EXPERT technique
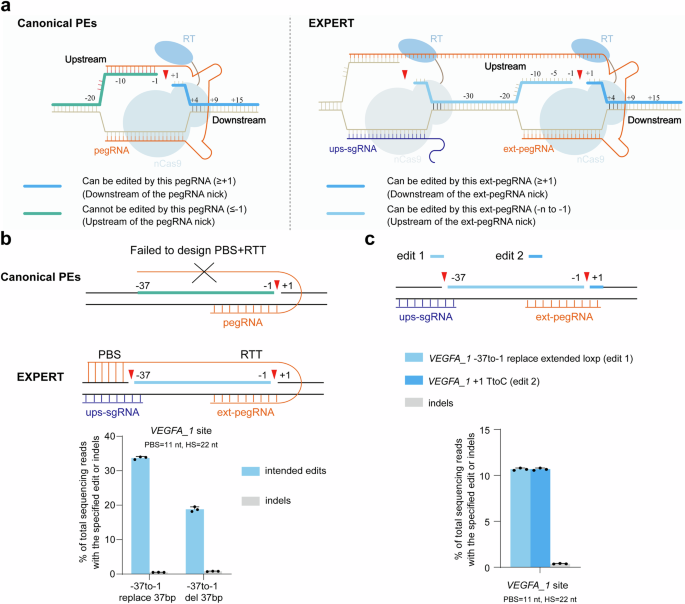
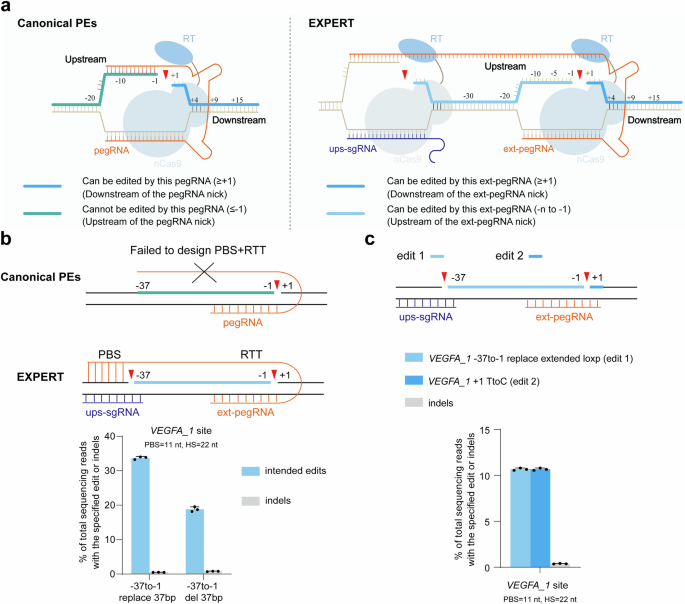
Determine 1a illustrates the design of EXPERT. The EXPERT, compared to the canonical PEs, has two variations: (1) it has an extra ups-sgRNA that targets the upstream genomic area of the pegRNA nick. In consequence, EXPERT generates two nicks on the identical strand, which discuss with as “cis nicks”. (2) it has a modified pegRNA, designated as ext-pegRNA, which has an elongated and modified 3′ extension. The ext-pegRNA contains a PBS and a reverse transcriptase template (RTT). The RTT consists of an edit sequence (ES) and a homologous sequence (HS) (Supplementary Fig. 1). The PBS on the three′ finish of the ext-pegRNA binds to the DNA strand of the three′ Flap, which is generated by the ups-sgRNA (Fig. 1a). To tell apart from the binding of canonical pegRNA, we discuss with this binding as “upstream binding”.
a Schematics of canonical PEs and EXPERT. The deep blue thick-lined space (downstream area of the pegRNA nick) represents the editable area for canonical PEs and EXPERT. However, the inexperienced thick-lined space (upstream area of the pegRNA nick) is uneditable by canonical PEs, whereas the area marked by the sunshine blue thick-lined space may be edited by EXPERT. nCas9, Cas9 nickase (H840A); RT, reverse transcriptase. b Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by EXPERT for 2 totally different edits, which canonical PEs can’t carry out. PBS, primer binding web site. RTT, reverse transcriptase template. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. c EXPERT performs simultaneous modifying on either side areas of the pegRNA nick on the VEGFA_1 web site. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. All sequencing knowledge had been collected from transfection-positive cells. Supply knowledge are supplied as a Supply Information file.
Each cis nicks and upstream binding are important for the differential modifying capability of the EXPERT in comparison with canonical PEs. We first confirmed the function of the 2 cis nicks in EXPERT, by evaluating it with two variants, EXPERT-a and EXPERT-b, which every generate just one nick utilizing both the ups-sgRNA or the ext-pegRNA, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 2a). These variants had been then used to edit the HEK4_2 locus and introduce a 40-bp sequence alternative in HEK293T cells (Supplementary Fig. 2b). As anticipated, EXPERT (with two cis nicks) achieved 6.1% effectivity, in distinction to the two.84% and beneath 0.1% efficiencies achieved by EXPERT-a and EXPERT-b, respectively. Mechanistically, we speculate that it is because EXPERT generates two cis nicks that improve the detachment of the unique single-stranded DNA fragment from the genome, thereby selling subsequent processes (Supplementary Fig. 2c). These outcomes confirmed the significance of the 2 cis nicks for the EXPERT.
