Agnieszka Fihel writes in regards to the high quality of multi-morbidity information and its significance in mortality analysis, based mostly on her research of Poland.
What’s multi-morbidity?
The notion of multi-morbidity turned very fashionable within the time of the COVID-19 pandemic. However what does multi-morbidity, in different phrases co-morbidity, really imply? The time period is normally used to explain the coexistence of a number of persistent ailments that will have related determinants or that consequence from the physiological strategy of particular person ageing (Anderson, 2011). An instance of somebody experiencing multi-morbidity is an overweight particular person hooked on smoking, who suffers from diabetes, hypertension, and persistent obstructive pulmonary illness.
Many well being and demography specialists acknowledge multi-morbidity as an vital and present matter. In ageing populations, a single trigger – no matter how exactly decided – now not adequately describes the morbidities accountable for a big proportion of deaths (Dorn and Moriyama, 1964: 401). Pinpointing just one reason for demise signifies that a big a part of the pathological situation isn’t thought-about within the evaluation (Israel et al., 1986). The significance of multi-morbidity has grown because of the 2020 pandemic, when it turned clear that COVID-19 is most harmful to these already affected by multi-morbidities (Mair et al., 2020).
Sadly, there are sometimes severe obstacles to investigating the subject at hand. The reason being that just a few nations make information on multi-morbidity from nationwide statistical techniques accessible to researchers and the bigger public. This limits the spectrum of study one can carry out. For instance, in demographic research, the mix of various morbidity circumstances is investigated solely in relation to mortality based mostly on info derived from the demise certificates – so-called a number of causes of demise (MCoD) research.
These paperwork embody the record of the ailments and medical circumstances that influenced the well being standing of a deceased particular person, i.e. people who contributed to worsening well being and (doubtlessly) led to demise. The principle situation behind demise is known as ‘the underlying reason for demise’, whereas all different circumstances that deteriorated well being standing are referred to as ‘contributing causes’. As an example, pancreatic most cancers could result in rising liver metastasis, diabetes on account of dysfunctionality of the pancreas and, within the closing hours, anemia. On this case, pancreatic most cancers initiated the chain of circumstances resulting in demise and constituted the underlying reason for demise, whereas all the opposite circumstances had been contributing causes.
The rise of analysis on a number of causes of demise (MCoD)
Although the primary MCoD analyses had been printed a number of many years in the past, the strategy gained reputation solely not too long ago. This was doable largely due to technological enhancements carried out in nationwide statistical techniques in regard to cause-of-death information assortment.
Consequently, as accessibility of cause-of-death information improved, novel strategies and measures of study had been proposed (Désesquelles et al., 2010; Egidi et al., 2018) and scientific networks (e.g. the A number of Causes-of-Demise Community) had been established.
Nonetheless, what is definitely the aim of MCoD analysis? Put merely, it’s to determine the hyperlinks between persistent ailments and pathologies. The principle goals are particularly:
- the investigation of the entire morbidity course of that results in demise, and
- highlighting the significance of ailments and threat elements which can be not often registered because the underlying causes, however are steadily licensed as contributing causes (e.g. bronchial asthma, diabetes or hepatitis).
The curious case of Poland
To date detailed MCoD research have been carried out for such nations as France, Italy, the UK and the US. My current analysis, to one of the best of my information, is the primary evaluation of this sort carried out in Poland.
Why is it so?
The principle motive is the comparatively low-quality of Polish cause-of-death information because of the frequent task of deaths to unknown and ill-defined causes. To make issues worse, these problematic causes signify solely half of a bigger class of so-called ‘rubbish’ codes (GCs), outlined as causes of demise that aren’t helpful in analyses of public well being and mortality.
