for firms to determine operations. The MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) Life Sciences Coverage goals to additional strengthen the sector by way of incentives.
These measures consolidate Genome Valley’s place as a producing chief, however whether or not they may catalyze discovery and pipeline innovation at scale continues to be to be seen. Initiatives just like the B-Hub enhance scale-up capability however want extra time to foster a real biotech innovation ecosystem. The coverage focus stays targeted towards infrastructure improvement and operational effectivity, fairly than the invention, funding, and medical improvement that outline main innovation hubs globally.
Nagappan trusts that the upcoming Life Sciences Coverage 2025-2030 will catalyze new partnerships and translational analysis. “This can additional help international firms and early-stage ventures alike in establishing or increasing their footprint right here.”
Telangana’s Imaginative and prescient 2030 units bold targets: contributing to 40% of India’s goal to achieve a life science market worth of $120 billion by 2030 and creating 400,000 new jobs. Whether or not these jobs will help manufacturing traces or biotech innovation stays a important query.
Within the meantime, Genome Valley is undoubtedly a producing and scale-up powerhouse for biopharma. In the present day, it stands as a world provider, environment friendly, scalable, and more and more subtle. However its transition from a producing hub to a biotech innovator is dependent upon whether or not this infrastructure increase may be matched by the emergence of proprietary science, clinical-stage merchandise, and venture-driven firms.
In spite of everything, it’s Genome Valley’s means to help the life science worth chain that units it aside. “The continued developments sign not simply quantitative development however qualitative transformation deepening Genome Valley’s means to help the total life sciences worth chain,” mentioned Nagappan.
Then once more, the social and environmental considerations are critical. Whereas Hyderabad Pharma Metropolis and Genome Valley are distinct tasks, it does elevate the query of the fee the area is able to pay to turn out to be a necessary biopharma accomplice within the {industry}, and the way these prices could also be managed sooner or later.
Partnering 2030: FME Industries Report
Which meals, materials, and electromechanical {industry} firms are perceived most extremely by analysis institutes? Which partnering channels work greatest? What do institutes need from {industry} companions?