We subsequent aimed to substantiate the function of the upstream binding. We constructed a number of PE2 variants (Supplementary Fig. 2a). (i) PE2: it generates one nick by utilizing the ups-sgRNA as its pegRNA. It doesn’t have the upstream binding. (ii) PE2-a: it generates one nick by utilizing the ups-sgRNA as its pegRNA. It doesn’t have the upstream binding. We included a truncated ext-pegRNA in PE2-a though it doesn’t create a 2nd nick. (iii) PE2-b: it generates two cis nicks, one utilizing the ups-sgRNA, and one other by utilizing the ext-pegRNA. PE2-b additionally doesn’t have the upstream binding. We in contrast these three PE2 variants with EXPERT, which has the upstream binding, to edit the identical HEK4_2 locus for introducing a 40-bp sequence alternative (Supplementary Fig. 2b). All these PE2 variants missing the upstream binding design, whatever the design to generate one nick or two cis nicks, achieved low environment friendly edits, starting from 0.05% to 0.37%, per the information that present PEs are inefficient for giant fragment edits. Remarkably, the effectivity achieved by EXPERT is 6.1%, 122.1-fold greater than that by PE2. These outcomes confirmed the important function of the upstream binding for the EXPERT.
One consideration with the era of two nicks in EXPERT is whether or not this may enhance the unintended indel charges on the on-target web site. Our leads to the above experiments counsel that the presence of two cis nicks doesn’t enhance the chance of indel occasions compared to the one nick system PE2. The indel price on the HEK4_2 web site for EXPERT was 0.28%, akin to that by PE2 (with 0.2% indels) (Supplementary Fig. 2b).
In abstract, by introducing an additional upstream information RNA (ups-sgRNA) to create an extra cis nick and an prolonged pegRNA (ext-pegRNA) that comprises an upstream binding sequence, we assemble a PE instrument EXPERT.
EXPERT expands the modifying vary permitting exact modifying on either side of the pegRNA nick with a minimal indel price
Canonical PEs are unable to edit the upstream area of the pegRNA nick. The EXPERT, because of the introduction of two cis nicks and using ext-pegRNA, in concept, ought to have the ability to edit that unreachable area by canonical PEs.
To validate this speculation, we carried out two edits on the VEGFA_1 web site, each situated within the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick: (i) changing a 37-bp sequence (VEGFA_1 -37to-1 exchange 37 bp); (ii) deleting a 37-bp sequence (VEGFA_1 -37to-1 del 37 bp) (Fig. 1b). The VEGFA_1 web site was chosen as a result of it gives a number of NGG sequences on the identical strand, thereby facilitating the design of ext-pegRNA and ups-sgRNA. For the primary edit, a excessive alternative effectivity at 33.7% with low indel price (0.52%) was achieved. Equally, for the second edit, the exact deletion price was excessive at 18.8% with a low indel price at 0.8%. We additionally tried a 3rd edit at this web site: (iii) VEGFA_1 -37to-1 exchange prolonged loxp and +1 TtoC, to check whether or not EXPERT permits for simultaneous modifying on either side of the ext-pegRNA nick. The outcomes confirmed that the effectivity of this simultaneous modifying on either side of the ext-pegRNA nick has reached 10.7%, with a low indel price at 0.38% (Fig. 1c).
These outcomes reveal that EXPERT has the unprecedented capability to edit upstream area of the pegRNA nick, and concurrently edit either side areas. All sorts of edits have low indel charges, which preliminarily helps the speculation that the presence of two cis nicks doesn’t elevate the incidence of indel occasions.
Results of the gap between the 2 cis nicks on the modifying effectivity of EXPERT
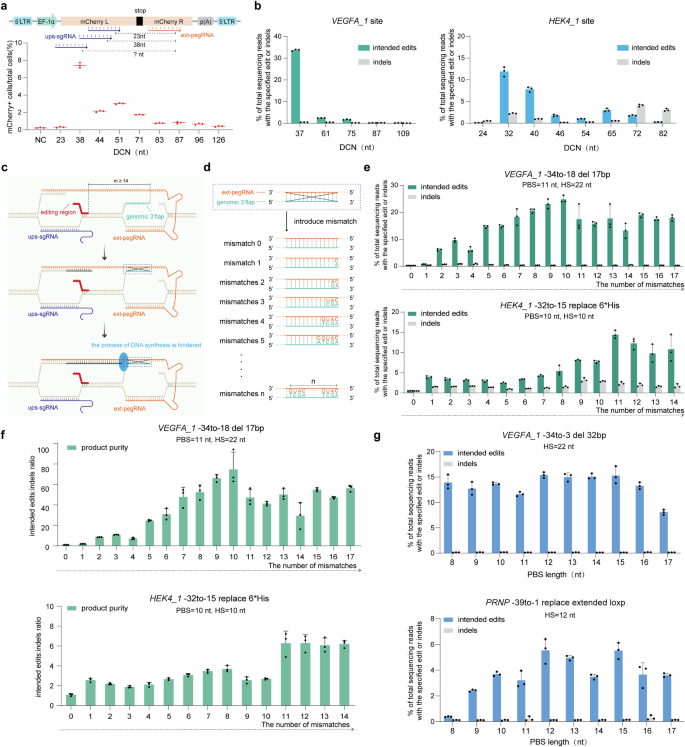
The distance between the 2 cis nicks (DCN) generated by ups-sgRNA and ext-pegRNA is a important parameter in EXPERT. To guage the influence of DCN on modifying effectivity, we utilized a 293T-reporter cell line containing a untimely TAG cease codon within the coding sequence of mCherry10, and examined EXPERT with DCNs of various sizes, starting from 23 to 126 nt. A profitable modifying on the cease codon sequence will restore the expression of mCherry sign, which is used as a proxy of profitable modifying (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. 3). The outcomes confirmed that the mCherry indicators had been detectable when the DCNs ranged from 38 to 96 nt, with extra strong indicators noticed when DCNs had been between 38 and 71 nt, and modifying efficiencies starting from 1.74% to 7.44%.