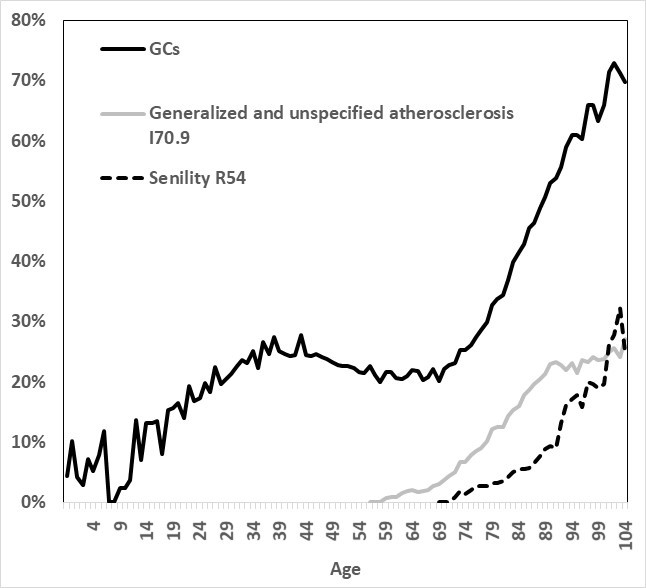
The standard of Polish information is unsatisfactory regardless of the World Well being Organisation’s (WHO) suggestions and actions carried out by public establishments as a way to enhance the standard of cause-of-death information in Poland. The share of deaths assigned to unknown and ill-defined causes has remained secure since 2000 and exceeds 6%. On the identical time the share of all GCs exceeds 20% and the image is even worse for older teams (Determine 1). Consequently, the standard of cause-of-death information is unequivocally assessed as low, and Poland is repeatedly excluded from worldwide mortality analyses carried out by the WHO.
Determine 1. Proportion of deaths on account of all Rubbish Codes and on account of chosen Rubbish Codes as underlying causes by age, Poland 2013

2013 – the 12 months with exceptionally exhaustive information
As in lots of different nations, the data on multi-morbidity circumstances in Poland are destroyed as soon as the underlying reason for demise is registered and validated. Nonetheless, the 2013 information had been an exception. For the aim of testing the automated coding system of underlying causes of demise, the scans of demise certificates in 2013 had been preserved and later made accessible for this analysis. Thus, info of all contributing causes accompanying the underlying causes could possibly be analysed on the particular person degree. This research makes use of information from:
- 387,988 everlasting Polish residents, deceased inside Polish territory in 2013;
- solely 10% demise certificates had no further MCoD talked about.
Amongst 90% demise certificates with a minimum of one MCoD, the info indicated that: 11% reported one MCoD, 61% reported two, 18% reported 3 or extra MCoD.
Don’t depend your chickens till they’ve hatched
The 2013 information provide a singular alternative to analysis the Polish context. Sadly, the informative worth of those information was comparatively low as lots of them involved ill-defined, unknown or different rubbish causes. Because of this I carried out data-quality evaluation. Logistic regression demonstrated that the likelihood of every further contributing point out that was not a rubbish code was increased when:
- demise occurred within the hospital, or
- the underlying trigger was well-defined (non-garbage) (Desk 1).
Conversely, when demise happened in dwelling, the likelihood of a further well-defined point out was virtually two occasions decrease than within the hospital. Additionally, within the occasion that heart problems was the underlying reason for demise, the possibility of every further well-defined point out was increased than for neoplasms and different (excluding exterior) causes.
Desk 1. Ordered logistic regression outcomes (Odds Ratios) for the variety of non-garbage contributing mentionsa,b,c, Poland 2013
| Variable | Variety of non-garbage contributing mentions |
| Intercourse (ref. males) | 1.073*** |
| Age | 0.999*** |
| Place of demise (ref. hospital) Different medical establishment Dwelling Different |
0.893*** 0.530*** 0.540*** |
| Certifying particular person (ref. physician based mostly on autopsy post-mortem) Physician with out post-mortem Different medical personnel |
0.879*** |
| Underlying trigger (ref. non-garbage code) Rubbish Code |
0.336*** |
| Underlying trigger (ref. cardiovascular) Neoplasms Exterior causes Different |
0.631*** 1.389*** 0.843*** |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.0509 |
| N | 387,988 |
Uncommon ailments imply high-quality information
Apparently, the common variety of non-garbage contributing codes was highest when the underlying trigger was a situation originating in:
- the perinatal interval,
- congenital malformations,
- deformations, or
- chromosomal abnormalities (Determine 2)
The above record contains comparatively uncommon circumstances. Likely, these deceased sufferers had detailed medical documentation and had been handled in extremely specialised establishments, which favour correct analysis and outline of well-defined ailments. In flip, probably the most frequent underlying causes of demise – like neoplasms and ailments of respiratory or circulatory techniques – had been not often registered with non-garbage contributing mentions. On common, out of two demise certificates with a respiratory or heart problems because the underlying trigger, just one included a non-garbage contributing code.