a Schematic diagram illustrating the modification of the cease codon within the 293T-reporter cell line to revive mCherry perform beneath DCNs of various sizes (high). Frequencies of edits launched by EXPERT beneath DCNs of various sizes had been quantified utilizing move cytometry (backside). Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. b Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by EXPERT beneath DCNs of various sizes had been quantified at VEGFA_1 and HEK4_1 websites. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. c Diagram of the hybridization of the three′ Flap of the unique DNA strand to complementary ext-pegRNA. The hybridization can hinder the reverse transcription means of RT enzymes, resulting in modifying failure. The daring crimson line space denotes the modifying area. “m” signifies the gap between the modifying area and ext-pegRNA nick. d The sample of introducing mismatch on ext-pegRNA area that hybridizes with the three′ Flap of the unique DNA strand. e Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by EXPERT beneath totally different numbers of mismatches on the ext-pegRNA area that hybridizes with the three′ Flap. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. f The product purity (supposed edits: indels ratio) launched by EXPERT beneath totally different numbers of mismatches on the ext-pegRNA area. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. g The influence of PBS size on modifying effectivity of EXPERT. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. All sequencing knowledge had been collected from transfection-positive cells. Supply knowledge are supplied as a Supply Information file.
We then assessed the influence of DCN on modifying effectivity by EXPERT at two endogenous loci: VEGFA_1 and HEK4_1. The outcomes confirmed that the modifying charges peaked when the DCNs had been between 32 and 40 nt (Fig. 2b). On the VEGFA_1 locus, the best modifying price of 33.7% with an indel price of 0.52% was achieved when the DCN was 37 nt lengthy. On the HEK4_1 locus, the best modifying price of 11.9% with an indel price of two.23% was achieved when the DCN was 32 nt lengthy. Curiously, at this web site (HEK4_1), a barely shorter DCN of 24 nt nearly fully abolished the supposed edits. Comparable outcomes had been noticed within the 293T-reporter cells: when a 23 nt DCN was used, the modifying price was solely 0.24%, whereas, with a 38 nt, the modifying price peaked at 7.44% (Fig. 2a). We speculate that these observations counsel {that a} DCN of 24 nt or shorter could trigger steric hindrance between two adjoining nCas9 proteins. Based mostly on this, DCNs of 24 nt or shorter must be averted in EXPERT.
These knowledge reveal that the gap between two nicks impacts the modifying effectivity of EXPERT. Our outcomes counsel utilizing a DCN between 32 and 40 nt because the beginning design.
Introducing mismatches on the ext-pegRNA improves the modifying effectivity of EXPERT
When the modifying area is away from both of the nick websites (i.e., the ext-pegRNA nick and the ups-sgRNA nick), there’s a risk for the genomic 3′ or 5′ Flap of the unique single-stranded DNA to hybridize with the complementary ext-pegRNA, which might doubtlessly hinder the synthesis by the reverse transcriptase and subsequently have an effect on the manufacturing of the newly synthesized DNA strand (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Fig. 4a). In help of this, EXPERT exhibited notably low modifying exercise when the modifying areas had been away (≥14 nt) from the ext-pegRNA nick, each on the VEGFA_1 web site (edit: VEGFA_1 -34to-18 del 17 bp, 0.3%) and the HEK4_1 web site (edit: HEK4_1 -32to-15 exchange 6*His, 0.54%) (Fig. 2e, mismatch quantity = 0). Equally, when the modifying area was away (≥14 nt) from the ups-sgRNA nick, EXPERT additionally confirmed low modifying exercise on the HEK4_1 web site (edit: HEK4_1 -18to-1 exchange 6*His, 0.28%) (Supplementary Fig. 4c, mismatch quantity = 0). Probably because of the similar cause, EXPERT additionally demonstrated poor efficiency in creating small edits within the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick (Supplementary Fig. 5a).
We thus hypothesized that introducing mismatches within the areas equivalent to DNA 3′ Flap complementarity on the ext-pegRNA will disrupt the hybridization of DNA Flap and ext-pegRNA, subsequently bettering the modifying effectivity of EXPERT.
We first examined if this technique improves the EXPERT’s modifying effectivity to the modifying areas which can be away from the ext-pegRNA nick. We launched mismatches ranging from the nucleotide on the ext-pegRNA equivalent to the primary nucleotide of the complementary DNA 3′ Flap, and examined the results of the variety of mismatches from 0 to 17 (Fig. 2nd and Supplementary Fig. 6). The outcomes demonstrated that when mismatches had been launched, as few as just one, the modifying effectivity could possibly be improved, for instance on the HEK4_1 web site from 0.54% to three.93%. The extent of enchancment was positively correlated with the variety of mismatches launched. The very best modifying effectivity was achieved with 10 or 11 mismatches at each examined websites: 24.81% on the VEGFA_1 web site and 14.43% at HEK4_1 web site (Fig. 2e). Evaluation of product purity (the ratio of supposed edits: indels) revealed that introducing mismatches enhanced product purity at each the VEGFA_1 and HEK4_1 websites (Fig. 2f).
We then examined if this technique improves the EXPERT’s modifying effectivity to the modifying areas which can be away from the ups-sgRNA nick. Following an identical technique, we launched mismatches ranging from the nucleotide on the ext-pegRNA equivalent to the primary nucleotide of the complementary DNA 5′ Flap, with the variety of mismatches various from 0 to 14 as a means to enhance EXPERT’s modifying effectivity to the modifying areas which can be away from the ups-sgRNA nick (Supplementary Fig. 4 and Supplementary Fig. 6). The outcomes once more demonstrated a constructive correlation between the modifying charges and the variety of mismatches. When three mismatches had been launched, the modifying effectivity reached ~10%. When 11 mismatches had been launched, the effectivity elevated to 12.4%, and beneath these situations, the best product purity was achieved (Supplementary Fig. 4c).
We additionally examined an alternate technique for introducing mismatches, particularly by introducing mismatches at intervals of each 3 and 5 nucleotides, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 7). The outcomes confirmed that the modifying effectivity of ext-pegRNA with such mismatches carefully resembles that noticed with ext-pegRNA containing 11 consecutive mismatches. These outcomes counsel an alternate mismatch design for ext-pegRNA to attain efficient modifying with EXPERT. Furthermore, EXPERT reveals differential unintended indel charges on the VEGFA_1 and HEK4_1 loci, probably attributable to the sequence traits of those websites or the modifying sequence. It is very important observe that incorporating applicable mismatches can improve modifying effectivity and cut back indel charges (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Fig. 4c).
Lastly, we evaluated EXPERT for introducing small edits (small insertions, small deletions and base substitutions) within the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick, with or with out the inclusion of mismatches (Supplementary Fig. 5). The outcomes demonstrated that EXPERT can carry out all these kind of small edits within the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick (Supplementary Fig. 5). Once more, introducing mismatches considerably improved modifying effectivity, according to our hypothesis that the launched mismatches cut back the homology between the ext-pegRNA and the genomic DNA 3′ Flap, thereby stopping their hybridization (Fig. 2c). However, it’s famous that, regardless of the decrease unintended on-target indel charges, the effectivity and product purity of the small edits achieved by EXPERT are typically decrease than these achieved by PE3 (Supplementary Fig. 5b).
All these outcomes reveal that the modifying effectivity of EXPERT may be improved by introducing mismatches.
Optimization of PBS size and HS Size in EXPERT
PBS performs an vital function in initiating reverse transcription and making certain environment friendly PE effectivity1,24. To evaluate whether or not the size of the PBS impacts the modifying effectivity of EXPERT, experiments had been performed at two loci: the VEGFA_1 and PRNP loci, with PBS lengths starting from 8 to 17 nt (Fig. 2g). The outcomes confirmed that PBS lengths starting from 9 to 16 nt might result in environment friendly modifying outcomes: 11.64% to fifteen.41% on the VEGFA_1 locus, and a pair of.42% to five.53% on the PRNP locus. From a sensible level, we might advocate utilizing PBS size of 12 nt as a result of at each loci this parameter led to the best modifying effectivity, and keep away from utilizing PBS shorter than 9 nt as apparently this drastically decreased the modifying price in a single examined locus.
Subsequently, we performed an investigation to find out the optimum size of HS. Evaluation of the modifying effectivity throughout totally different HS lengths revealed that efficient modifying could possibly be achieved with HS lengths starting from 12 to 22 nt (Supplementary Fig. 8). When the HS size is shorter than 16 nt, just one locus reveals an modifying effectivity larger than 6% (1 out of 12 or 8%). In distinction, when the HS size is 16 nt or longer, six loci present an modifying effectivity exceeding 6% (6 out of seven or 86%) (Supplementary Fig. 8). Due to this fact, we advocate an HS size of 16 nt or longer as the start line in EXPERT design.
Use of a Helper gRNA additional improves EXPERT for the insertion and alternative of huge DNA fragments on the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick
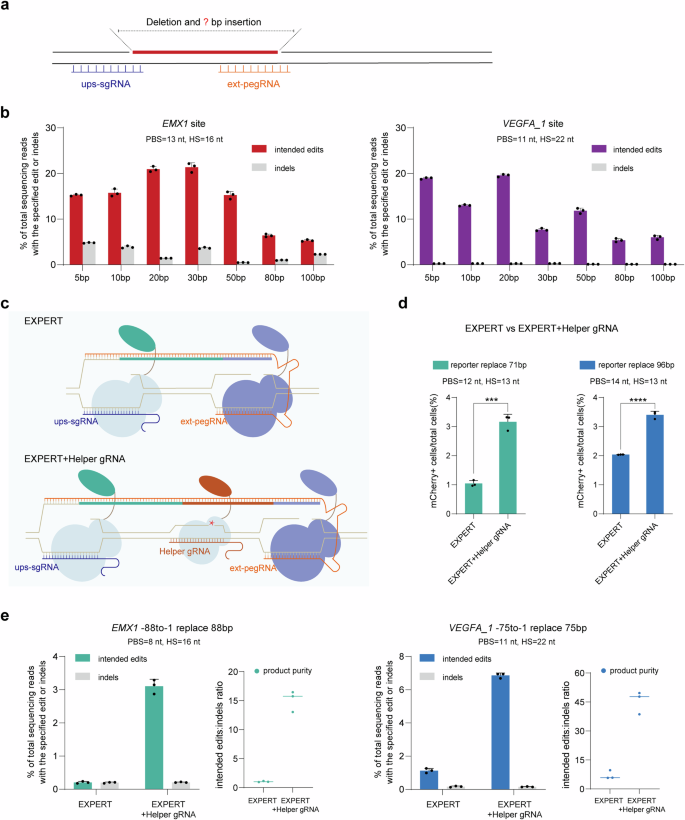
Subsequent, we investigated the capability of EXPERT to insert DNA fragments of various sizes (5, 10, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100 bp) on the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick (Fig. 3a, b). We examined these two loci: EMX1 and VEGFA_1. In each websites, larger than 10% modifying charges had been achieved when the lengths of the insertion fragment had been 50 bp. Nevertheless, it’s clear that the charges sharply dropped when the insertion measurement was massive (e.g., 80 and 100 bp), though larger than 5% insertion charges of the 100 bp fragment had been nonetheless achieved at each websites (Fig. 3b).
a Schematic diagram for deletion of the sequence between two nicks and insertion of fragments of various lengths. b Frequencies of fragment insertions of various lengths (5, 10, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100 bp) and indels launched by EXPERT on the EMX1 and VEGFA_1 websites, respectively. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. c Schematics of EXPERT and EXPERT + Helper gRNA. Compared to EXPERT, EXPERT + Helper gRNA incorporates an extra sgRNA within the center area between the ups-sgRNA and ext-pegRNA, known as the Helper gRNA. d Frequencies of edits launched by EXPERT and EXPERT + Helper gRNA had been quantified utilizing move cytometry. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. The P worth was calculated utilizing a two-tailed t-test, and no changes had been made for a number of comparisons. Preporter exchange 71 bp = 0.0002, Preporter exchange 96 bp = 0.00005; ***P P e Frequencies of supposed edits, indels, and product purity launched by EXPERT and EXPERT + Helper gRNA. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. All sequencing knowledge had been collected from transfection-positive cells. Supply knowledge are supplied as a Supply Information file.
These outcomes point out that EXPERT is able to inserting massive DNA fragments (as much as 100 bp) on the upstream area of the ext-pegRNA nick, however the effectivity stays to be improved. To handle this, we included an additional gRNA, positioned between the ups-sgRNA and ext-pegRNA, which we discuss with because the Helper gRNA (Fig. 3c). We cause that this Helper gRNA would direct the nCas9-RT to create a 3rd cis nick, and recruit an extra nCas9-RT enzyme between the unique two nicks, thereby selling the detachment of the unique DNA strand and growing the general reverse transcription.
We examined this design within the 293T-reporter cell line. The addition of the Helper gRNA to the system resulted in a 3-fold enchancment for a 71-bp alternative edit and a 1.7-fold enchancment for a 96-bp alternative edit (Fig. 3d). This was additional confirmed at two endogenous websites: (i) an 88-bp alternative on the EMX1 web site; and (ii) a 75-bp alternative on the VEGFA_1 web site (Fig. 3e). The alternative effectivity on the EMX1 locus elevated from 0.21% to three.1%, a 15-fold enchancment. Likewise, on the VEGFA_1 locus, the effectivity elevated 6.1-fold from 1.13% to six.86%. In all circumstances, the indel charges had been at low ranges starting from 0.15% to 0.2%, additional indicating that introducing nicks on the identical DNA strand doesn’t elevate the chance of producing DSBs.
These findings reveal that together with a Helper gRNA within the EXPERT improves its capability for giant fragment alternative modifying with out elevating the indel price.
EXPERT enhances the product purity of prime modifying for giant fragments
The usage of the ups-sgRNA within the EXPERT raises the query of whether or not it introduces greater indel charges. To systematically consider this, we in contrast EXPERT with the consultant single-pegRNA system PE2 and the two-pegRNA system twinPE.
Comparability of EXPERT with PE2
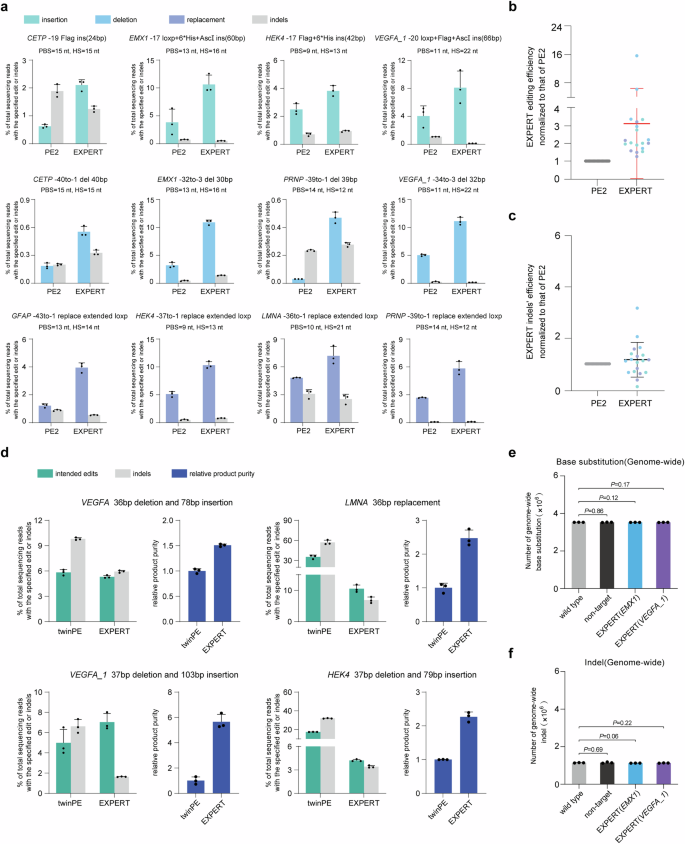
We first in contrast the modifying end result and the indel charges between EXPERT and the single-pegRNA system PE2, each of which induce nicks on a single DNA strand. The ups-sgRNA was used because the pegRNA for PE2. We performed comparative experiments between EXPERT and PE2 in 19 totally different edits (together with insertions, deletions, and replacements) at 9 loci. Detailed data of particular edits is proven in Fig. 4a and supplementary Fig. 9.
a Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by PE2 and EXPERT at a number of loci. Extra mismatches had been launched within the insertion-type edits. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. b Statistical evaluation of normalized modifying frequencies, setting the frequencies induced by PE2 as 1. n = 19 modifying from impartial experiments proven in (a) and supplementary Fig. 9. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. c Statistical evaluation of normalized frequencies of indels, setting the frequencies induced by PE2 as 1. n = 19 modifying from impartial experiments proven in (a) and supplementary Fig. 9. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. d Frequencies of supposed edits, indels, and relative product purity launched by twinPE and EXPERT at totally different loci. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. e Numbers of genome-wide base substitutions. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. The P worth was calculated utilizing a two-tailed t-test, and no changes had been made for a number of comparisons. f Numbers of genome-wide indels. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. The P worth was calculated utilizing a two-tailed t-test, and no changes had been made for a number of comparisons. All sequencing knowledge had been collected from transfection-positive cells. Supply knowledge are supplied as a Supply Information file.
The outcomes demonstrated an general enchancment within the modifying effectivity by EXPERT over that of PE2 when modifying massive fragments (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Fig. 9). For insertion edits spanning from 24 to 66 bp, EXPERT achieved 1.5 to three.4-fold greater modifying effectivity than PE2 (Supplementary Fig. 10). For deletions edits spanning from 30 to 43 bp, the development by EXPERT over PE2 ranged from 1.7 to fifteen.7-fold (Supplementary Fig. 10). For equidistant base replacements edits starting from 34 to 43 bp, the development by EXPERT over PE2 is between 1.3 to three.2-fold (Supplementary Fig. 10). The general efficiency, counting these kind of edits in all loci, is 1.3 to fifteen.7-fold higher by EXPERT than that by PE2, with a mean enchancment of three.12-fold (Fig. 4b). No variations of on-target indel charges had been noticed between EXPERT and PE2 edited cells (Fig. 4c).
The above outcomes point out that the EXPERT technique enhances the modifying effectivity of PE2 for giant fragment edits with out growing the on-target indel charges.
Comparability of EXPERT with twinPE
We subsequent in contrast EXPERT with one two-pegRNA system twinPE. EXPERT induces each nicks on the identical DNA strand (i.e., cis nicks), whereas the twinPE induces one nick on every strand (known as trans nicks). We speculate that trans nicks, compared to cis nicks, enhance the chance of DNA DSBs and subsequent indels. To validate this hypothesis, we performed comparative experiments between EXPERT and twinPE at 4 totally different loci. Briefly, they’re: (i) VEGFA 36 bp deletion and 78 bp insertion, (ii) LMNA 36 bp alternative, (iii) VEGFA_1 37 bp deletion and 103 bp insertion, (iv) HEK4 37 bp deletion and 79 bp insertion. The twinPE pegRNA pairs used for every locus had been chosen after a pre-screening course of (Supplementary Fig. 11).
Our findings reveal diverse however comparable modifying efficiencies between these two methods: EXPERT confirmed greater effectivity on the VEGFA_1 locus, whereas twinPE outperformed EXPERT on the LMNA and HEK4 loci, and each methods exhibited comparable efficiency on the VEGFA locus (Fig. 4d). Importantly, purity evaluation demonstrated that EXPERT achieved greater purity in all edits, with will increase starting from 1.5 to five.7-fold in comparison with twinPE (Fig. 4d). It must be famous that though a pre-screening course of for twinPE pegRNA pairs has been performed, a extra thorough screening (together with extra pegRNA pairs, various PBS lengths, and totally different combos) will likely be important sooner or later to allow a extra complete comparability of the efficiency between EXPERT and twinPE.
We additionally need to level out that in contrast to the two-pegRNA methods which require two separate PAM sequences (NGG) on each DNA strands, the EXPERT solely wants PAM sequences on one strand, which permits EXPERT to focus on extra areas. Such comparability experiment can’t be performed as a result of these areas are solely targetable by EXPERT however not by twinPE or any two-pegRNA methods.
Low genomic off-target occasions by EXPERT
Subsequent, we evaluated the gRNA (ext-pegRNA or ups-sgRNA)-independent and gRNA-dependent off-target (OT) results of EXPERT utilizing whole-genome sequencing (WGS). The EXPERT-expressing plasmids carrying three sorts of concentrating on RNAs had been used: (i) with non-target gRNAs because the automobile management; (ii) concentrating on the EMX1 locus (EMX1 -17 loxp + 6 * His + AscI ins); and (iii) concentrating on the VEGFA_1 locus (VEGFA_1 -34to-3 del 32 bp). The plasmids had been transfected into HEK293T cells, respectively. The genomic DNA of transfected cells of those teams, in addition to these of the non-transfected wild-type cells, had been subjected to WGS.
We first decided whether or not EXPERT induces gRNA-independent OT mutations genome-wide. The evaluation confirmed that there was no important distinction within the degree of genome-wide base substitutions and indels among the many 4 teams of cells, indicating that EXPERT doesn’t induce whole-genome gRNA-independent OT results (Fig. 4e, f).
Subsequent, we evaluated the gRNA-dependent OT results of EXPERT. We decided the on-target modifying efficiencies of EXPERT with amplicon sequencing and assessed the frequencies of indels in potential OT websites by WGS. The outcomes confirmed that the frequencies of indels for all predicted potential OT websites are beneath 0.1% (Supplementary Fig. 12).
These outcomes reveal that each gRNA-independent and gRNA-dependent OT results by EXPERT are minimal.
The EXPERT technique is suitable with totally different PE methods
In concept, using ups-gRNA and ext-pegRNA is suitable with all PE methods so long as they’re based mostly on nicking the goal DNA.
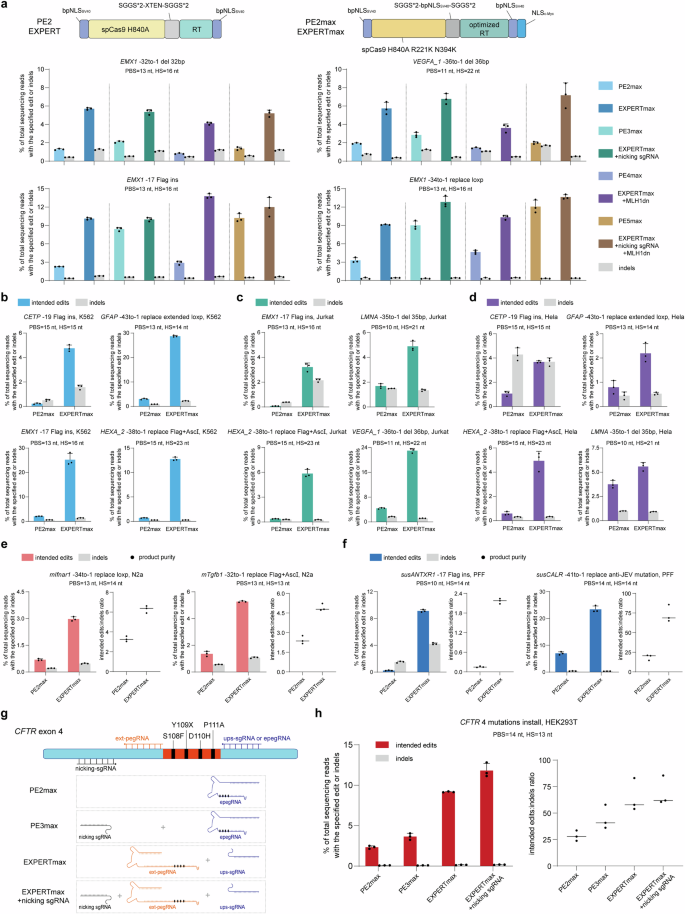
To reveal this, we constructed EXPERTmax by introducing ups-sgRNA and ext-pegRNA to the PE2max (Fig. 5a), and performed edits at totally different loci. Detailed data of edit sort is proven in Fig. 5a. Evaluating to PE2max, EXPERTmax resulted in a mean of three.7-fold greater modifying effectivity in all loci examined (Fig. 5a and Supplementary Fig. 13).
a Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by PE2max, PE3max, PE4max, PE5max and their corresponding EXPERTmax methods. Extra mismatches had been launched within the insertion-type edits. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. b Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by PE2max and EXPERTmax in K562 cells. Extra mismatches had been launched within the insertion-type edits. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. c Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by PE2max and EXPERTmax in Jurkat cells. Extra mismatches had been launched within the insertion-type edits. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. d Frequencies of supposed edits and indels launched by PE2max and EXPERTmax in Hela cells. Extra mismatches had been launched within the insertion-type edits. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. e Frequencies of supposed edits, indels, and product purity launched by PE2max and EXPERTmax in N2a cells. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. f Frequencies of supposed edits, indels, and product purity launched by PE2max and EXPERTmax in PFF cells. Extra mismatches had been launched within the insertion-type edits. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. g Schematic diagram of advanced mutations in CFTR exon 4. The supposed edits that carried 4 mutations had been carried out in HEK293T cells utilizing PE2max, PE3max, EXPERTmax, and EXPERTmax + nicking sgRNA, respectively. h Frequencies of supposed edits, indels, and product purity launched by PE2max, PE3max, EXPERTmax, and EXPERTmax + nicking sgRNA, respectively. Bars characterize the imply of n = 3 impartial organic replicates. Information are offered as imply ± s.d. All sequencing knowledge had been collected from transfection-positive cells. Supply knowledge are supplied as a Supply Information file.
We additional in contrast EXPERTmax with later variations of PEmax (PE3max, PE4max, and PE5max). Evaluating to PE2max, PE3max makes use of an extra nicking sgRNA, PE4max makes use of an extra MLH1dn element, whereas PE5max makes use of each extra parts (i.e., nicking sgRNA and MLH1dn).
With out together with the extra nicking sgRNA, EXPERTmax had a mean 1.7-fold greater modifying effectivity than PE3max (Supplementary Fig. 14). Inclusion of the extra nicking sgRNA barely however not dramatically additional improved the EXPERTmax’s modifying effectivity, leading to a mean 1.9-fold greater than these by PE3max. EXPERTmax + MLH1dn outperformed PE4max by a mean of three.6-fold, and EXPERTmax + MLH1dn + extra nicking sgRNA resulted in a mean 2.4-fold enhance in modifying effectivity in comparison with PE5max (Fig. 5a and Supplementary Fig. 13). Moreover, product purity outcomes demonstrated that EXPERTmax persistently achieved greater purity in comparison with its corresponding PEmax methods (Supplementary Fig. 15).
These outcomes reveal that the EXPERT technique is suitable and readily adaptable to different PE methods.
Environment friendly prime modifying by EXPERTmax in several cell varieties from a number of species
We subsequent assessed EXPERTmax in several cell varieties in several species.
First, we used EXPERTmax to edit 4 totally different human cell traces: the lymphoblast cell line K562, the leukemia T lymphocyte cell line Jurkat, the cervical carcinoma-derived cell line Hela, and the human fetal lung fibroblast HFL1, respectively.
In K562 cells, the modifying effectivity of EXPERTmax was 9.6–21.6 instances greater than that of PE2max. The common enchancment was 15.4-fold (Fig. 5b and Supplementary Fig. 16a). As an example, the effectivity of inserting a Flag tag on the EXM1 web site (EMX1 -17 Flag ins) elevated from 2.07% to 25.27%. In Jurkat cells, the modifying effectivity of EXPERTmax was 2.9–46 instances greater than that of PE2max. The common enchancment was 17.4-fold (Fig. 5c and Supplementary Fig. 16b). The effectivity of inserting a Flag tag on the EXM1 web site (EMX1 -17 Flag ins) elevated from 0.07% to three.22%, representing a exceptional 46-fold enhance. Equally in Hela cells, the effectivity by EXPERTmax was 1.5 to eight.4-fold greater than that by PE2max, with a mean enchancment of 4-fold (Fig. 5d and Supplementary Fig. 16c). As well as, the general product purity of EXPERTmax was greater than that of PE2max in these three cell traces (Supplementary Fig. 17). In HFL1 cells, the effectivity of EXPERTmax was 1.5 to 25.8-fold greater than that of PE2max, whereas the unintended indel charges remained both decrease than or akin to these of PE2max (Supplementary Fig. 18). These findings reveal that the EXPERT may be utilized in several human cell varieties.
We then examined EXPERTmax in a mouse cell line N2a and in pig fetal fibroblast (PFF) cells to evaluate its applicability in non-human species. In N2a cells, the supposed edits are “-34to-1 exchange loxp” on the Ifnar1 locus, and “-32to-1 exchange Flag+AscI” on the Tgfb1 locus. In pig PFF cells, the supposed edits are “-17 Flag ins” on the ANTXR1 locus, and “-41to-1 exchange anti-JEV mutation” on the CALR locus. The outcomes demonstrated that EXPERTmax considerably enhanced modifying effectivity in each mouse and pig cells. In comparison with PE2max, the modifying effectivity of EXPERTmax was 3.9–4.3 instances greater in N2a cells (Fig. 5e) and three.4–39.7 instances greater in PFF cells (Fig. 5f). Of observe, in PPF cells on the susANTXR1 web site, the modifying effectivity elevated from 0.23% to 9.13%, representing a 39.7-fold enhance. In step with findings in HEK293T cells, the unintended indel charges didn’t considerably enhance in comparison with PE2max for many edits. In consequence, the general product purity achieved by EXPERTmax was additionally greater than that by PE2max (Fig. 5e, f).
These findings counsel that EXPERTmax can be utilized in several mammalian species. Notably, in pig species, there have been no earlier reviews of utilizing PE methods for giant fragment edits (e.g., alternative of 41 bp), as tried right here. EXPERTmax achieved a rare effectivity of 23.4%.
Producing disease-relevant mutations by EXPERTmax
We then employed EXPERTmax to generate disease-relevant mutations in human cells as a proof-of-concept demonstration for its potential use in human biomedical analysis. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a deadly inherited illness brought on by mutations within the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, which is inherited in an autosomal recessive method25,26,27. Up to now, over 1900 mutations have been recognized, with greater than 300 identified to trigger the illness28. Conventional gene-editing methods usually have restricted capabilities, resulting in suboptimal therapeutic outcomes. To reveal EXPERT’s applicability in CF gene modifying, right here we labored to generate a big fragment mutant sequence (36 bp) in exon 4 that carries a number of identified CFTR mutations (Fig. 5g). This area can’t be edited by canonical PEs utilizing the initially chosen pegRNA as a result of it’s situated on the upstream area of this pegRNA. Nevertheless, it may be achieved utilizing EXPERT by utilizing this pegRNA spacer. We in contrast the modifying efficiencies amongst (i) PE2max (utilizing the ups-sgRNA because the pegRNA); (ii) PE3max (utilizing the ups-sgRNA because the pegRNA); (iii) EXPERTmax (utilizing the initially chosen pegRNA because the ext-pegRNA); and EXPERTmax (utilizing the initially chosen pegRNA because the ext-pegRNA) + an extra nicking sgRNA (as utilized in PE3max) (Fig. 5g). The outcomes demonstrated that the utilization of EXPERTmax (9.18%) considerably enhanced the modifying effectivity compared to PE2max (2.33%) and PE3max (3.66%). The usage of “EXPERTmax + nicking sgRNA” additional enhanced the effectivity over that by EXPERTmax alongside, reaching a mean modifying effectivity of 11.8%, 3.2 instances greater than that by PE3max and 5.1 instances greater than that by the PE2max. Furthermore, EXPERTmax exhibited remarkably low indel charges and confirmed greater product purity in comparison with PEs (Fig. 5h). These findings counsel the potential worth of EXPERTmax in translational analysis of human illnesses akin to CF.