Determine 2. The common variety of rubbish and of non-garbage contributing mentions by underlying trigger group a, Poland 2013

Underlying versus contributing demise causes
As already talked about, the same old goal of MCoD evaluation is to show how the ailments not often registered as underlying causes contribute to the morbidity course of resulting in demise. To this finish, Désesquelles et al. (2010) proposed to calculate the age-standardised mortality charges for:
- circumstances registered as underlying reason for demise, and
- the identical circumstances talked about in demise certificates as underlying or contributing causes of demise.
The ratio of the latter to the previous is the so-called Standardized Ratio of A number of to Underlying trigger (SRMU). Every time a illness is steadily chosen because the underlying trigger however not because the contributing trigger, the SRMU is low. A SRMU equal to 1 represents a state of affairs when a illness is chosen solely because the underlying trigger; as an illustration, HIV is nearly all the time licensed because the underlying, not contributing reason for demise. The SRMU equals 2 when a illness is chosen as typically because the underlying and the contributing trigger. In flip, when a illness is never assigned because the underlying reason for demise, however typically assigned because the contributing reason for demise, which normally refers to diabetes, the SRMU is increased than 2.
As proven in Determine 2, the SRMUs in Poland turned out to be the best for the next ICD-10 chapters:
- ailments of the blood and blood-forming organs – which had been indicated virtually 17 occasions extra typically because the underlying or contributing causes than because the underlying causes solely,
- ailments of the pores and skin and subcutaneous tissue (virtually 15 occasions extra),
- ailments of the genitourinary system (5 occasions extra),
- psychological and behavioural issues (4.5 occasions extra),
- infectious and parasitic ailments (4 occasions extra).
Throughout the extra detailed teams of causes, the SRMUs are probably the most elevated for dementias (excluding Alzheimer’s; SRMU of 20), hyperplasia of prostate (19), septicaemia (10), renal failure (9), weight problems and ailments of the thyroid gland (each virtually 8). For these ailments and teams of causes, lack of info is best when the single-cause-of-death strategy is utilized. These outcomes are in line with the MCoD research obtained for different nations.
Opposite to expectations, the SRMUs are comparatively low for some ailments typical of ageing societies, equivalent to neurological issues (Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s illness), acute and persistent respiratory ailments, different infectious and parasitic ailments, senility, and a few persistent ailments, equivalent to cerebrovascular ailments and diabetes mellitus. On the identical time, some deaths on account of these ailments are hidden within the ‘different’ classes (primarily unknown or unspecified) of the ICD-10 chapters. Due to this fact, as a way to examine ailments typical of up to date populations, it’s essential not solely to concentrate on typical ailments of previous age, but in addition to determine different particular causes, equivalent to quantity depletion or vascular dementia which can be frequent morbidity circumstances present in older adults.
Permitting the correct recording of multi-morbidity circumstances advances our understanding of the interrelations between completely different ailments. This physique of analysis supplies grounds for higher, simpler, well being insurance policies devoted to sufferers with persistent ailments. As an example, the MCoD information aggregated on the nationwide degree point out the extent to which diabetes sufferers endure from hypertension and the way lethal the coexistence of those two circumstances may be. This constitutes indeniable suggestions for stakeholders to enhance therapy devoted to these affected by these circumstances.
The submit relies on the paper Investigating multiple-cause mortality in Poland by Agnieszka Fihel. The paper was printed in Studia Demograficzne, Concern 2(178), 2020.
Concerning the creator: